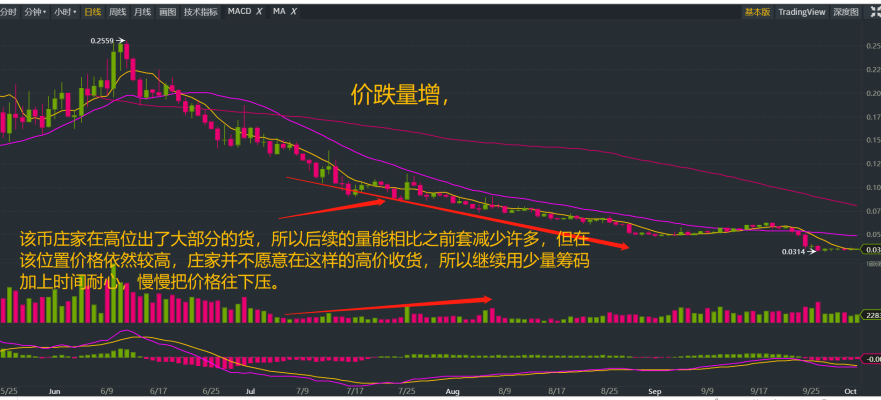
Volume-Price Relationship: Price Drops, Volume Increases
When the price drops while the trading volume increases, a divergence occurs between volume and price. If the price has already fallen significantly and the decline does not show signs of narrowing, with a large increase in trading volume, it reflects that selling pressure has not been eliminated, and the market is likely to continue to decline.
Price Increases, Volume Increases
After a round of selling, if the price rises with an increase in volume, it indicates that buying interest has entered, and the selling has ended, providing an opportunity to enter at a lower point during the pullback.
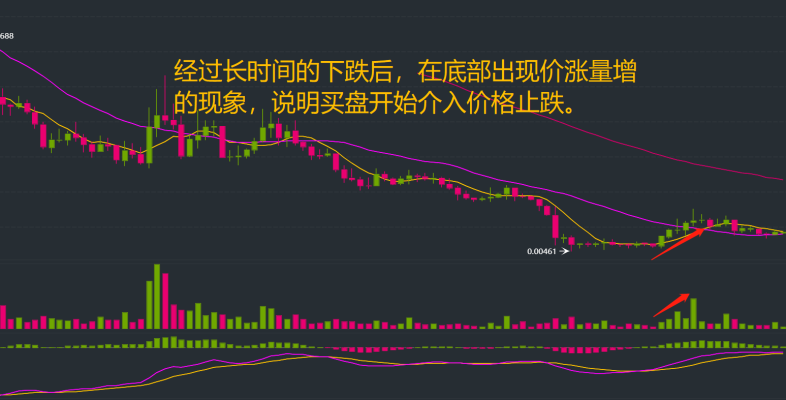
Price Stabilizes, Volume Increases
When the price stops falling and the trading volume increases compared to previous days, it reflects that buying interest has entered, and the selling is about to end.

How to Distinguish Between Real and Fake Selling Pressure
This can be analyzed mainly from the fundamental and technical aspects, combined with changes in the market, the positions held by major players, and the price levels.
When the price is at a low, it may be a fake sell-off aimed at accumulating or shaking out positions. At this time, the sell-off is often orchestrated through matched orders, and the trading volume is shrinking.
If the price has already dropped significantly and has been consolidating at the bottom for a long time, a short-term sell-off is mostly a trap for short sellers. If a sell-off occurs after a period of consolidation at mid to high price levels, it is likely that the major players have distributed most of their positions, making it a real sell-off.
If there is a significant volume during a downward sell-off, it may be a real sell-off, and one should not mistake it for "bottom volume" and jump in to buy. Conversely, it may be a fake sell-off.
If the overall trend is upward, there are no negative news for the project, and the price is not high, a significant sell-off may be for shaking out positions, indicating a fake sell-off. If the overall trend is sluggish, market sentiment is weak, and the price is high, major players may sell off in line with the trend, indicating a real sell-off.
