This article focuses on the cross-border acquiring business of cryptocurrencies, comparing its business model differences with traditional cross-border acquiring.
Written by: Zheng Hongde, Shao Jiadian
If money is understood as a form of energy, every innovation in payment media and tools is accompanied by leaps in social efficiency and the restructuring of power dynamics—from shells to gold and silver, paper money, and then to mobile payments. The emergence of cryptocurrencies marks another leap in this process, while a revolution driven by PayFi (Payment Finance) is quietly rising, redefining the underlying logic of global value exchange through wallets as entry points.
As the name suggests, PayFi combines Pay and DeFi, integrating the concepts of payment and decentralized finance, aiming to achieve the efficient application of cryptocurrencies in payment scenarios through blockchain technology while optimizing the time value of funds. People comment that in the world ultimately pointed to by PayFi, there are no dormant deposits, only perpetual value…
In this vision of PayFi, the "Pay" part is particularly crucial. The cross-border acquiring business of cryptocurrencies, as its core link, realizes low-cost, real-time settlement of cross-border payments through blockchain technology, becoming a bridge connecting global consumers and merchants. However, the rapid development of the cross-border acquiring business of cryptocurrencies is also accompanied by complex legal compliance challenges, especially under the strict regulations in mainland China and the international diverse framework, where its legality and compliance become the primary concerns for enterprises in entrepreneurship and business development.
In this article, Mankun Law Firm focuses on the cross-border acquiring business of cryptocurrencies, comparing its business model differences with traditional cross-border acquiring, providing professional advice to entrepreneurs who wish to seize opportunities and engage in related businesses, revealing the legal compliance challenges they face.
Traditional Acquiring vs. Cryptocurrency Acquiring: Reshaping Cross-Border Payments
1. What is Acquiring?
Acquiring services refer to the services provided by financial institutions or payment service providers to merchants for payment acceptance, fund clearing, and settlement. In simple terms, it helps merchants receive payments from consumers and transfer the funds to the merchant's account.
A cryptocurrency acquiring platform refers to a system that allows merchants to accept payments from consumers using cryptocurrencies. The acquiring platform is responsible for converting the cryptocurrencies paid by consumers into fiat currency and ultimately transferring it to the merchant's bank account.
2. Traditional Cross-Border Acquiring: Profit Eaters
Cross-border acquiring businesses typically involve enterprises accepting payments from global customers, especially in areas such as cross-border e-commerce, service trade, and digital entertainment. However, traditional cross-border acquiring faces the following issues:
High Cost Burden: Traditional cross-border payments rely on banks or third-party payment institutions (such as PayPal, Stripe), and each transaction often comes with multiple fees—payment gateway fees, cross-border handling fees, currency conversion fees, etc., which can accumulate to 3%-6% of the transaction amount, or even higher. For small and medium-sized enterprises with already thin profits or e-commerce businesses with high-frequency small transactions, this is a significant cost pressure.
Long Settlement Cycles: In the traditional system, the journey of funds from customer payment to enterprise account is like a "long trek." Bank cross-border transfers usually take 3-5 working days, or even longer, especially when involving small currency countries (such as Kenya's shilling or Peru's sol), where clearing delays can last up to a week. This not only slows down the cash flow turnover of enterprises but may also affect the normal operation of the supply chain.
Exchange Rate Fluctuation Risks: Cross-border payments often involve multiple currency conversions, and each conversion carries the uncertainty of exchange rate fluctuations. Especially in emerging markets, currency depreciation or foreign exchange controls may lead to additional losses for enterprises.
Difficulty Supporting Small Currencies: Traditional payment systems are well-equipped to support developed market currencies like the US dollar, euro, and Chinese yuan, but often struggle with small currencies in emerging markets (such as the Vietnamese dong or Nigerian naira). Many payment institutions either do not support these currencies or raise costs through multiple conversions, making it difficult for enterprises to penetrate these high-potential markets.
