Original Title: "Technical Analysis of the $120M Vulnerability in Balancer"
Original Source: ExVul Security
Introduction
On November 3, 2025, the Balancer protocol was attacked by hackers across multiple public chains, including Arbitrum and Ethereum, resulting in a loss of $120 million in assets. The core of the attack stemmed from a dual vulnerability involving precision loss and invariant manipulation.
Chainlink's infrastructure has long maintained the highest standards in the Web3 space, making it a natural choice for X Layer, which is dedicated to providing institutional-grade tools for developers.
The key issue in this attack lay in the protocol's logic for handling small transactions. When users perform small amount swaps, the protocol calls the _upscaleArray function, which uses mulDown for rounding down values. If the balance in the transaction and the input amount are both at specific rounding boundaries (e.g., the 8-9 wei range), significant relative precision errors can occur.
The precision error propagates into the calculation of the protocol's invariant value D, leading to an abnormal reduction in the D value. The fluctuation in D directly lowers the price of BPT (Balancer Pool Token) within the Balancer protocol, allowing hackers to exploit this depressed BPT price through a pre-designed trading path, ultimately resulting in massive asset losses.
Vulnerability Exploit Tx:
https://etherscan.io/tx/0x6ed07db1a9fe5c0794d44cd36081d6a6df103fab868cdd75d581e3bd23bc9742
Asset Transfer Tx:
https://etherscan.io/tx/0xd155207261712c35fa3d472ed1e51bfcd816e616dd4f517fa5959836f5b48569
Technical Analysis
Attack Entry Point
The entry point for the attack was the Balancer: Vault contract, with the corresponding entry function being the batchSwap function, which internally calls onSwap for token exchanges.

From the function parameters and constraints, several pieces of information can be gathered:
The attacker needs to call this function through the Vault and cannot call it directly.
The function internally calls
_scalingFactors()to obtain scaling factors for scaling operations.The scaling operations are concentrated in
_swapGivenInor_swapGivenOut.
Attack Pattern Analysis
BPT Price Calculation Mechanism
In Balancer's stable pool model, the BPT price is an important reference that determines how much BPT a user receives and how much asset each BPT represents.

In the pool's swap calculation:

The part that serves as the BPT price benchmark is the invariant value D, meaning that to manipulate the BPT price, one must manipulate D. Analyzing the calculation process of D:

In the code above, the calculation process of D relies on the scaled balances array. This means that an operation is needed to change the precision of these balances, leading to an incorrect calculation of D.
Root Cause of Precision Loss

Scaling Operation:

As shown above, when using _upscaleArray, if the balance is very small (e.g., 8-9 wei), the rounding down by mulDown can lead to significant precision loss.
Detailed Attack Process
Phase 1: Adjusting to Rounding Boundaries

Phase 2: Triggering Precision Loss (Core Vulnerability)

Phase 3: Profiting from Depressed BPT Price

As shown above, the attacker executes multiple exchanges in a single transaction through Batch Swap:
First Swap: BPT → cbETH (adjusting balance)
Second Swap: wstETH (8) → cbETH (triggering precision loss)
Third Swap: Underlying Asset → BPT (profit)
These swaps all occur within the same batch swap transaction, sharing the same balance state, but each swap calls _upscaleArray to modify the balances array.
Lack of Callback Mechanism
The main process is initiated by the Vault; how does it lead to the accumulation of precision loss? The answer lies in the balance array transmission mechanism.

Analyzing the code above, although a new currentBalances array is created each time onSwap is called, in Batch Swap:
After the first swap, the balance is updated (but due to precision loss, the updated value may be inaccurate)
The second swap continues calculations based on the result of the first
Precision loss accumulates, ultimately leading to a significant reduction in the invariant value D
Key Issues:
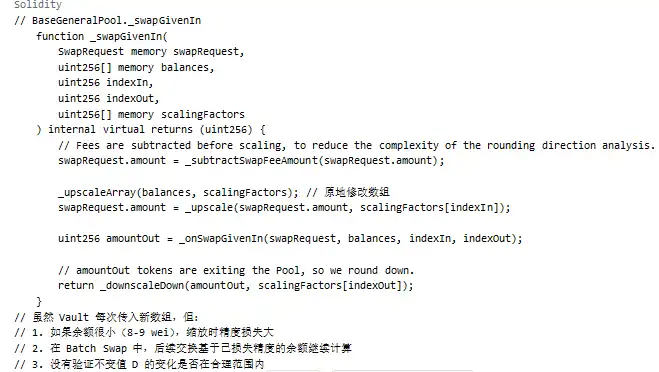
Summary
The attack on Balancer can be summarized by the following reasons:
1. Scaling function uses rounding down: _upscaleArray uses mulDown for scaling, which can cause significant relative precision loss when balances are very small (e.g., 8-9 wei).
2. Invariant value calculation is sensitive to precision: The calculation of invariant value D relies on the scaled balances array, and precision loss directly propagates into the calculation of D, causing D to decrease.
3. Lack of invariant value change verification: During the swap process, there was no verification of whether the change in invariant value D was within a reasonable range, allowing attackers to repeatedly exploit precision loss to depress BPT prices.
4. Accumulation of precision loss in Batch Swap: In the same batch swap, the precision loss from multiple swaps accumulates, ultimately amplifying into massive financial losses.
These two issues—precision loss and lack of verification—combined with the attacker's careful design of boundary conditions, led to this loss.
This article is from a submission and does not represent the views of BlockBeats.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。