A real sell-off may occur when negative news hits at high levels; conversely, a fake sell-off may occur when negative news hits at low levels, often turning into positive news after the negative impact.
Retail Investors' Strategies During a Sell-Off Phase
The sell-off phase is a time of extreme market pessimism and investor psychological vulnerability. The following points can serve as reference strategies during this phase:
When signs of a sell-off are detected, decisively exit the market. This includes breaking down after consolidation, falling below important support levels, or other indicators signaling a sell.
For cryptocurrencies that have risen significantly, once major players start to distribute, the price will begin to weaken, and after a rebound, it will continue to decline. Therefore, after the rebound ends and the price falls back, exit promptly after the moving averages form a death cross.
Basic Operating Principles
When negative news hits during a downtrend, exit at a high to avoid deep losses; when positive news appears during a downtrend, it is also a good time to sell at a high. In a bear market, negative news continues to drive prices down; in a bull market, positive news continues to push prices up.
The trend in a downtrend is to continuously make new lows. Therefore, bullish candles in a downtrend are false signals, and one should sell on bullish candles; bearish candles are real, and one should avoid bearish candles. A doji appearing during a downtrend often signals the end of a rebound.
The selling opportunity during a downtrend is when the price rebounds and reaches a high.
In a downtrend, selling when short-term indicators show a golden cross is a good time, as golden crosses in a bear market are often false; death crosses are real, so they should be avoided.
When there is a significant volume at resistance levels, it is a good time to sell at a high. The reason is that in a downtrend, there is already little money in the market, and a slight increase in volume can exhaust the available funds.
Low volume in a downtrend is not a bottom but a continuation of the decline; in a bear market, do not assume that a project with major players is safe, as they can also be trapped.
The 20-day and 30-day moving averages in a bear market serve as pressure lines for mid-term declines; when the price rebounds to these levels, it is often a time to distribute at a high.
Precautions During a Sell-Off
Do not blindly sell off. Blindly cutting losses during a crash without considering costs is unwise. Stop-loss should be chosen for positions that are currently slightly underwater and have limited rebound potential; for those that have dropped too sharply, it may be better to wait for a rebound before deciding to sell.
Do not rush to recover losses. In a severe crash, investors are often heavily trapped, facing significant paper losses. Some investors rush to recover losses by increasing trading frequency or investing more funds. This approach is not only futile but can also worsen losses. In a weak market, investors should trade less or avoid trading altogether, patiently waiting for the market to warm up and for clearer trends before entering.
Do not be overly impatient. In a crashing market, some investors may become self-destructive, engaging in reckless trading out of frustration. Remember that no matter how angry one gets, emotions can settle down over time. If significant losses occur, it is difficult to recover, so investors should never use their funds to vent their frustrations.
Do not panic excessively. Panic is the most common emotion among investors during a crash. In the market, there are rises and falls, slow and fast movements; this is a natural law. As long as the market exists, it will not fall indefinitely, and there will eventually be a time for recovery. Investors should take advantage of the market's low points to study and prepare for the upcoming bull market to avoid making mistakes when the market turns favorable.
Do not dwell on regrets. Regret often traps investors in a vicious cycle of continuous trading mistakes. Therefore, investors should quickly free themselves from the shackles of regret to learn from failures, improve their trading skills, and strive to avoid or minimize mistakes in future trades.
Do not rush to catch rebounds. Especially in a market where the downtrend is not over, trying to catch a rebound is like taking fire from a fire; a slight misstep can lead to significant losses. There is always money to be made in the market, but our own funds can be lost completely, so do not risk being trapped for the sake of small profits from rebounds.
Follow the WeChat Official Account - Bit Bear

This article is exclusively planned and published by Bit Bear (WeChat Official Account: Bit Bear). For more real-time investment strategies, solutions, spot trading, short, medium, and long-term contract trading techniques, operational skills, and knowledge about candlestick patterns, you can join Bit Bear for learning and communication. Fans can experience the group for free, with real-time strategy sharing throughout the day!
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