These pain points intertwine to form an invisible barrier that devours enterprise profits, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises lacking the bargaining power to negotiate lower rates with large banks. The traditional cross-border acquiring model has become inadequate to meet modern business demands for efficiency, cost, and flexibility. It is against this backdrop that various cryptocurrency acquiring platforms attempt to open a new path for enterprises using digital currencies and blockchain technology.
3. Cryptocurrency Acquiring: Reshaping Cross-Border Payments
Business Model
Cryptocurrency acquiring optimizes the cross-border payment process through blockchain technology and digital currencies (such as stablecoins, Bitcoin, etc.), bypassing traditional financial intermediaries to achieve low-cost, high-efficiency fund clearing. Platforms like KUN Pay and BlockBee provide merchants with cryptocurrency payment systems, allowing enterprises to quickly connect through APIs or customized interfaces, accept consumer cryptocurrency payments, and convert them into fiat currency transferred to their accounts, promoting business expansion and efficiency improvement.
Practical Cases: KUN Pay & BlockBee
KUN Pay: Launched by KUN, focusing on B2B scenarios, targeting enterprise-level clients, providing cross-border acquiring services based on stablecoins (such as USDT). It supports real-time settlement, fiat currency conversion, global commission distribution, and scheduled payments, particularly suitable for cross-border e-commerce and service trade enterprises.
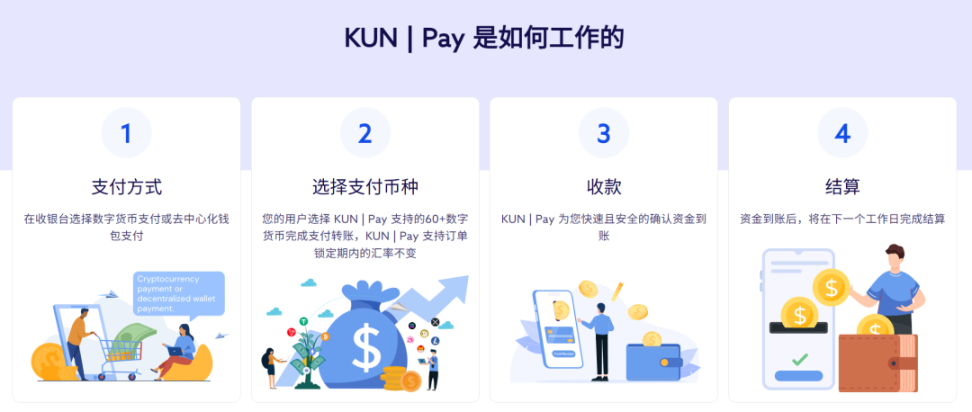
BlockBee: A lightweight payment gateway that supports multiple cryptocurrencies (such as Bitcoin, Ethereum) for acquiring, providing simple API integration and real-time fiat currency conversion functions, suitable for small and medium merchants and individual users, emphasizing quick deployment and flexibility.
Significant Advantages of Cryptocurrency Acquiring
Significant Cost Reduction: Traditional acquiring fees of 3%-6% are reduced to 0.5%-1%, eliminating payment gateway fees and multiple conversion costs, saving expenses for small and medium-sized enterprises with thin profits.
Accelerated Settlement Speed: Blockchain technology compresses settlement time from 3-5 days to a few minutes or even seconds, enhancing cash flow efficiency and helping enterprises operate quickly.
Mitigated Exchange Rate Risks: By using stablecoins or real-time conversion mechanisms, it avoids multiple currency conversions and exchange rate fluctuations, particularly benefiting businesses in emerging markets.
Coverage of Small Currencies: Cryptocurrencies break geographical limitations, supporting the acceptance of small currencies like the Vietnamese dong and Nigerian naira, helping enterprises explore high-potential markets.
