Introduction
In 2013, a 19-year-old programmer, Vitalik Buterin, proposed a bold idea: he published a white paper titled "Ethereum," outlining a blockchain blueprint that transcended the functionalities of Bitcoin. To turn this vision of a "world computer" into reality, he and his team raised approximately $18 million through an Initial Coin Offering (ICO), and the Ethereum network officially launched in 2015, sparking a revolutionary wave of Web3 smart contracts and Dapps. Over the past decade, it has experienced fervor and lows, technological iterations, the rise of financial applications, and numerous challenges from within and outside the ecosystem, undergoing rebirth and growth through repeated shocks. Today, Ethereum has evolved from a daring idea into a cornerstone of the blockchain field.
This article will review Ethereum's development milestones and technological evolution, analyze its revolutionary journey in areas such as DeFi, NFTs, and DAOs, and explore key themes such as Layer 2 scaling, competitive landscape, and future challenges. Through this series of analyses, we will witness Ethereum's ten-year journey from the vision of a "world computer" to a global decentralized financial infrastructure, and look forward to the potential evolution of Ethereum in the next decade.
A Decade of Ethereum's Development

The past decade of Ethereum is also the most colorful main storyline in the history of blockchain development. Over the last ten years, Ethereum has gone through several peaks and valleys, gradually growing from an early "hacker paradise" into a new type of infrastructure supporting hundreds of billions in value. Each milestone event not only propelled Ethereum's evolution but also reflected the changes and maturation of the entire crypto industry.
2013-2015 Beginnings: Vitalik published the white paper, crowdfunding in 2014, and on July 30, 2015, the genesis block was born, marking the official launch of the Ethereum mainnet and the beginning of the smart contract platform era.
2016 Ideals and Crises: The smart contract platform began to take shape, but the major security incident "The DAO" occurred, leading to a community hard fork and the birth of Ethereum Classic (ETC).
2017 Prosperity and Challenges: The ICO boom ignited, and Ethereum became the platform for numerous token issuances; the ERC-721 standard was introduced, marking the first appearance of NFT applications like CryptoKitties.
2018-2019 Winter Dormancy: The ICO bubble burst, and the price of ETH plummeted from a peak of $1448 to $84; the Ethereum community focused on technological upgrades (such as Byzantium, Constantinople hard forks) to lay the foundation.
2020 Rise of DeFi: Decentralized finance exploded, with "liquidity mining" igniting the DeFi summer, and protocols like Uniswap and Compound grew rapidly, while network congestion and high gas fees became prominent issues.
2021 Peak Moment: The London upgrade implemented EIP-1559, introducing a fee-burning mechanism; Layer 2 solutions Arbitrum and Optimism launched on the mainnet; the NFT craze swept through (e.g., BAYC), and the price of ETH reached an all-time high of nearly $4878.
2022 Turning Point and Transformation: The "Merge" was completed, transitioning from proof of work to proof of stake, reducing energy consumption by 99%; however, the crypto market cooled (Terra collapse, FTX incident), and ETH briefly fell below $1000.
2023 Revival and Upgrades: The Shanghai/Shapella upgrade enabled staking withdrawals, marking Ethereum's completion of the PoS transition; the Rollup ecosystem matured with Arbitrum, zkSync, and StarkNet ZK Rollup solutions being implemented.
2024 Scaling and Integration: The Cancun/Dencun upgrade (including EIP-4844) reduced Layer 2 fees by about 90% and improved data availability; the U.S. approved ETH spot ETFs, leading to a significant influx of traditional institutions.
2025 Moving Forward: (Pectra upgrade, etc.) Account abstraction features were introduced, allowing for more flexible wallets and contract accounts; Ethereum's market cap approached $500 billion, becoming a global decentralized financial infrastructure.
From pioneering the smart contract platform to embracing proof of stake consensus, Ethereum has repeatedly surpassed itself at critical junctures. The experiences and lessons accumulated throughout this development process have not only strengthened the resilience of the Ethereum network but also guided the direction of future technological evolution.
Technological Evolution: From "World Computer" to Sharding and Rollup
At its inception, Ethereum was referred to as the "world computer," with its core innovation being the introduction of a Turing-complete smart contract platform, expanding blockchain into a programmable decentralized computer. Developers can deploy smart contracts on Ethereum, allowing the blockchain to support various complex applications rather than being limited to simple transfers. Since the mainnet launched in 2015, tens of millions of smart contracts have been deployed on Ethereum, supporting a thriving application ecosystem. However, early Ethereum utilized a proof of work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which, while ensuring decentralization and security, also limited performance. The ICO boom of 2017-2018 and the popularity of applications like CryptoKitties led to network congestion and skyrocketing fees, exposing throughput bottlenecks. The ability to process only a few dozen transactions per second was insufficient to meet the growing demand, with gas fees exceeding $50 at peak times. The performance and cost dilemma prompted the Ethereum community to initiate an ambitious "Ethereum 2.0" upgrade roadmap, aiming to significantly enhance scalability and sustainability while maintaining decentralization and security.
