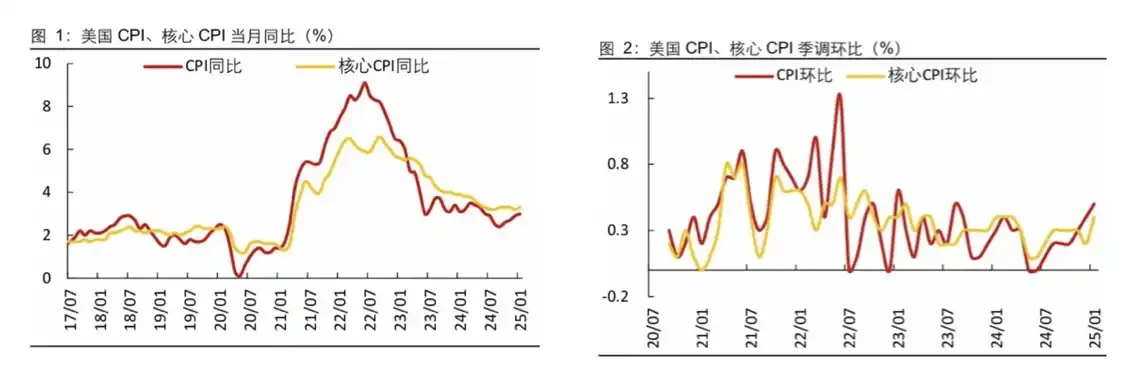
In January, wholesale prices in the United States rose due to increased food and energy costs. According to the PPI and CPI data for January 2025 released by the Bureau of Labor Statistics last week, the PPI month-on-month growth rate increased to 0.4%, down from the revised previous value of 0.5%, but higher than the expected 0.3%. The year-on-year growth rate rose to 3.5%, exceeding the market expectation of 3.2%, marking the largest increase since February 2023. The core PPI increased by 0.3% month-on-month and 3.6% year-on-year; the CPI increased by 3.0% year-on-year, up from the previous value of 2.9%, matching the market expectation of 2.9%. The core CPI increased by 3.3% year-on-year, up from the previous value of 3.2%, with a market expectation of 3.1%.
Both CPI and PPI exceeded expectations, with the month-on-month increase in food prices expanding and the month-on-month increase in energy prices declining. The CPI has rebounded for four consecutive months, indicating that the risk of inflation rebounding remains strong. The tariffs imposed by Trump have brought about a secondary inflation risk, suggesting that it is likely that the pace and intensity of interest rate cuts will slow down this year before inflationary pressures ease.
How to interpret the recent CPI and PPI data?
According to the monetary policy report submitted by Powell to Congress, which outlines the Federal Reserve's views on interest rates, inflation, employment, and the economy over the past year, the Fed mainly focuses on the PCE index. In assessing the inflation outlook, it primarily considers: core goods, housing services, and core non-housing services. Powell clarified the Fed's pace of interest rate adjustments in his speech on February 11, stating, "If the economy remains strong and inflation does not sustainably fall back to 2%, the current policy restrictions can be maintained for a longer time."
The inflation data released on February 12 was significantly high, essentially laying the groundwork for this. From an inflation perspective, interest rate cuts before mid-year this year are not to be considered for now. According to detailed data, the decline in core goods has expanded, inflationary pressures have weakened, and the stubborn point of inflation remains core non-housing services.