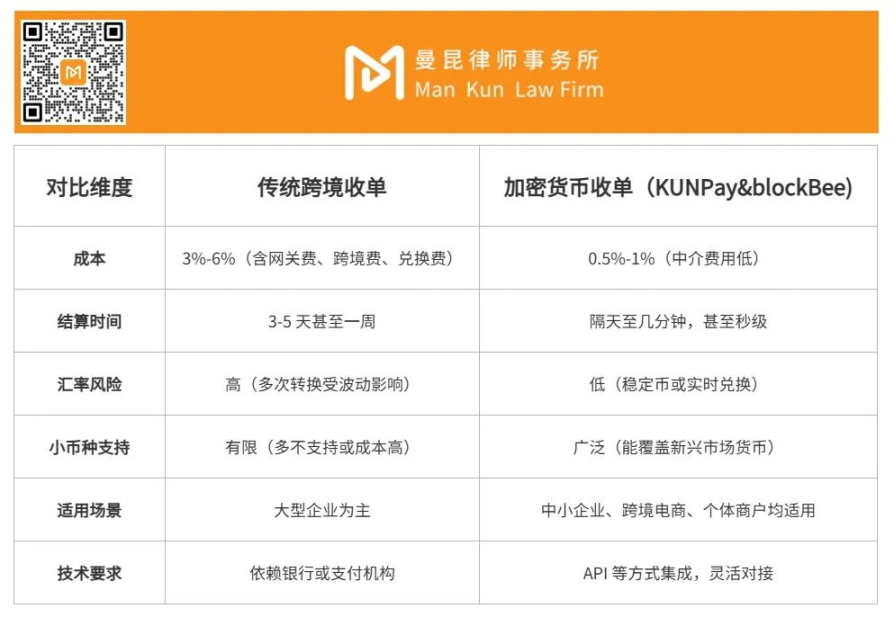
Comparative Summary
KUN Pay and BlockBee both demonstrate the core value of cryptocurrency cross-border acquiring: low cost, high speed, and transparency. Compared to traditional cross-border acquiring, both reduce costs, enhance efficiency, and expand market coverage, providing small and medium-sized enterprises with new tools for global competition, with unlimited potential. This revolutionary payment model naturally attracts many entrepreneurs to dive in, but entrepreneurship and business development are not without challenges, and compliance is a key aspect that cannot be ignored. Enterprises face many legal risks when developing and operating cryptocurrency acquiring businesses.
Want to seize the opportunity? Avoid pitfalls in entrepreneurship: Compliance Key Points Analysis
1. Can Cryptocurrency Acquiring Business Be Conducted in Mainland China?
Conducting cryptocurrency cross-border acquiring business in mainland China, especially targeting domestic residents, faces significant legal obstacles and may even constitute the following crimes:
Illegal Business Operations
According to the "Notice on Further Preventing and Dealing with Risks of Virtual Currency Trading Speculation" issued on September 24, 2021, the exchange of legal currency for virtual currency is classified as illegal financial activity and is strictly prohibited. The acquiring operation provides users with services for exchanging, trading, or settling cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies, which may violate Article 225 of the Criminal Law of the People's Republic of China regarding "illegal business operations," facing administrative penalties or even criminal liability.
Money Laundering
Cryptocurrencies have characteristics of anonymity and confidentiality, and their sources may involve upstream criminal activities (such as fraud, illegal fundraising). If the operator knows or should know that the source of funds is illegal but still provides acquiring and exchange services, facilitating the transfer or conversion of funds, it may constitute "money laundering" as defined in Article 191 of the Criminal Law.
Foreign Exchange Management and User Risks
Cryptocurrency acquiring businesses involve cross-border fund flows, which may touch upon the red line of foreign exchange management. According to Article 45 of the Foreign Exchange Management Regulations, conducting foreign exchange business without approval from the State Administration of Foreign Exchange is illegal and may face administrative penalties such as fines and confiscation of illegal gains.
Therefore, it is not recommended for cryptocurrency cross-border acquiring operators to conduct exchange, trading, or settlement business between cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies in mainland China to avoid potential legal violations. Ensuring that the business complies with Chinese laws and regulations is essential to avoid legal risks due to violations.