1. Change in Consensus Mechanism: PoW to PoS
After years of research and preparation, Ethereum underwent the epic upgrade known as The Merge in 2022. Prior to this, the Ethereum team had launched an independent PoS beacon chain in 2020 as a test and had postponed the "difficulty bomb" on the PoW chain multiple times to allow for a smoother transition. Finally, on September 15, 2022, the Ethereum mainnet successfully completed the merge without downtime, transitioning from the energy-intensive PoW to the efficient proof of stake (PoS) consensus. This transformation reduced Ethereum's energy consumption by 99.95% and introduced a staking mechanism: users holding ETH could stake to earn approximately 4% annualized returns while participating in network validation and security maintenance. This made ETH assets "productive" and enhanced network security. As of July 31, 2025, over a million validators had participated in staking on Ethereum, locking up approximately 36.11 million ETH (about 29.17% of circulating supply) to protect network operations. The PoS mechanism also significantly reduced Ethereum's new coin issuance rate by about 90%, combined with the fee-burning mechanism, leading to net deflation of ETH during busy periods.
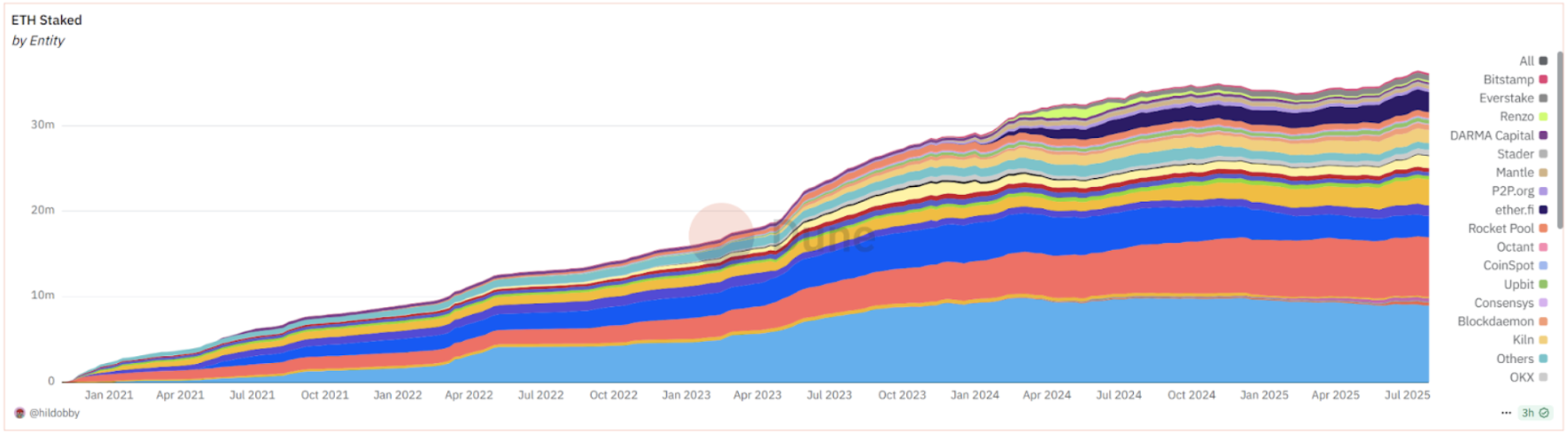
Source: https://dune.com/hildobby/eth2-staking
2. Key Proposals and Protocol Upgrades
Alongside the change in consensus, a series of Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) were implemented, shaping the economic and performance characteristics of the network. The most impactful among them is EIP-1559: this proposal introduced a base fee burning mechanism during the London upgrade in August 2021, which directly burned a portion of each transaction fee. Since its implementation, over 4 million ETH have been burned, optimizing the fee market and, to some extent, reducing the supply growth of ETH, creating deflationary expectations for ETH. Additionally, EIP-4844, deployed in March 2024, significantly enhanced Ethereum's data throughput capacity. By introducing "blob" transactions, it reduced the cost of submitting data for Layer 2 Rollups, with statistics showing that its implementation directly halved the gas costs for Rollups. These EIPs not only improved the user experience on Ethereum but also laid the groundwork for larger-scale scalability in the future.
3. Moving Towards Sharding and Modular Architecture
To fundamentally break through performance bottlenecks, Ethereum has planned a "sharding" technology route. The concept of sharding involves splitting the blockchain state and transaction load across multiple parallel shard chains for processing, thereby achieving parallel scalability. The Ethereum consensus layer will coordinate these shards, allowing them to share security while processing transactions independently. This solution is expected to increase Ethereum's TPS to the hundred thousand level, reducing the cost of a single transaction to mere fractions of a cent. According to the roadmap, full sharding may be gradually introduced in 2025-2026. Although complete sharding has not yet been implemented, its concept has been partially realized in the current Rollup scaling solutions. Rollups are Layer 2 networks built on Ethereum that alleviate the main chain's load by executing a large number of transactions off-chain and then submitting the result data in batches to the main chain. Over the past few years, both Optimistic Rollup and ZK Rollup technologies have advanced simultaneously, giving rise to numerous Layer 2 networks such as Optimism, Arbitrum, zkSync, and StarkNet. The Ethereum mainnet is gradually transforming into a settlement layer for these Layer 2 solutions: the mainnet provides final security and data availability, while Rollups handle high-throughput transaction processing. This collaboration has evolved Ethereum's architecture from a single-layer chain to a multi-layer modular network.
