Original Title: "Arkstream Capital: 2025 When Crypto Assets Return to 'Financial Logic'"
Original Source: Arkstream Capital
TL;DR
Core change in 2025: Pricing framework "externalized." No longer primarily relying on a single public chain cycle/narrative for self-circulation, but instead dominated by policy and compliance + macro liquidity/risk appetite + leverage and risk control; price elasticity depends on which entry points funds come from, what assets are bought, and how to exit under pressure.
Funding entry shifts from "on-chain leverage single channel" to multiple parallel channels: ETF (standardized allocation) + stablecoin USD base (on-chain settlement/turnover) + DAT (public company financing capability → spot demand function) + listing path (IPO) (mapping capabilities such as licensing/custody/clearing/institutional services to tradable stock cash flows).
Internal evolution of the industry: Shifting from "narrative-driven" to "product line-driven" — stablecoin stratification (cash layer vs yield efficiency tools, the latter being more cyclical), on-chain perpetuals entering infrastructure and moving towards market share battles, prediction markets expanding from crypto-native to event contract markets, making it easier for industry rhythms to couple with macro/political variables.
Listing path/IPO: In 2025, 9 crypto/related companies complete IPOs, raising a total of approximately $7.74 billion; valuations range from approximately $1.8 billion to $23 billion; initial circulation ranges from approximately 7.6% to 26.5%.
Potential IPO candidates for 2026: Anchorage Digital, Upbit, OKX, Securitize, Kraken, Ledger, BitGo, Tether, Polymarket, Consensus (about 10 companies).
Observable funding entry: Total supply of stablecoins ~ $205 billion → ~ $300 billion+ (structure: USDT ~ $186.7 billion, USDC ~ $77 billion); net inflow of IBIT ~ $25.4 billion within the year; number of companies adopting DAT reaches hundreds, with total holdings in the hundred billion dollar range; on-chain perpetuals have nearly $10.81 trillion in transactions over the past 30 days, with open interest ~ $15.4 billion; prediction market annual trading volume in 2025 ~ $44 billion; USDe ~ $15 billion → ~ $8.5 billion → ~ $6-7 billion.
The main narrative of the crypto market in 2025 will no longer revolve around the technological cycle of a single public chain or the self-circulation of on-chain narratives, but will enter a deepened phase dominated by "external variable pricing and competition for financial entry." Policy and compliance frameworks will determine the access boundaries for long-term capital, macro liquidity and risk appetite will determine whether trends can continue, and derivatives leverage and platform risk control mechanisms will reshape volatility patterns and drawdown speeds at critical junctures. More importantly, a key narrative that will be repeatedly validated by the market starting in 2025 is that what determines price elasticity is no longer just the "intensity of on-chain narratives," but rather which entry points funds come through, what investable assets they land on, and how they exit under pressure. External variables and internal evolution jointly drive the transformation of the crypto industry in 2025, further establishing two clear paths for the future development of the crypto industry.
Institutional Acceleration and Breakthrough in Securitization: The Dominant Phase of External Variables in the 2025 Crypto Market
"Financialization" underwent a structural shift in 2025. The way funds enter is no longer limited to on-chain native leverage but has diversified into multiple parallel, clearly stratified channels. Crypto allocations have expanded from a single "asset exposure (spot/ETF)" to a dual structure of "asset exposure + industrial equity," and market pricing has shifted from a single-axis drive of "narrative-position-leverage" to a comprehensive framework of "institutional-fund flow-financing capability-risk transmission."
On one hand, standardized products (such as ETFs) incorporate crypto assets into the risk budget and passive allocation framework of investment portfolios; the expansion of stablecoin supply solidifies the on-chain USD settlement base, enhancing the market's endogenous settlement and turnover capabilities; corporate treasury (DAT) strategies directly map the financing capabilities and balance sheet expansions of public companies to spot demand functions. On the other hand, crypto companies "securitize" their licensing, custody, trading, clearing, and institutional service capabilities into publicly traded company stocks through IPOs, allowing institutional funds to purchase cash flows and compliance moats of crypto financial infrastructure in a familiar manner for the first time, and introducing a clearer benchmarking system and exit mechanism.
