
The Federal Reserve officially began its interest rate cut cycle in September 2025, marking a macro policy turning point that is creating an unprecedented favorable environment for crypto assets. Although the market has experienced short-term fluctuations, the cheap liquidity brought by rate cuts, institutional allocation demand, and the global desire for alternatives to traditional finance are laying a new foundation for the crypto market.

In August, the U.S. core PCE remained at 2.7%, significantly above the policy target. However, due to a cooling job market, the Federal Reserve initiated a preemptive rate cut in September: on September 17, 2025, the Federal Reserve made a long-anticipated decision to cut rates by 25 basis points, lowering the target range for the federal funds rate from 4.25%-4.50% to 4.00%-4.25%, thus officially starting the rate cut cycle of 2025. This follows three rate cuts implemented in 2024, marking another instance of the Federal Reserve adopting an accommodative monetary policy.
In the latest statement from the monetary policy meeting, the Federal Reserve removed the key phrase "the labor market remains robust" and instead emphasized that "job growth has slowed, and the unemployment rate has risen." This shift indicates that the Federal Reserve has officially shifted its policy focus towards protecting the job market in its dual mandate of inflation and employment.
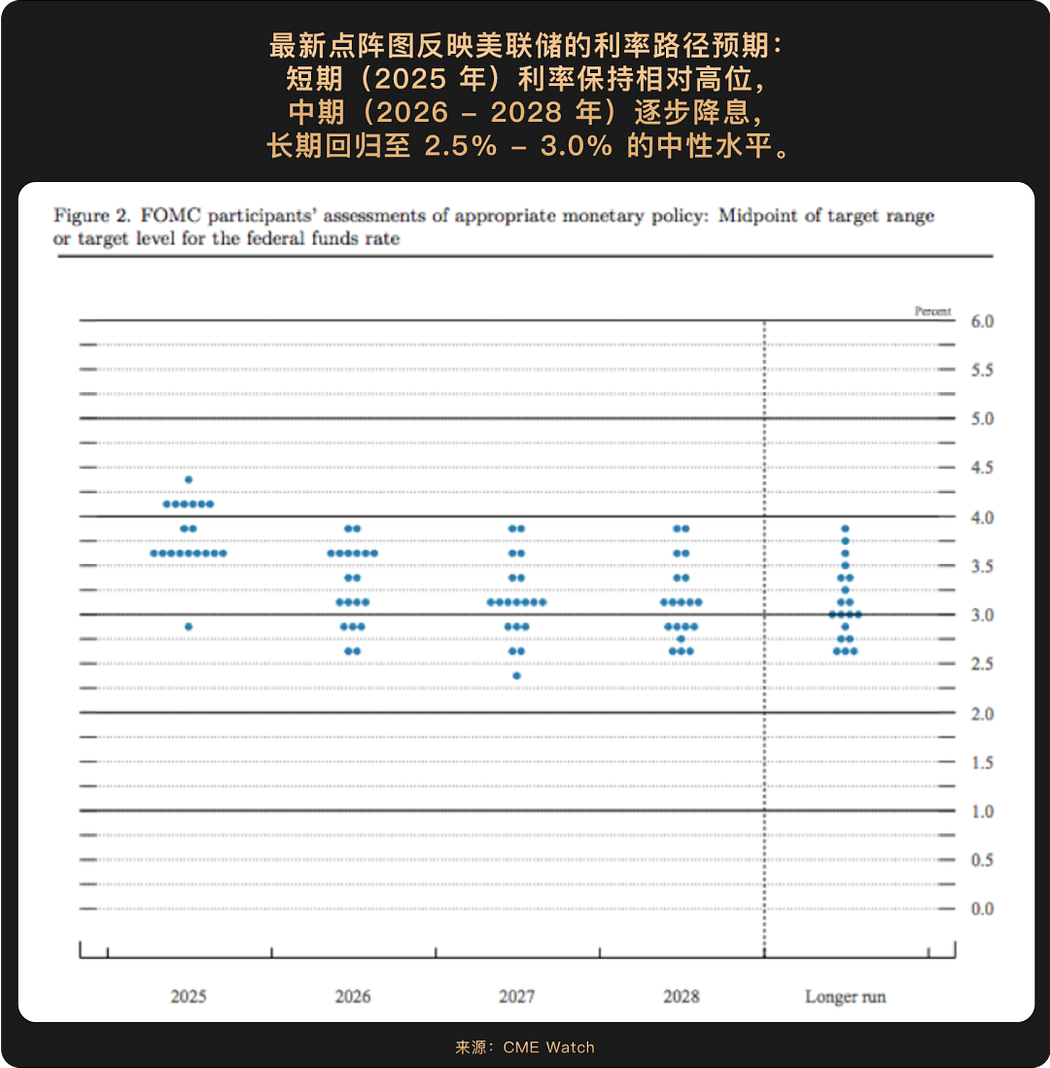
Powell candidly stated at the press conference that "there is no risk-free path," highlighting the cautious attitude towards this round of preemptive rate cuts. The new dot plot shows that Federal Reserve officials predict a median interest rate of 3.6% by the end of 2025, suggesting there is room for two more rate cuts this year. The market reacted strongly; according to CME Watch, the probability of a rate cut in October has risen to 91.9%, and the probability of a third rate cut in December exceeds 60%. Although there are slight differences between the dot plot guidance and market expectations, the accommodative tone has been largely established. The market had previously priced in a small number of rate cuts this year, but after this meeting, this pricing has further increased.