4. Leap in Performance and Scalability
Through the PoS upgrade and Layer 2 scaling strategies, Ethereum's technological evolution over the past decade has consistently focused on enhancing performance and lowering barriers to use. Today, a collaborative operation pattern has formed between the mainnet and various Layer 2 networks: the mainnet processes approximately 1.8 million transactions daily while maintaining high security and decentralization; simultaneously, the total transaction volume on Layer 2 networks has multiplied compared to the main chain, with over 5 million transactions executed daily across various Ethereum Layer 2 solutions. Thanks to the diversion provided by Layer 2, congestion on the Ethereum mainnet has significantly eased, and users' routine gas fees have dropped from peak levels of several dozen dollars per transaction to just a few cents on the mainnet and less than a cent on Layer 2. As a result, the on-chain interaction experience on Ethereum is approaching the speed and cost of Web2 applications. It can be said that from the change in consensus mechanism, virtual machine optimization to sharding and Rollup scaling, each technological upgrade has made Ethereum stronger and more efficient while maintaining decentralization.
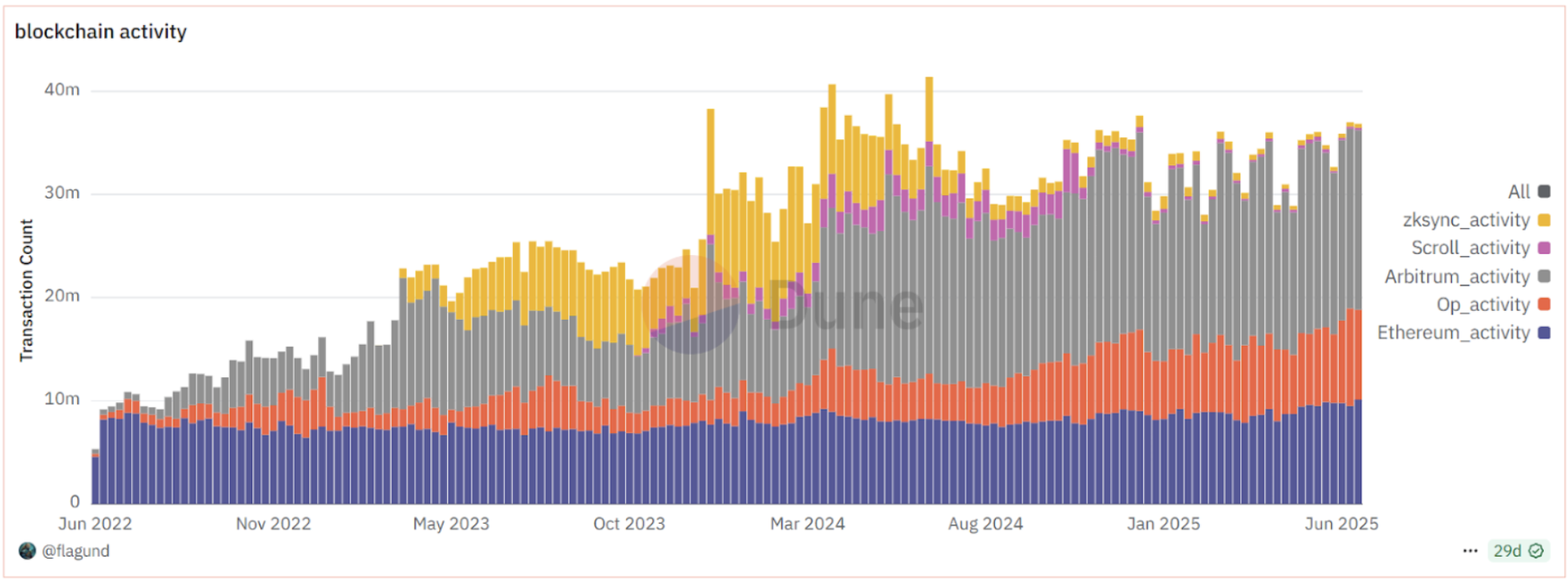
Source: https://dune.com/flagund/l2-stats-vs-ethereum
4. Development of Ethereum's Ecological Applications
The evolution of the technological architecture has laid the foundation for the prosperity of the application ecosystem. Over the past decade, an unprecedented world of open finance and digital assets has emerged on Ethereum, achieving multi-domain explosions from decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
1. DeFi Revolution: Ethereum's New Financial System
In 2017, the first decentralized financial applications began to appear on Ethereum, with MakerDAO launching the over-collateralized stablecoin DAI, laying the groundwork for digital currency lending. The decentralized exchange Uniswap, launched in 2018, introduced the automated market maker (AMM) model, enabling code-based token swaps without intermediaries, triggering a transformation in trading models. Between 2019 and 2020, protocols like Compound and Aave further expanded the on-chain lending market. The real explosion began with the "DeFi Summer" of 2020: Compound issued governance tokens, leading the liquidity mining craze, with users eagerly depositing assets into various protocols to earn incentives. The total value locked (TVL) in Ethereum skyrocketed from under a billion dollars to hundreds of billions within months, with network transaction volume and fees surging accordingly. By the end of 2021, the DeFi landscape reached an all-time high, with the total TVL of various protocols surpassing $100 billion for the first time. Although the market experienced fluctuations and adjustments afterward, by mid-2025, the DeFi ecosystem had regained momentum, with the global TVL rising to approximately $150 billion, of which nearly 60% (about $85 billion) was achieved on the Ethereum network, firmly maintaining its position as the largest DeFi public chain.