The role of IPOs in the funding structure is to "buy industry, buy cash flow, buy compliance capability." This path rapidly opened up in 2025, becoming one of the preferred choices for leading crypto companies and an external variable for the crypto industry.
In the previous five years, this path had not been clearly defined, not because the public market formally closed off the listing of crypto companies, but because the practical aspects of listing had long been in a state of "high barriers, difficult pricing, difficult underwriting":
On one hand, unclear regulatory standards combined with high-intensity enforcement made core businesses such as trading, brokerage, custody, and issuance face higher densities of legal uncertainty disclosures and risk discounts in their prospectus materials (for example, the SEC sued Coinbase in 2023, accusing it of operating as an unregistered trading platform/broker/clearing agency, which reinforced the uncertainty of "business nature possibly being retroactively defined").
On the other hand, the tightening of accounting and auditing standards for custody-type businesses raised compliance costs and the threshold for institutional cooperation (for example, SAB 121 proposed stricter asset/liability presentation requirements for "custody of crypto assets for clients," which the market widely believes significantly increased the asset burden and audit friction for financial institutions engaging in crypto custody business).
At the same time, industry credit shocks and macro tightening compounded, causing the overall IPO window in the U.S. stock market to shrink, with many projects preferring to delay or change paths even if they wanted to leverage the public market (for instance, Circle terminated its SPAC merger at the end of 2022, and Bullish halted its SPAC listing plan in 2022). More critically, from the execution perspective of the primary market, these uncertainties would be amplified into real "underwriting frictions": underwriters need to conduct stress tests through internal compliance and risk committees during the project initiation phase to assess whether business boundaries might be retroactively defined, whether key revenues might be reclassified, whether custody and client asset isolation would introduce additional balance sheet burdens, and whether potential enforcement/litigation might trigger significant disclosure and compensation risks; once these issues are difficult to standardize and explain, it leads to significantly increased due diligence and legal costs, longer risk factors in the prospectus, unstable order quality, ultimately reflecting in more conservative valuation ranges and higher risk discounts. For issuing companies, this directly changes strategic choices: rather than pushing forward in an environment where "explanation costs are high, pricing is suppressed, and post-listing volatility is uncontrollable," it is better to delay issuance, turn to private financing, or seek mergers/other paths. The aforementioned constraints collectively determined that during that phase, IPOs were more like a "choice question" for a few companies, rather than a sustainable financing and pricing mechanism.
The key change in 2025 is that the aforementioned resistances have seen a clearer "relief/easing," allowing the listing path to regain continuity expectations. One of the most representative signals is the SEC's release of SAB 122 in January 2025 and the withdrawal of SAB 121 (effective that month), which directly removed the most controversial and "heavy asset burden" accounting obstacles for institutions participating in custody and related businesses, improving the scalability of the banking/custody chain and reducing the structural burdens and uncertainty discounts for related companies at the prospectus level. During the same period, the SEC established a crypto asset working group and signaled the promotion of a clearer regulatory framework, lowering the uncertainty premium regarding "whether rules will change or be retroactive" at the expectation level; meanwhile, legislative progress in the stablecoin sector further provided "framework-level" certainty, making it easier for traditional capital to incorporate key links such as stablecoins, clearing, and institutional services into the valuation system in an auditable and comparable manner.
These changes will rapidly transmit along the execution chain of the primary market: for underwriters, it becomes easier to transform from "inexplicable, unpriceable" to "disclosable, measurable, comparable" compliance conditions — conditions that can be written into the prospectus and horizontally compared by buyers, making it easier for the underwriting syndicate to provide valuation ranges, grasp issuance rhythms, and invest research coverage and distribution resources. For issuing companies, this means that IPOs are no longer just a "financing action," but a process of engineering revenue quality, client asset protection, internal control, and governance structure into "investable assets." Furthermore, although the U.S. stock market does not have a clear "cornerstone investor" system like the Hong Kong stock market, anchor orders and long-term accounts (large mutual funds, sovereign funds, some crossover funds) during the book-building phase function similarly: when regulatory and accounting frictions ease and industry credit risks clear, high-quality demand is more likely to return to the order book, helping stabilize pricing and ensure more continuous issuance, thus making IPOs more likely to transition from "occasional windows" back to "sustainable financing and pricing mechanisms."