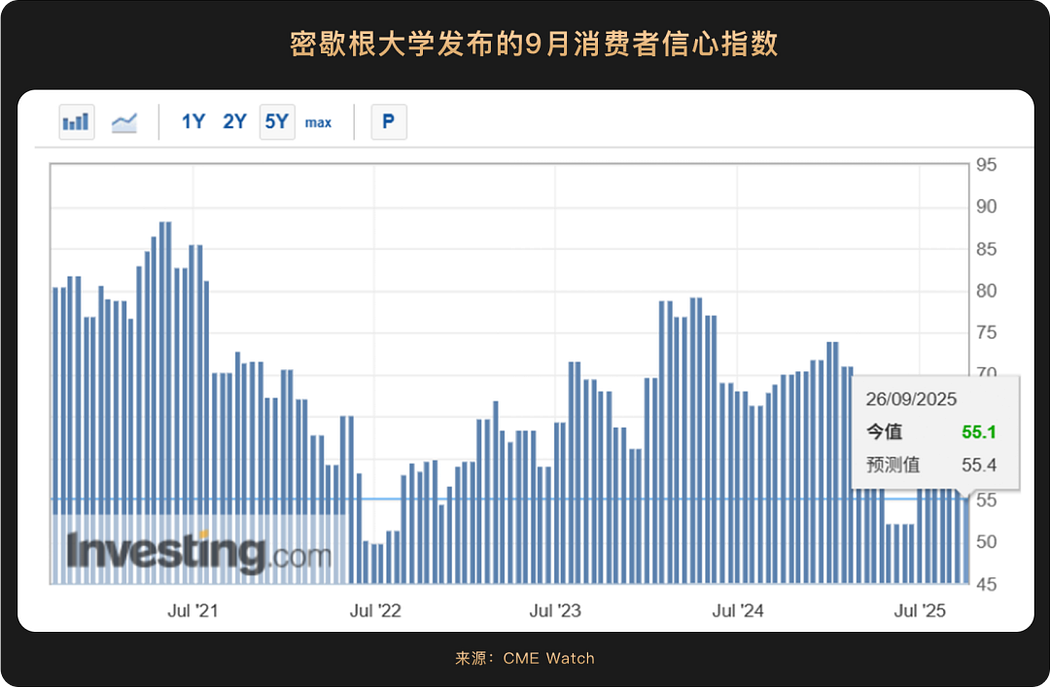
Additionally, the final consumer confidence index for September released by the University of Michigan was 55.1, a decrease of about 5% from August's 58.2, falling short of the market expectation of 55.4, and down significantly by 21.4% compared to the same period last year, marking the lowest level since May 2025. Recent data shows signs of cooling in the labor market (which is one of the reasons the Federal Reserve decided to cut rates in September), and the market is highly focused on the upcoming non-farm payroll data for September, as any signs of weakness could reinforce the Federal Reserve's rate cut expectations.
Overall, the current macroeconomic picture in the U.S. presents a scenario of strong economic growth but insufficient consumer confidence, with a policy outlook full of uncertainties, while the Federal Reserve will continue to cautiously balance the dual goals of employment support and inflation control within a data-dependent framework, making each interest rate decision akin to walking a tightrope.