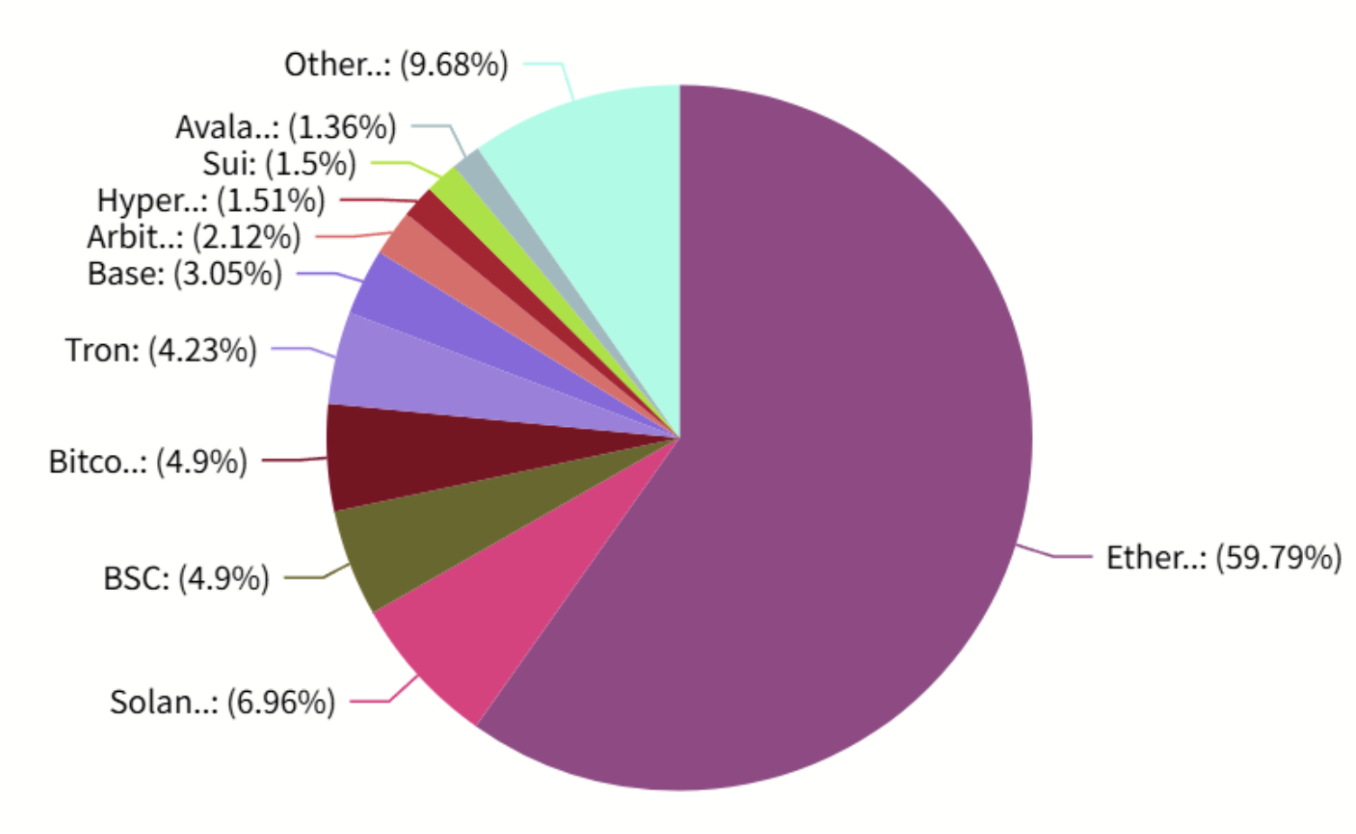
Source: https://defillama.com/chains
A number of representative DeFi projects have emerged on Ethereum, each pioneering new financial models:
Uniswap Decentralized Exchange: The first to introduce the automated market maker (AMM) model, automatically matching trades using a constant product formula, eliminating the need for order books and centralized intermediaries, enabling peer-to-peer asset exchanges, and at one point surpassing many traditional exchanges in trading volume on Ethereum.