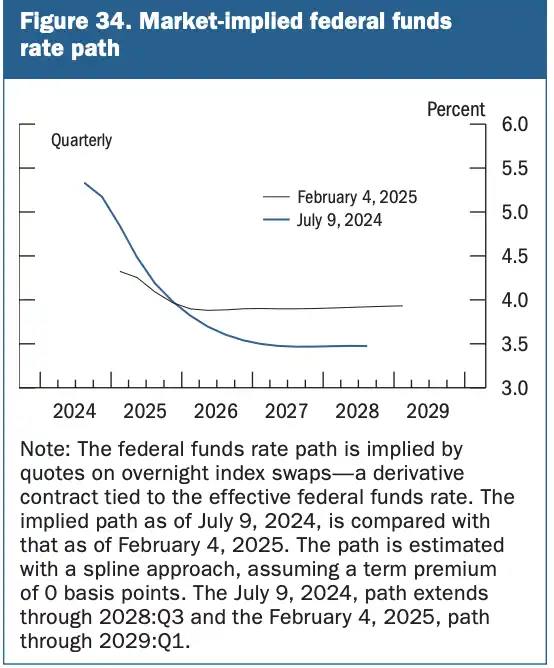
Wall Street traders have currently pushed the expectation for the next interest rate cut to December this year. One point to note is that the wildfire incident in Los Angeles in January may affect market pricing regarding inflation. A significant part of the market's concern about inflation rebounding stems from the continuous rebound in inflation over four months. The CPI increase caused by the wildfire can be considered a systemic risk event; excluding the wildfire conditions may not necessarily lead to the conclusion of a four-month continuous rebound. Furthermore, from the perspective of the Trump administration's efforts to end the Russia-Ukraine war, if the war ends quickly, it may lead to a decline in the prices of construction materials, energy, and agricultural products, thereby reducing inflation. In the future, new data may gradually rescue pessimistic expectations and raise expectations for the frequency and intensity of interest rate cuts.
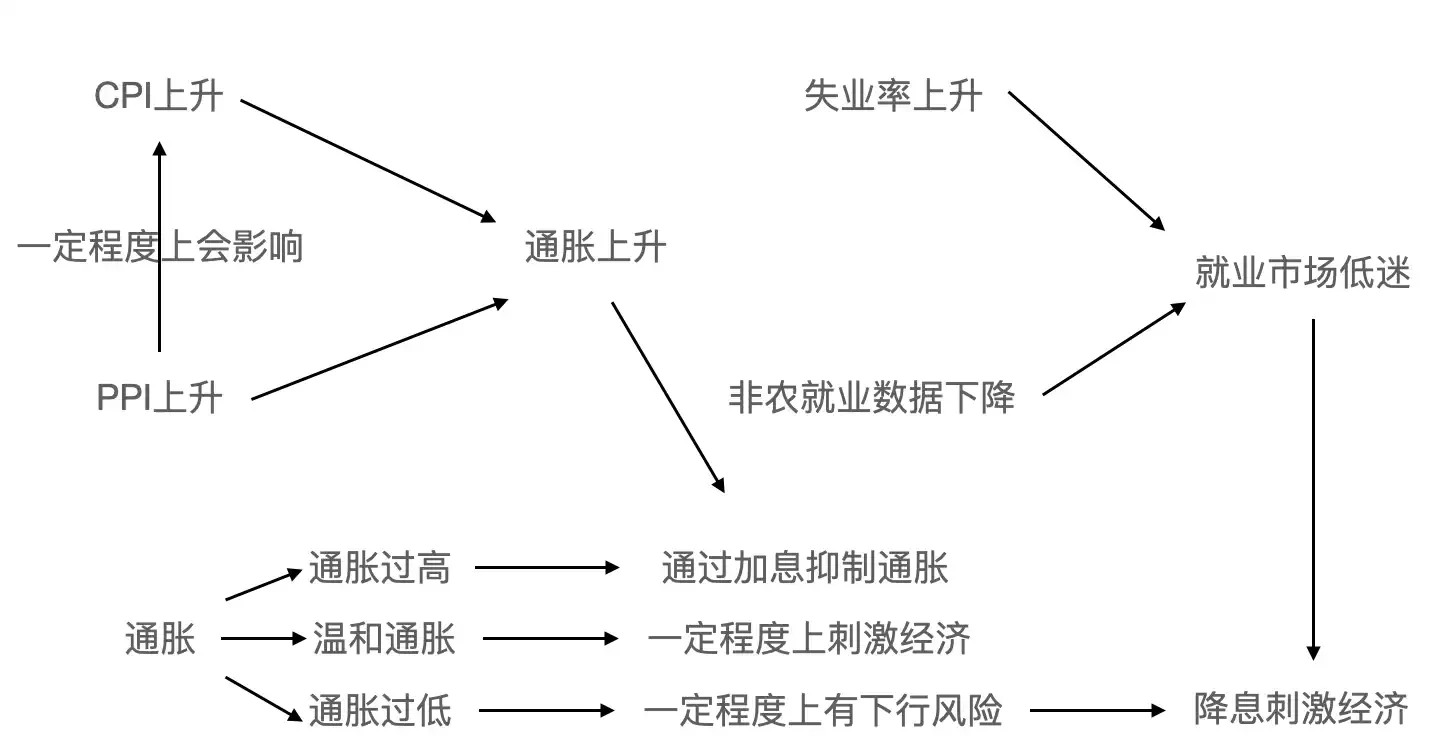
The transmission principle of inflation, employment, and interest rate cuts
Powell: "The focus of our interest rate cuts should continue to be on controlling inflation and promoting employment."