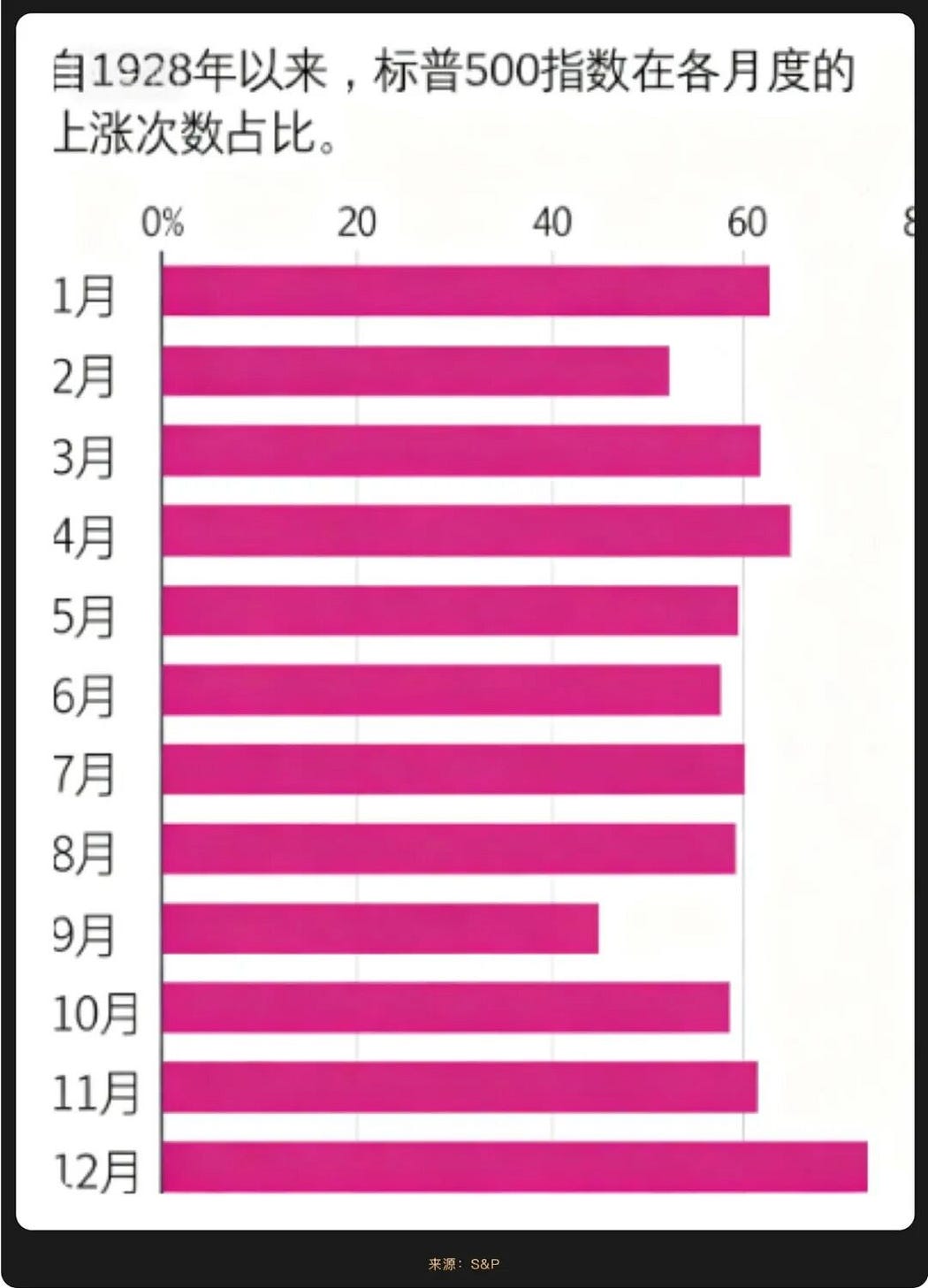
Historical data shows that U.S. stocks often perform poorly in September, leading to the notion of a "September curse." However, driven by the news of rate cuts, the Nasdaq, S&P 500, and Dow Jones indices all rose together this September, reaching historical highs. Technology stocks performed particularly well, with Intel (NASDAQ: INTC) seeing a one-day increase of over 22%, and AI-related sectors continuing their leading trend since the beginning of the year.