Sky (formerly MakerDAO) Stablecoin System: Introduced an over-collateralization mechanism to issue the decentralized stablecoin DAI, allowing users to collateralize crypto assets to borrow stablecoins, creating a model for loans and stablecoin issuance without banks, providing a fundamental value anchoring tool for the DeFi ecosystem.
Aave Lending Protocol: Offers an unpermissioned lending market, using algorithms to adjust interest rates in real-time, allowing users to deposit assets to earn interest or collateralize to borrow other assets. Aave also introduced innovative features like flash loans, allowing users to borrow without collateral and repay within a single transaction, greatly expanding the use cases of decentralized finance.
Through these protocols, many traditional financial services (such as currency exchange, lending, derivatives trading, etc.) have been transplanted onto the blockchain and reshaped. The vigorous development of this open finance proves that blockchain can support high-value financial activities and provide 24/7 global services. Ethereum's powerful smart contract foundation and security allow for free combinations between protocols, and this Lego-like innovation further accelerates the iteration of financial products. It is no exaggeration to say that DeFi has sparked a paradigm shift in the financial industry: moving from centralized institutional monopolies to decentralized network collaboration, from manual reviews to automated execution. In this process, Ethereum has become the foundational layer supporting the global "value internet."
2. NFT Craze: A New Realm of Digital Assets
At the end of 2017, a game on Ethereum called CryptoKitties allowed people to experience the joy of blockchain NFT digital collectibles for the first time: users could own and breed unique virtual cats. The game unexpectedly became a sensation, even causing the Ethereum network to congest due to excessive transactions. NFTs are a token standard (commonly ERC-721) that marks the ownership of unique assets on the blockchain, turning digital content such as artworks, collectibles, and game items into unique and freely tradable assets.
After an initial exploratory phase, the NFT market experienced a full-blown explosion in 2021: phenomenon projects such as CryptoPunks and the Bored Ape Yacht Club (BAYC) emerged on Ethereum, with these pixelated avatars and cartoon apes becoming hot "digital fashion brands," auction prices often reaching hundreds of ETH, and celebrities and institutions rushed to endorse them. In March 2021, digital artist Beeple's NFT artwork was auctioned at Christie's for a staggering $69.3 million, marking the official entry of digital art into the mainstream auction stage. As the primary hosting platform, Ethereum contributed the vast majority of NFT trading volume, thoroughly bringing blockchain technology into the realms of art, entertainment, and fashion in popular culture. The major trading platform OpenSea once topped the Ethereum DApp revenue rankings in 2021. Major brands and sports leagues also expanded their fan economy by issuing NFTs, such as the NBA's "Top Shot" moments NFTs, and game developers attempted to put game items on-chain for trading. Of course, the NFT craze also exacerbated congestion on the Ethereum network, with gas fees soaring to exorbitant levels during popular NFT minting periods, often deterring ordinary users due to high transaction costs.