Ultimately, the marginal improvements in policy and accounting standards will specifically reflect the rhythm of the annual market and the flow of funds through the primary market and funding allocation chain. From the perspective of the annual development in 2025, the aforementioned structural changes appear more like a relay-style manifestation.
At the beginning of 2025, the convergence of regulatory discounts prompted a reassessment of institutional expectations, with core assets benefiting first from clearer allocation paths; subsequently, the market entered a repeated confirmation period regarding macro hard boundaries, with interest rate paths and fiscal policies embedding crypto assets more deeply into the volatility models of global risk assets (especially U.S. growth stocks). By mid-year, the reflexivity of DAT gradually became evident: the number of public companies adopting treasury-like strategies rose to the hundreds, with total holdings reaching the hundred billion dollar level, and balance sheet expansion became an important source of marginal demand; at the same time, ETH-related treasury allocations heated up, making the transmission of "balance sheet expansion — spot demand" no longer revolve solely around BTC. By the third and fourth quarters, against the backdrop of multiple parallel channels and the rebalancing of funds between different entry points, the valuation center and issuance conditions in the public market began to more directly influence the allocation of funds in the crypto sector: whether issuances were smooth and whether pricing was recognized gradually became barometers for measuring "industry financing capability and compliance premium," indirectly transmitting through the reallocation of funds between "buying coins/buying stocks" to spot pricing. As Circle and others provide "valuation anchors," and more companies advance their IPO applications and preparations, IPOs further evolve from "pricing references" to core variables affecting funding structures: ETFs primarily address the question of "can they be allocated, how to include them in the portfolio," while IPOs further resolve "what to allocate, how to benchmark, how to exit," driving some funds from the high-turnover on-chain leverage ecosystem to more long-term industrial equity allocations.
More importantly, this "entry competition" is not just a theoretical framework but can be directly observed in funding data and market behavior. As the on-chain USD settlement base, the supply of stablecoins is expected to rise from approximately $205 billion to the $300 billion range by 2025, stabilizing near the end of the year, providing a thicker settlement and liquidity buffer for on-chain trading expansion and deleveraging processes; ETF fund flows solidify as explicit pricing factors, and under macro volatility and institutional rebalancing disturbances, IBIT still achieves a net inflow of about $25.4 billion for the year, increasing the explanatory power of "net flow/rebalancing rhythm" on price elasticity; the scaling of DAT allows the balance sheets of public companies to directly influence the spot supply-demand structure, potentially strengthening trend expansion during upswings, while during downturns, valuation premium contractions and financing constraints may trigger reverse transmission, thereby coupling the volatility of traditional capital markets with the crypto market. Meanwhile, IPOs also provide another set of quantitative evidence: In 2025, a total of 9 crypto/crypto-related companies completed IPOs, raising approximately $7.74 billion, indicating that the public market financing window not only exists but also has real capacity for carrying out financing.