This round of increases is supported by dual driving forces: on one hand, the opening of the rate cut cycle significantly enhances risk appetite, aligning with the historical pattern where equity assets benefit first during a preemptive rate cut cycle; on the other hand, the AI industry is experiencing substantial performance growth, with cases like Nvidia's (NASDAQ: NVDA) $10 billion investment in OpenAI providing solid support for technology stock valuations.
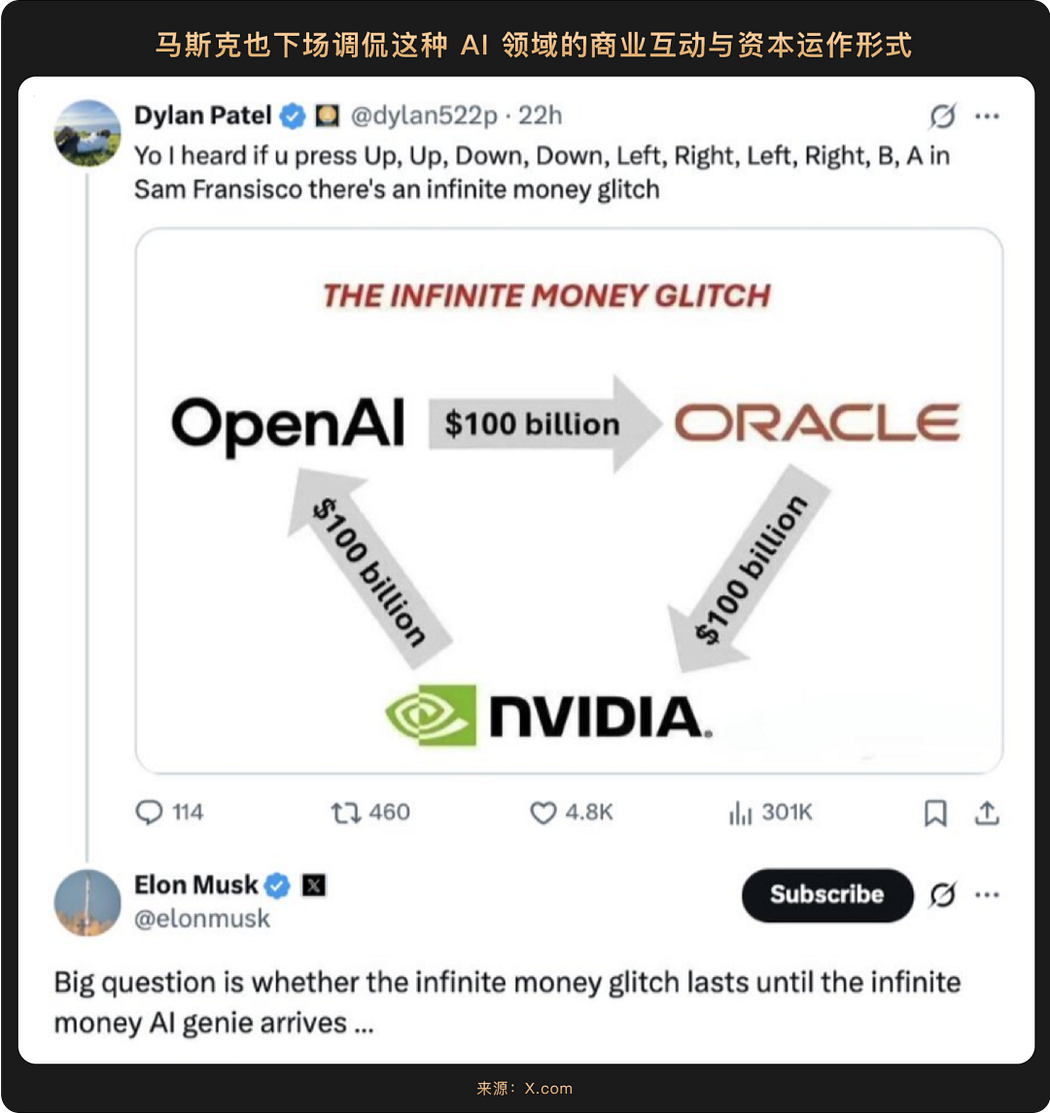
Interestingly, the $10 billion transactions between Nvidia, OpenAI, and Oracle (NASDAQ: ORCL) seem to create a new valuation framework for Silicon Valley: Nvidia's $10 billion investment will gradually be realized with the deployment of OpenAI's 10-gigawatt computing power data center, which requires 400,000 to 500,000 GPUs per gigawatt, with a total of 10 gigawatts equivalent to Nvidia's annual shipment volume—this means that the investment funds will ultimately flow back to Nvidia through OpenAI's GPU procurement orders, while Nvidia can also gain profit sharing from OpenAI through equity; Oracle's involvement further strengthens the closed loop, as it initially invested $40 billion to purchase Nvidia chips to build OpenAI's "Stargate" data center, and then provided computing power to OpenAI through a $300 billion cloud service contract, forming a closed-loop funding flow chain of "OpenAI→Oracle→Nvidia→OpenAI."