After several years of development, the NFT market gradually returned to rationality after the initial frenzy. Although the crypto winter starting in 2022 caused NFT prices and trading volumes to decline, this field did not disappear; instead, it began to evolve towards more practical applications. For example, an increasing number of NFTs are being used as game assets, allowing players to truly own tradable game equipment; some NFTs are used for digital identity and membership credentials, granting holders special rights; mainstream brand NFTs emphasize practical value in fan interaction. Currently, daily trading volume of NFTs on Ethereum still reaches $10 million, and "digital collectibles" have become an indispensable part of the blockchain field.
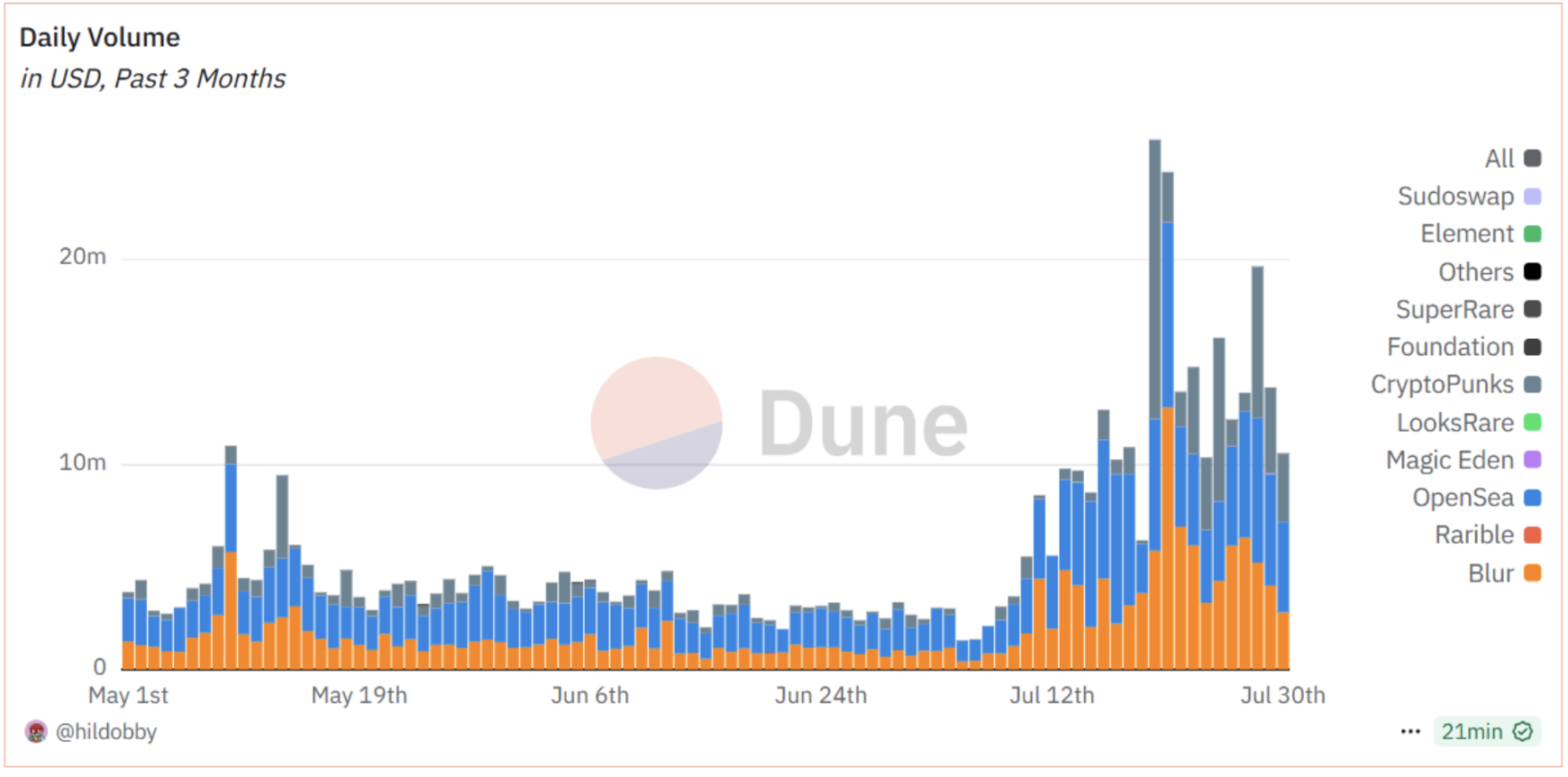
Source: https://dune.com/hildobby/ethereum-nfts
3. DAO Governance: Reshaping Organizational Collaboration
Ethereum has not only nurtured new asset forms but also given rise to new organizational structures: decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). A DAO is an organizational structure that achieves community autonomy through smart contracts and token voting, aiming for all participants to jointly make decisions and manage funds without centralized leadership. As early as April 2016, the first large-scale DAO experiment, called "The DAO," was born on Ethereum, raising over $150 million in ETH and attempting to allow token holders to vote on funding entrepreneurial projects. However, The DAO suffered a hacker attack due to code vulnerabilities, resulting in a loss of about $60 million. This incident led to a famous hard fork in Ethereum's history, with a new chain created to recover the losses retaining the name Ethereum, while the old chain that opted for non-intervention became Ethereum Classic (ETC). Although The DAO failed, the concept of autonomous organizations it initiated has continued to develop. In recent years, many projects and communities have adopted the DAO governance model: for example, MakerDAO holders vote to determine stable fee rates and parameters, the Uniswap community proposes upgrades to protocol functions, and there are investment-focused DAOs like LAO and PleasrDAO, which aims to collect rare items, and even the sensational ConstitutionDAO in 2021, where thousands of people crowdfunded on Ethereum to bid for a copy of the U.S. Constitution. The development and upgrade process of Ethereum itself also reflects a form of open governance: anyone can propose an EIP improvement proposal, and after community discussion and consensus through client implementation, the network is upgraded. This multi-party collaboration and open debate governance model has had a profound impact on many subsequent crypto projects, becoming a model for "community governance."
Ethereum provides a reliable infrastructure for the operation of DAOs: on-chain multi-signature wallets are used to hold funds, governance tokens are used for voting decisions, and smart contracts execute voting results, with all processes being transparent and verifiable. This transparent and trustworthy mechanism greatly reduces the trust costs required for large-scale collaboration, allowing strangers to form "digital communities" around common goals. DAOs conceptually disrupt traditional organizational boundaries but also face some real challenges. For example, many DAO governance votes have low participation rates, and how to incentivize a broad base of token holders to actively exercise their rights is a challenge; additionally, the decision-making process is often public and slow, making it difficult to respond promptly to rapidly changing market conditions. Furthermore, a few "whales" holding large amounts of tokens have significant influence in DAOs, and exploring how to prevent governance from being monopolized is also a direction that needs to be addressed.