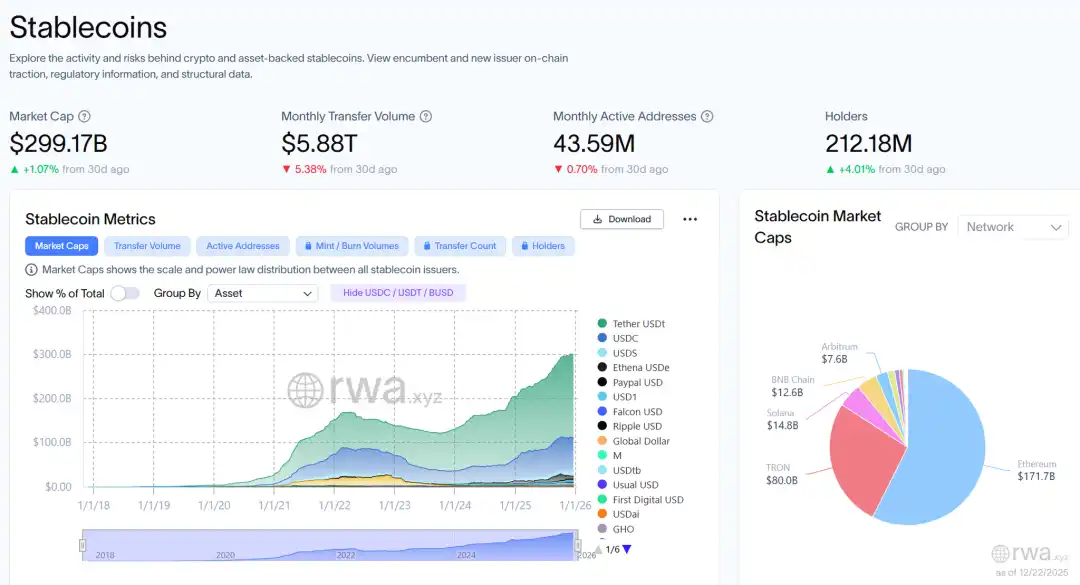
Source: rwa.xyz / Growth of Stablecoins in 2025

Source: CoinMarketCap / Annual Data on ETF Funds
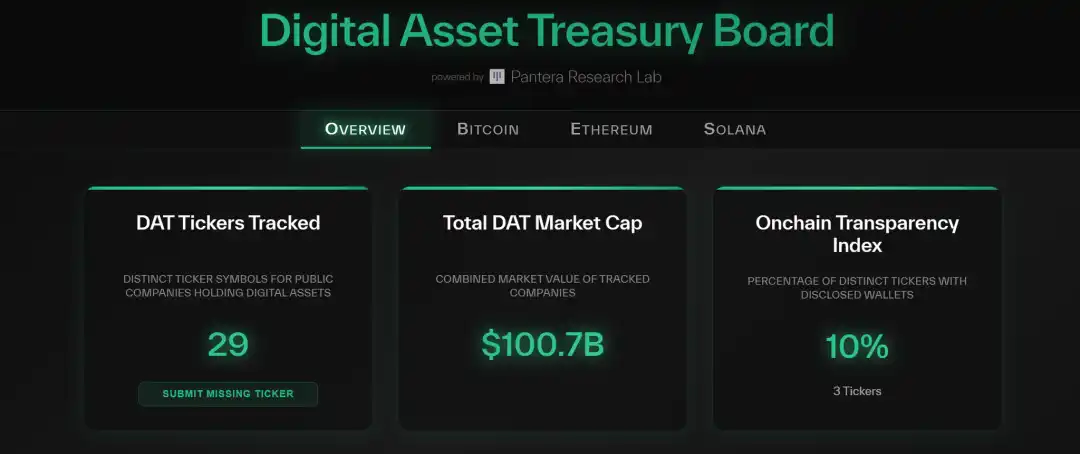
Source: Pantera Research Lab / Data on DAT
In this context, IPOs have become an "external structural variable" in the crypto market of 2025: on one hand, it expands the range of compliant funds that can be allocated, providing valuation anchors and benchmarking systems for stablecoins, trading/clearing, brokerage, and custody in the public market, and changes the holding period and exit mechanism of funds through the "stock" form; on the other hand, its marginal increment is not linear and is still constrained by macro risk appetite, secondary market valuation centers, and issuance windows.
Overall, 2025 can be summarized as a year of "accelerated institutionalization, strengthened macro constraints, and the restart of securitization": the advancement of institutional and compliance pathways has increased the configurability of crypto assets, expanding funding entry from a single on-chain structure to a parallel system of ETFs, stablecoin bases, DAT, and IPOs; at the same time, interest rates, tariffs, and fiscal frictions continue to shape liquidity boundaries, bringing market conditions closer to the "macro-driven volatility" of traditional risk assets. The resulting differentiation in sectors and the return of "public company vehicles" will form an important prelude to 2026.