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a macroeconomic indicator that measures changes in the price level of consumer goods and services. It reflects the degree of inflation or deflation by statistically analyzing the price changes of a basket of representative goods and services. When the CPI continues to rise, it means that consumers need to pay more money for the same quantity of goods and services, which is usually seen as a signal of inflation. The Producer Price Index (PPI) mainly measures the trend and extent of changes in the factory prices of industrial products. Changes in the PPI can affect the CPI because fluctuations in producer costs gradually transmit through the supply chain to the consumer end.
Generally, moderate inflation has a stimulating effect on the economy, but if inflation is too high, it can affect economic stability and residents' living standards. When the inflation rate is below the target level and shows a continuous downward trend, it may indicate insufficient economic growth momentum. In this case, interest rate cuts may be used to stimulate the economy, raise inflation expectations, and bring inflation back to a reasonable range. However, if inflation is at a high level, central banks typically adopt tightening monetary policies such as interest rate hikes to curb inflation.
Non-farm employment data reflects changes in employment numbers in industries outside of agriculture. An increase in this data indicates that businesses need to hire more labor to expand production or operations, suggesting a prosperous job market and an overall positive employment situation; the unemployment rate refers to the ratio of unemployed individuals to the labor force.
When the job market performs poorly, such as high unemployment rates and persistently low non-farm employment data, economic growth may be hindered. To stimulate the economy and increase job opportunities, monetary policies such as interest rate cuts may be implemented to lower financing costs for businesses, encouraging them to expand investment and production, thereby creating more jobs.
Does BTC have other upward logic?
According to reports on February 13, the U.S. federal budget deficit expanded to a record $840 billion in the first four months of this fiscal year. On February 14, Dalio also stated publicly that the U.S. must reduce its budget deficit from 7.5% of GDP to 3%, or it will enter a debt death spiral. The U.S. is now like a patient on the verge of a heart attack needing urgent intervention.
Currently, signs of a U.S. debt crisis have emerged, with over $36 trillion in U.S. debt, and interest payments have accounted for 4% of annual GDP and 22% of annual fiscal revenue. Nearly a quarter of government revenue is needed to pay interest. From this perspective, if the Federal Reserve continues to maintain high interest rates, the risk of a debt crisis will increase. A more likely scenario is to ignore the turmoil in the macro environment, abandon short-term policy opportunities, and focus on the main contradiction—the debt crisis—by cutting interest rates and injecting liquidity.

In addition to the narrative of injecting liquidity into the risk market through macro interest rate cuts, another very important narrative for the crypto market is the inclusion of BTC in strategic reserves, not only at the national level but also at the state fiscal level. This means that if this reserve is approved, state finances will directly purchase BTC, totaling a purchasing power of 250,000 BTC, which means that nearly 1% of BTC liquidity will be locked up. The resulting emotional boost and supply reduction effect may once again create a flywheel effect in the cryptocurrency market.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