5. Competition and Challenges Facing Ethereum
Currently, the number of decentralized applications (dApps) running on the Ethereum mainnet has exceeded 4,000, covering various fields such as lending, trading, payments, gaming, and social networking. The scale of the developer ecosystem remains the largest among global public chains. The increasing number of applications and users further solidifies Ethereum's position as the "value internet" and its "ecological moat." However, behind this prosperity, Ethereum also faces unprecedented competitive pressures and internal challenges.
1. Competitive Landscape: Ethereum's Position Amidst the Race of Hundreds of Chains
Looking back over the past decade, there have been many competing chains that claimed to be "Ethereum killers," but most have been short-lived. Launched in 2017, EOS claimed to outperform Ethereum in performance and raised a record $4.2 billion through an ICO. However, EOS quickly exposed issues of governance centralization after its launch: just a few days after the mainnet went live, its nodes caused community uproar due to frozen accounts, leading to a significant decline in EOS's development activity and economic activity thereafter. The Binance Smart Chain (BSC), which emerged in 2020, attracted a large number of users and DeFi projects with extremely low fees. However, BSC uses a permissioned proof-of-stake consensus with only 21 validators, selected daily from 11 super nodes on the Binance chain, resulting in highly concentrated actual control. The potential risks brought by this centralized architecture have made many community members wary of BSC. Solana, which rose to prominence in 2021, is known for its throughput of thousands of TPS and sub-second confirmation times, being viewed as a "high-speed chain" for consumer applications. During the NFT and meme coin craze, Solana's on-chain trading volume surged, showing momentum to challenge Ethereum. However, Solana's high performance also came with a decrease in decentralization, as its network experienced multiple large-scale outages (with the longest downtime lasting several hours), preventing users from transferring assets and raising questions about its reliability.
Of course, competitors are still rapidly iterating. Solana, benefiting from the wealth effect brought by memes, once saw gas fees exceed those of Ethereum; the concept of modular blockchains is also on the rise, with projects like Celestia focusing on providing data availability layers and EigenLayer proposing "re-staking" solutions that reuse Ethereum's trust layer, all exploring new blockchain architectures. These new narratives and technological paths not only expand the boundaries of blockchain applications but also challenge Ethereum's role: in a future landscape characterized by multiple chains and layers, how Ethereum can maintain its core position while collaborating and thriving with other chains is a new topic that needs to be considered.
2. Challenges and Responses Facing Ethereum
After a decade-long journey, Ethereum has established its leading position in the industry, but there are still many internal challenges that need to be overcome. These challenges include both technical bottlenecks and tests related to the market and governance.
Long-term Scalability Bottleneck: The limited transaction processing capacity and high gas fees of the Ethereum mainnet not only draw criticism from ordinary users but also greatly limit Ethereum's appeal to the mainstream public. This issue has directly led to the emergence of various scaling solutions, with the rise of Layer 2 networks being the most significant. However, while Layer 2 alleviates pressure on the mainnet, it also brings new challenges: different Layer 2 networks operate independently and lack direct interoperability, leading to liquidity being dispersed across various Rollup ecosystems. This fragmentation somewhat undermines the original intention of Layer 2 to enhance user experience.
Balancing Performance Improvement and Decentralization: The well-known "impossible triangle" theory in the blockchain field states that decentralization, security, and scalability cannot all be achieved simultaneously. Since its inception, Ethereum has always prioritized decentralization and security, which means that the threshold for running nodes is relatively low, allowing more global participants to independently maintain the network; however, the cost is that the capacity of individual blocks and block production speed are limited, affecting transaction throughput and confirmation times.
Security Challenges: As a programmable blockchain, Ethereum's smart contracts have repeatedly exposed vulnerabilities and suffered attacks, each time sounding the alarm for developers and users: once on-chain code is released, it cannot be changed, making security audits and risk prevention crucial.
Uncertainty in the External Environment: As DeFi integrates with traditional finance and NFTs penetrate mainstream culture, regulatory agencies in various countries are increasingly concerned about the compliance risks of on-chain activities. Some applications on Ethereum, such as decentralized exchanges and stablecoin issuance, may fall under existing financial regulatory frameworks. Compliance pressures may drive some large participants to withdraw or shift to permissioned chain environments, thereby affecting the flow of talent and capital within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Ethereum's Own Governance and Roadmap Execution: As a decentralized open-source protocol, Ethereum upgrades its network functions through the EIP proposal process, requiring extensive community discussion and multi-client implementation for all consensus layer changes. This open and transparent governance model ensures that all stakeholders have the opportunity to participate, but at the same time, the decision-making process is lengthy and coordination costs are high. Recent major upgrades (such as the Berlin, London, and Paris hard forks) have all experienced multiple delays and controversies. The rise of Ethereum's "staking as a service" platforms has led to a trend of centralization in the staking market: a few entities like Lido, Coinbase, Kraken, and Binance control over half of the ETH staking share, raising concerns about Ethereum's governance and transaction scrutiny.
In response to the above challenges, the Ethereum community is adopting a multi-faceted strategy:
Promoting a Rollup-Centric Approach: In the short term, rapidly scaling through Rollup solutions like Optimism and Arbitrum, while in the medium to long term, advancing sharding technology to increase on-chain data processing capacity by an order of magnitude, supporting further cost reductions for Rollups.