IPO Window Warms Up: From Narrative Premium to Financial Terminology
In 2025, the IPO window for crypto-related companies in the U.S. stock market clearly warmed up, evolving from a "conceptual window opening" to a set of publicly marketable samples that can be quantitatively tested: throughout the year, a total of 9 crypto/crypto-related companies completed IPOs, raising approximately $7.74 billion, indicating that the public market has restored its capacity to absorb financing for "compliant and accessible digital financial assets" to a considerable scale, rather than just symbolic small amounts. In terms of valuation, this group of IPOs covers a valuation range of approximately $1.8 billion to $23 billion, essentially covering stablecoins and digital financial infrastructure, compliant trading platforms and trading/clearing infrastructure, regulated brokerage channels, as well as on-chain credit/RWA and other key segments, allowing the industry to begin to have a trackable and comparable equity asset sample pool; this not only provides valuation anchor points for the "stablecoin—trading—brokerage—institutional services—on-chain credit/RWA" chain but also allows the market's pricing language for crypto companies to systematically migrate towards a financial institutional framework (emphasizing compliance and licensing, risk control and operational resilience, revenue quality and sustainable profits). In terms of market performance, the 2025 sample generally exhibited a common characteristic of "strong initial phase, followed by rapid differentiation": in terms of issuance structure, many companies had tight initial circulation (approximately 7.6%–26.5%), making short-term price discovery more elastic when the risk appetite window opened; the secondary market showed overall strength on the first day, with some assets experiencing double-digit re-pricing, while others also saw double-digit positive returns, and many companies maintained strong performance in the first week and month, reflecting that buyers had a "sustained absorption" of such assets during the window period rather than a one-time pricing; however, after 1–6 months, differentiation significantly increased, aligning more closely with the traditional risk asset logic of "macro + quality" — companies more focused on retail and trading businesses were more sensitive to shifts in risk appetite and experienced quicker drawdowns, while assets more focused on upstream infrastructure and institutional absorption capabilities were more likely to receive sustained re-ratings.
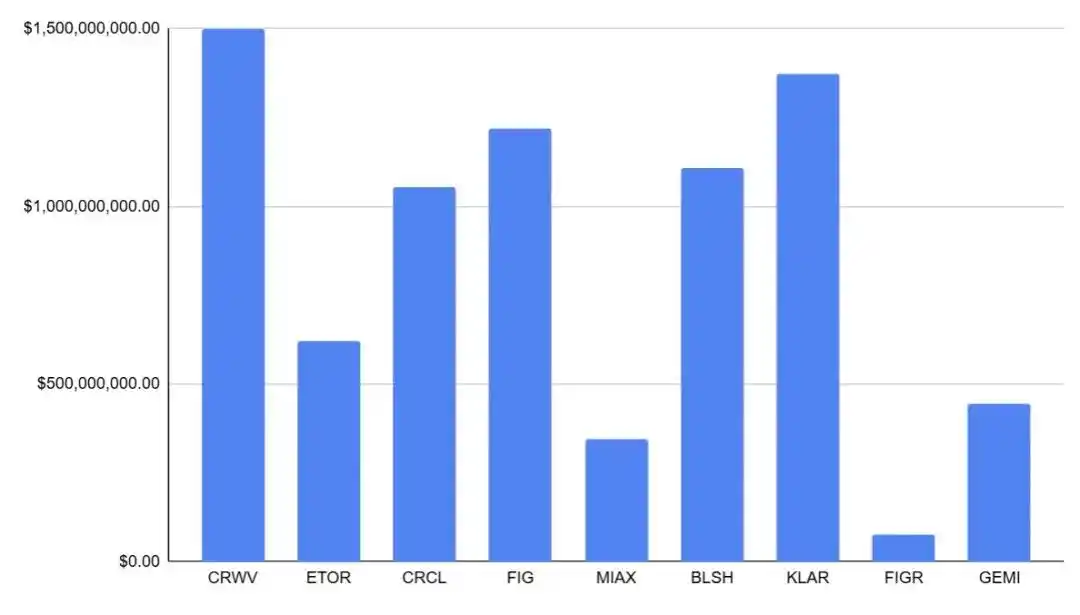
Source: nasdaq.com / Total IPO Amounts of Crypto Companies in the U.S. Stock Market in 2025
More critically, the "return" of U.S. stock market crypto company IPOs is highly sought after because it simultaneously meets three key concerns of the public market during a window period: buyable, comparable, and exitable.