This model will drive a reconstruction of technology stock valuations, as Nvidia strengthens its pricing power and performance visibility in the AI chip sector by binding downstream core customers; Oracle achieves a leapfrog in the cloud service market; and OpenAI secures ongoing funding and computing power support for sustainable development. This strong alliance further intensifies the Matthew effect in the AI industry, with resources continuously concentrating on leading enterprises, enhancing the certainty and collaborative efficiency of all parties' businesses, and redefining the competitive paradigm of tech giants in the AI era, providing investors with a new framework for analyzing the value of technology stocks.
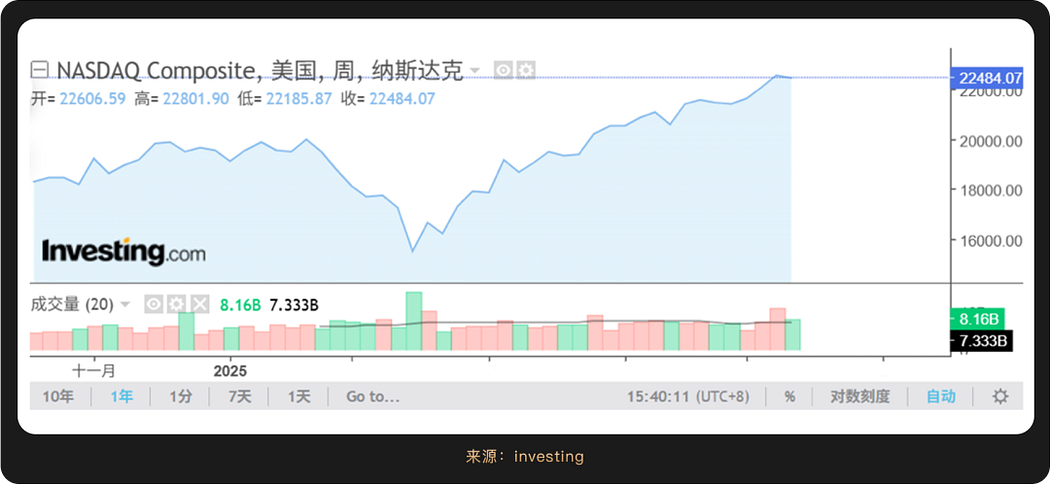
However, Federal Reserve Chairman Powell has also clearly warned that the current valuation of the U.S. stock market is "quite high," a statement that is particularly critical in the context of new highs. Currently, both the S&P 500 and Nasdaq have risen over 20% this year, and the valuations of AI concept stocks have partially overdrawn future performance, with any hawkish signals potentially triggering profit-taking. It is worth noting that Powell emphasized that this rate cut "is not the beginning of an aggressive easing cycle," which means that the release of liquidity will maintain a gradual pace.
Looking ahead, the U.S. stock market still faces multiple tests. The resilience of inflation is the main constraint, as the August core PCE year-on-year rate of 2.7% remains significantly above the policy target. If subsequent data rebounds, it may force the Federal Reserve to slow down the pace of rate cuts. Additionally, there are certain internal disagreements within the Federal Reserve regarding the policy path, and the risk of government shutdown may delay the release of key data, all of which will exacerbate market volatility.