Ensuring Decentralization: Maintaining high decentralization standards and shifting scaling efforts to Layer 2. After transitioning to PoS, Ethereum is focusing on technologies such as light clients, state expiration, and data sampling, aiming to reduce the resource requirements for full nodes, making it possible for more ordinary users to run Ethereum nodes on home computers or mobile phones.
Strengthening Security and Developer Support: Establishing bug bounty programs and optimizing smart contract development frameworks to reduce security incidents; through annual DevCon developer conferences and hackathon events, gathering global developers to share knowledge and collaborate on innovations, injecting continuous vitality into the ecosystem.
Regulatory Communication and Innovation Protection: Currently, industry organizations, including the Ethereum Foundation, are actively communicating with regulators in various countries, hoping to establish rules that encourage innovation while protecting users. For example, regarding anti-money laundering (AML) and sanctions compliance issues, developers are researching methods to provide on-chain auditing tools without sacrificing privacy.
Improving Governance Mechanisms: The Ethereum community is already attempting to introduce diversified staking clients, promote trustless staking pools (such as Rocket Pool and SSV Network), and impose economic penalties for censorship behavior in extreme cases.
6. Latest Developments and Future Outlook for Ethereum
On July 30, 2025, Ethereum celebrated an important milestone: its tenth anniversary. In the current market landscape, Ethereum, as the world's second-largest crypto asset and the leading smart contract platform, is gradually becoming an indispensable part of global investment portfolios, with its influence permeating the intersection of the crypto economy and traditional finance, harboring the potential to drive the next wave of innovation.
Market Capitalization and Institutional Participation: The era of institutions in Ethereum has arrived, with significant inflows of institutional funds into Ethereum spot ETFs. Public companies like Bitmine and SharpLink are establishing ETH treasury strategies, viewing ETH as a long-term value reserve and strategic asset.
Regulatory Improvements and Mainstream Recognition: The regulatory environment has improved compared to five years ago. The U.S. Congress is pushing legislation to recognize ETH as a commodity rather than a security, and "on-chain dollar" stablecoins are also included in the regulatory framework, clearing obstacles for large institutions to confidently enter the Ethereum ecosystem. Companies like Visa have been using Ethereum to settle USDC since 2021, and banks like JPMorgan are also attempting to issue tokenized deposits on Ethereum-compatible networks, indicating that Ethereum is integrating into the mainstream financial system.
RWA On-Chain: Since 2024, "tokenization of real-world assets" has become a new trend, with firms like Blackstone and Franklin issuing tokenized funds based on Ethereum. Currently, over 70% of on-chain RWA issuance occurs on Ethereum and its Layer 2 solutions. In the future, more traditional assets such as bonds and equities may achieve digital circulation through the Ethereum network, expanding the boundaries of blockchain applications.
Technical Roadmap Outlook: In the coming years, Ethereum's development focus will shift from theoretical research to enhancing practical impact. On the technical side, in addition to the implementation of sharding technology to achieve "hundred times today's" scalability, there will also be a focus on improving user experience: account abstraction will allow users to manage complex private keys without hassle, and features like social recovery wallets will gradually be realized; privacy technologies (such as ZK-EVM) will enhance transaction confidentiality; these advancements will lower the barriers for ordinary users.
Looking back at the first decade of Ethereum, we see a journey of rebirth from the ashes amid skepticism, where Ethereum has consistently relied on the wisdom and perseverance of its community to find breakthroughs whenever it encounters bottlenecks. If the past decade has seen Ethereum reshape the underlying logic of digital finance, the next decade holds the promise of this "world computer" becoming a public infrastructure integrated into the backend of various industries, playing a key role in finance, commerce, governance, and more, achieving true interconnectivity and free flow of value. From the initial vision in the white paper to the now operational global network, the story of Ethereum is still being written. The next chapter of the decade is worth our anticipation.
About Us
Hotcoin Research, as the core investment research hub of the Hotcoin ecosystem, focuses on providing professional in-depth analysis and forward-looking insights for global crypto asset investors. We build a "trend assessment + value discovery + real-time tracking" integrated service system, offering in-depth analysis of cryptocurrency industry trends, multi-dimensional evaluations of potential projects, and all-weather market volatility monitoring, combined with weekly updates from the "Hotcoin Selected" strategy live broadcast and daily news briefings from "Blockchain Today," providing precise market interpretations and practical strategies for investors at different levels. Leveraging cutting-edge data analysis models and industry resource networks, we continuously empower novice investors to establish cognitive frameworks and assist professional institutions in capturing alpha returns, collectively seizing value growth opportunities in the Web3 era.
Risk Warning
The cryptocurrency market is highly volatile, and investment itself carries risks. We strongly recommend that investors conduct investments based on a full understanding of these risks and within a strict risk management framework to ensure the safety of their funds.
Website: https://lite.hotcoingex.cc/r/Hotcoinresearch
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