First, it transforms the previously hard-to-access "cash flows of crypto financial infrastructure" into stock assets that traditional accounts can directly hold, naturally fitting the compliance and risk control frameworks of long-term funds such as mutual funds, pensions, and sovereign funds;
Second, IPOs provide the industry with a batch of horizontally comparable equity samples for the first time, allowing buyers to no longer rely solely on "narrative intensity/transaction volume extrapolation" for valuation but to layer it using familiar financial institutional language — compliance costs and licensing barriers, risk preparedness and internal control governance, customer structure and retention, revenue quality and capital efficiency — when pricing methods become more standardized, buyers are more willing to offer higher certainty premiums during the window period;
Third, IPOs partially shift the exit mechanism from "on-chain liquidity and emotional cycles" to "public market liquidity + market making/research coverage + index and institutional rebalancing," enabling funds to confidently provide stronger order quality during the issuance phase (including more stable long-term demand and anchor orders), which in turn reinforces the re-pricing momentum during the initial phase. In other words, the enthusiasm does not solely stem from risk appetite but from the risk premium decline brought about by "institutional accessibility": when assets become easier to audit, easier to compare, and easier to incorporate into risk budgets, the public market is more willing to pay a premium for them.
Among these, Circle is the most representative case of a "stablecoin sector equity valuation anchor": its IPO was priced at $31, raising approximately $1.054 billion, corresponding to an IPO valuation of about $6.45 billion, while the secondary market strongly re-priced it during the window period — approximately +168.5% on the first day, about +243.7% in the first week, and around +501.9% in the first month, peaking at $298.99 with a maximum increase of about +864.5%, and even maintaining around +182.1% over a six-month sample point. The significance of Circle lies not in the "increase itself," but in that it transformed "stablecoins" from assets that previously relied more on on-chain growth narratives into a publicly traded equity that the market prices as a "financial infrastructure cash flow" that is auditable, comparable, and can be included in risk budgets for the first time: compliance moats and settlement network effects are no longer just concepts but are directly reflected in the elevation of valuation centers through issuance pricing and sustained secondary absorption. At the same time, Circle also validated the typical "buying method" of the U.S. stock market for such assets — when the window opens, a small circulation combined with high-quality buyer demand amplifies price elasticity; however, after the window shrinks, valuations return more quickly to fundamentals, with differentiation in cycle sensitivity and profit quality. This also constitutes our core reason for being optimistic about U.S. stock market crypto company IPOs: the public market does not indiscriminately raise valuations, but it completes layering more quickly and clearly, and once high-quality assets establish a comparable valuation anchor in the public market, their capital costs will decrease, refinancing and acquisition currencies will become stronger, and the positive cycle of growth and compliance investment will be easier to realize — this is more important than short-term fluctuations.
Looking ahead to 2026, the market focus will shift from "whether a window exists" to "whether subsequent listing projects can continue to advance and form a more continuous issuance rhythm." According to current market expectations, potential candidates include Anchorage Digital, Upbit, OKX, Securitize, Kraken, Ledger, BitGo, Tether, Polymarket, Consensus, etc., totaling about 10 companies, covering a more complete industrial chain from custody and institutional compliance entry, trading platforms and brokerage channels, stablecoins and settlement bases, asset tokenization and compliant issuance infrastructure, to hardware security and new information markets. If these projects can continue to land in the public market and receive relatively stable funding absorption, their significance will not only be "a few more financings" but will further standardize investors' logic of buying into crypto companies: they will be more willing to pay premiums for compliance moats, risk control and governance, revenue quality, and capital efficiency, while also being quicker to filter through valuation centers and secondary performance during macro headwinds or weakened issuance conditions. Overall, we are optimistic about the directional trend of U.S. stock market crypto company IPOs: 2025 has already validated the public market's absorption capacity through quantity, financing scale, and market re-pricing; if 2026 can continue this trend of "continuous issuance + stable absorption," IPOs will resemble a sustainable capital cycle — pushing the industry from "narrative-driven phase market" further towards "sustainable pricing in the public market," allowing companies with genuine compliance and cash flow quality to continuously expand their leading advantages at lower capital costs.