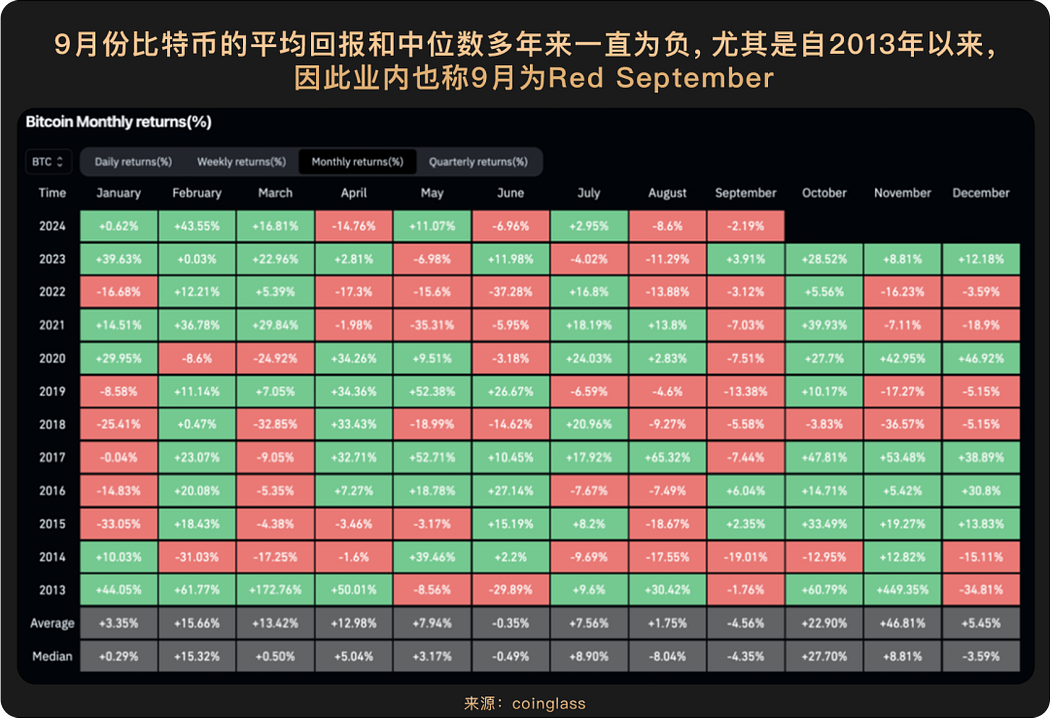
Although Bitcoin experienced a pullback in September, briefly falling below $110,000, it formed strong support in the $90,000 to $105,000 range, once again validating the institutional behavior model of "buy on expectations, hold through volatility." For example, on September 25-26, due to macro risk aversion stemming from concerns that the U.S. federal government might face a "shutdown" due to budget issues, along with profit-taking by long-term Bitcoin holders and market declines triggering high-leverage liquidations, funds flowed out of risk assets like Bitcoin. However, institutional investors viewed this as a buying opportunity. On the day of the price drop on September 25, the U.S. spot Bitcoin ETF recorded a net inflow of $241 million. Among them, BlackRock's IBIT single fund alone saw an inflow of nearly $129 million, bringing total holdings to 768,000 BTC (approximately $85.2 billion).
Historical data also shows that after the Federal Reserve initiated "preemptive rate cuts" in 2019, Bitcoin experienced nearly six months of initial fluctuations. As the long-term effects of the low-interest-rate environment gradually became apparent, Bitcoin stabilized at $7,000 by the end of 2019 and continued its upward trend in 2020, breaking through $29,000 by the end of 2020, representing an increase of over 200% compared to the peak of $10,000 at the beginning of the rate cuts in July 2019; if calculated from the $7,000 low at the end of 2019, the increase exceeds 300%.