2. What About Going Overseas to Conduct Cryptocurrency Cross-Border Acquiring Business? Many Compliance Challenges
Although it cannot operate in mainland China, small and medium-sized enterprises see opportunities for profit overseas. Many entrepreneurs are eager to explore international markets through cryptocurrency acquiring businesses. This is indeed a promising track, but compliance issues act like "roadblocks." From company establishment to licensing, operations, and taxation, any misstep could lead to failure. Here are some compliance key points:
Facing Multi-Country Regulations: Payment Licenses and AML/KYC are Basic Skills
When going overseas to do cryptocurrency acquiring, the first step in compliance is to understand the regulations of each country; otherwise, fines, account closures, or even business suspensions await.
Licenses Are Essential
Every place requires a "pass" to operate legally:
In the United States, registration as a Money Services Business (MSB) with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) is required, and in addition to federal regulations, corresponding licenses must be applied for according to state laws.
In the European Union, obtaining a CASP license under the Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) is necessary.
In Hong Kong, if the business involves currency exchange or remittance services, a Money Service Operator (MSO) license must be applied for.
AML/KYC Must Keep Up
The world is focused on anti-money laundering and identity verification:
In the United States, strict implementation of AML and KYC policies is required, including verifying customer identities, conducting transaction monitoring, and submitting Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs).
In the European Union and Hong Kong, compliance with AML regulations, implementation of KYC policies, and adherence to the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) "travel rule" are necessary, recording the identity information of both parties in transactions and fulfilling customer due diligence obligations.
The Cost of Non-Compliance: Operating without a license can lead to fines, business closures, and shattered entrepreneurial dreams; failing to verify identities or report transactions may lead to bankruptcy and being blacklisted, restricting global business operations.
Tax Issues Cannot Be Avoided
Cryptocurrency cross-border acquiring businesses involve converting cryptocurrencies into fiat currencies, which may create tax obligations in multiple jurisdictions. To reduce risks, acquiring operators should disclose tax responsibilities to users and clearly state tax compliance requirements in service terms to avoid business operations or license renewal issues due to tax violations.
In the United States, converting cryptocurrencies into fiat currency is considered asset disposal, and users must report capital gains tax to the IRS. Operators should provide transaction records and remind users of their annual tax obligations to avoid penalties for unreported income.
In the European Union, tax rules vary by country. For example, Germany treats cryptocurrencies as "private assets," and gains from exchanges held for less than a year are subject to income tax. Operators need to remind users to keep exchange receipts to cooperate with tax audits.
In Hong Kong, the Hong Kong Inland Revenue Department has not yet established specific tax policies for cryptocurrencies, but if an operating entity conducts business in Hong Kong, the revenue generated from its exchange services is subject to profits tax. Individual users currently do not need to pay taxes on exchanges but should pay attention to policy changes.
The cost of non-compliance: at best, back taxes and fines; at worst, license revocation, customer loss, and reputational damage.
Summary by Mankun Law Firm
The rise of PayFi has brought revolutionary opportunities to the cross-border acquiring business of cryptocurrencies. Platforms like KUN Pay and BlockBee have achieved low-cost, high-efficiency global payments through blockchain technology, reshaping the landscape of traditional cross-border acquiring. However, this innovation is not without boundaries. Under the strict regulations in mainland China and the diverse international legal framework, compliance has become a core issue for enterprises in business development.
In mainland China, the cryptocurrency acquiring business is classified as illegal financial activity due to relevant policies, with a high risk of crossing the lines of "illegal business operations" and "money laundering." Operators should strictly avoid targeting domestic residents. In overseas scenarios, while the market potential is enormous, multi-country regulations, license acquisition, AML/KYC obligations, and tax compliance pose significant challenges. Compliance is not only a legal bottom line but also a safeguard for the survival and development of enterprises.
For entrepreneurs looking to engage in cryptocurrency acquiring business and seize the PayFi opportunity, only by steadily operating within the compliance framework can they turn potential into reality. Shanghai Mankun Law Firm specializes in legal services in the Web3 field and is willing to safeguard your overseas journey. If you have any questions, feel free to consult us!
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