Industry Structural Differentiation and Product Line Formation: Internal Evolution of the Crypto Industry
To determine whether this public market path can continue and which companies are more likely to be "accepted" by the market, the key is not to reiterate "whether a window exists," but to return to the structural evolution that has already occurred within the industry in 2025: growth drivers are shifting from single-point narratives to multiple sustainable product lines, forming volatility and differentiation mechanisms that are closer to traditional risk assets under macro and regulatory constraints — it is within this mechanism that capital markets will decide which business models deserve a more stable valuation center and lower capital costs.
In 2025, the structural changes within the crypto industry became clearer than ever: market growth no longer primarily relies on the spillover of risk appetite driven by a single narrative, but is instead propelled by several more sustainable "product lines" — trading infrastructure becoming more specialized, application forms aligning more closely with mainstream finance, and funding entry becoming more compliant, gradually forming a closed loop across on-chain and off-chain. At the same time, funding behavior and pricing rhythms are more deeply integrated into the global risk asset framework: volatility resembles "risk budget rebalancing under macro windows," rather than the relatively independent market driven primarily by on-chain narratives and internal liquidity cycles. For practitioners, this means the focus of discussion shifts from "which narrative will explode" to "which products can consistently generate trades, retain liquidity, and withstand stress tests from macro volatility and regulatory constraints."
Within this framework, the traditional "crypto four-year cycle" further weakened in 2025. The cycle logic has not disappeared, but its explanatory power has been significantly diluted: channels such as ETFs, stablecoins, and corporate treasuries have brought larger volumes of funds into an observable and rebalancing asset allocation system; at the same time, interest rates and the boundaries of U.S. dollar liquidity have become harder constraints, making risk budgets, leverage pricing, and deleveraging paths more aligned with traditional markets. The result is that upward movements increasingly depend on the resonance of "macro risk appetite + net inflows," while downward movements are more easily amplified in "liquidity tightening + deleveraging." The performance across various sectors throughout the year resembled a set of synergistic evolutions: what truly drives structural upgrades is not the explosion of a single narrative, but the continuous thickening of funding entry and trading scenarios through the expansion of stablecoins, the deepening of derivatives, and the emergence of event contracts as underlying financial products, simultaneously reinforcing risk transmission.
Stablecoins in 2025 exhibited two main lines of advancement that progressed simultaneously but at different paces: one is "compliance certainty elevation," and the other is "cyclical fluctuations of yield models." The key to the former is that, with the emergence of compliance frameworks and more comparable market samples, the business models of stablecoins can be more easily priced by mainstream funds based on cash flow and risk attributes; the latter is reflected in yield-type/synthetic dollars being highly sensitive to basis, hedging costs, and risk budgets, showing significant contraction after expansion. Taking Ethena's USDe as an example, its supply peaked at nearly $15 billion in early October, then fell to around $8.5 billion in November, experiencing a brief decoupling during the deleveraging window in mid-October. The industry-level insight is that yield-type stablecoins are closer to being "amplifiers of macro and basis" — contributing liquidity during favorable conditions and amplifying volatility and risk repricing during adverse conditions.
The upgrade of trading infrastructure accelerated in 2025, centered around on-chain derivatives. Platforms like Hyperliquid continued to approach centralized trading platforms in terms of depth, matching, capital efficiency, and risk control experience, achieving a monthly trading volume of approximately $300 billion at mid-year, indicating that on-chain derivatives have the foundational capacity for scaling. Meanwhile, new entrants like Aster and Lighter are pushing the sector from "single platform dividends" to "market share competition" through product structure, fees, and incentive systems. The essence of competition lies not in short-term trading volume but in the ability to maintain usable depth, clearing order, and stable risk frameworks during extreme market conditions; the expansion of derivatives also makes volatility more "macro-oriented" — when interest rates and risk appetite switch, on-chain and off-chain deleveraging often occurs more synchronously and rapidly.