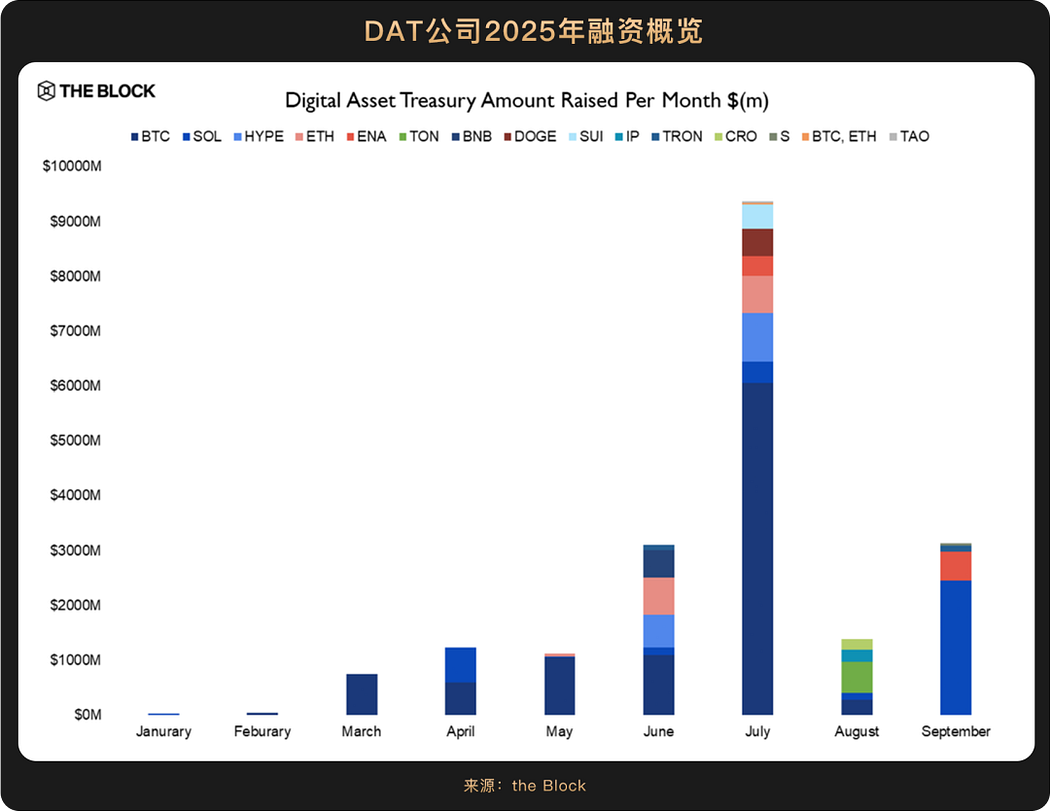
The initiation of the rate cut cycle means a decline in interest rates in traditional financial markets, and in a low financing cost environment, companies are naturally more willing to invest funds into high-growth potential assets, making institutional investors' actions clearer. However, unlike the rate cut situation in 2019, the current cycle has introduced a significant new variable: the allocation of crypto treasury by publicly listed companies.
Moreover, these companies' allocation of crypto assets is moving away from early marginal experiments and tentative holdings, transitioning to long-term and strategic allocations. In September, the board of directors of Nasdaq-listed company Jiuzi Holdings (NASDAQ: JZXN) approved a crypto asset investment plan of up to $1 billion, with management emphasizing that they "do not pursue short-term trading profits," but rather view crypto assets as a "long-term store of value to hedge against macroeconomic uncertainties," highlighting the long-term and strategic nature of their allocation behavior. On the regulatory front, in September, the U.S. SEC and FINRA announced investigations into over 200 publicly listed companies that have announced crypto treasury plans, focusing on unusual stock price fluctuations prior to their announcements. This move poses challenges in the short term, but in the long run, clearing out those "pseudo-treasury" companies attempting to manipulate market capitalization through the "crypto narrative" is a way for the market to distinguish between the genuine and the false, establishing a healthier development environment for truly strategic treasury allocation models. For market participants, the dynamics of treasury allocations will become another reliable "window" for understanding industry direction.
In short, the evolution of crypto treasury allocation reflects the overall trajectory of the crypto market from the margins to the mainstream, from speculation to practicality, and from individual to institutional involvement. As the rate cut cycle continues, driven by both a low-interest-rate environment and technological innovation, corporate treasury allocations in crypto are expected to deepen and diversify further. Companies that write crypto assets into their balance sheets express their confidence in the future of crypto assets in the most direct way possible—with real money. This confidence, underpinned by the ample ammunition provided by rate cuts, is likely to become a key force driving the next wave of growth.

Looking ahead, at least three factors are creating a favorable environment for crypto assets, making them a more attractive choice:
Macroeconomic "fuel" — — There will be 2-3 more rate cuts within the year;
Political cycle reinforcement — — The pro-crypto policies of the Trump administration and challenges to the independence of the Federal Reserve highlight the hedging properties of decentralized assets;
Global economic "real-virtual linkage" — — The rise in gold prices suggests recession concerns, while crypto assets possess both the store of value attributes of gold and the growth potential of technology, making them a superior allocation choice during the rate cut cycle.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。