Prediction markets in 2025 expanded from crypto-native applications to a broader event contract market, becoming a new incremental trading scenario. Platforms like Polymarket saw significant increases in participation and trading volume for event contracts; monthly trading volume grew from less than $100 million in early 2024 to over $13 billion in November 2025, with sports and politics becoming the main categories. The deeper significance lies in that event contracts transform macro and public issues into tradable probability curves, naturally fitting media dissemination and information distribution, making it easier to form cross-layer user entry points, and further strengthening the coupling between crypto and macro variables (and even political variables).
Overall, the structural upgrade in 2025 is pushing the industry from "narrative-driven price discovery" towards "product-driven capital organization." The layering of stablecoins, the infrastructuralization of on-chain derivatives, and the contextualization of event contracts collectively expand funding entry and trading scenarios, also allowing for faster and more systematic risk transmission; against the backdrop of enhanced macro and interest rate constraints, the market cycle structure is further aligning with mainstream risk assets, and the explanatory power of the four-year cycle continues to weaken.
Dual Main Lines of Stablecoins: Compliance Certainty and Yield Cycles
In 2025, stablecoins upgraded from on-chain trading mediums to the USD settlement layer and funding base of the crypto system, completing a clear layering: USDT/USDC continue to form the mainstream fiat stablecoin "cash layer," providing a liquidity network covering global trading and settlement; yield-type/synthetic dollars like USDe/USDF resemble "efficiency tools" driven by risk appetite and basis, exhibiting significant cyclicality in expansion and contraction.
The most direct signal throughout the year is the substantial thickening of the on-chain USD base: the total supply of stablecoins expanded from approximately $205 billion to over $300 billion, highly concentrated at the top (around $186.7 billion for USDT and about $77 billion for USDC near year-end); issuers collectively hold about $155 billion in U.S. Treasury bills, making stablecoins closer to a "tokenized cash + short-duration Treasury" infrastructure combination. The usage side is also reinforced: stablecoins account for about 30% of on-chain crypto trading volume, with cumulative on-chain activity exceeding $4 trillion for the year, and the estimated daily trading volume for payment-type on-chain transactions is in the range of $20–30 billion, with real demand for cross-border settlement and fund allocation continuing to rise.
On the institutional level, the GENIUS Act, which was implemented in July, incorporates requirements for licensed issuance, 1:1 reserves, redemption, and disclosure for payment-type stablecoins, and sets an entry path for foreign issuers, leading to the institutionalization of "compliance premiums": USDC benefits more from enhanced compliance and institutional availability, while USDT should not be simply classified as a compliant stablecoin under the U.S. framework; its advantage lies in the global liquidity network, but availability in the U.S. market will depend more on implementation details and channel compliance.
The yield-type sector has completed its repositioning: taking Ethena's USDe as an example, supply fell from about $14.8 billion in early October to around $6–7 billion by year-end, validating its structured attribute of "expanding in favorable conditions and contracting in adverse conditions."
Looking ahead to 2026, stablecoins remain the most certain growth trajectory: competition among mainstream fiat stablecoins will shift from scale to channels and settlement networks, while yield-type products will continue to provide liquidity during favorable conditions but will be priced more strictly based on stress tests and redemption resilience.
Upgrade of On-Chain Derivative Platforms and Share Wars
In 2025, on-chain perpetual contracts transitioned from "available products" to the infrastructure stage capable of "supporting mainstream trading": matching and latency, margin and clearing mechanisms, risk parameters, and risk control interactions are increasingly approaching the engineering standards of centralized trading platforms, allowing on-chain derivatives to begin to possess the ability to divert mainstream transactions and participate in price discovery during certain periods. Meanwhile, funding and risk transmission became more "macro-oriented": during the window of switching risk appetite and interest rate expectations in the U.S. stock market, the volatility and deleveraging rhythm of on-chain perpetual contracts more easily resonated with traditional risk assets, significantly increasing the market cycle's sensitivity to "macro liquidity — risk budgets."
On the scale side, a sustainable track of "on-chain derivatives" has formed. As of the end of 2025, the 30-day trading volume of on-chain perpetual contracts was approximately $1.081 trillion, with the total market open interest around $15.4 billion, reflecting that this sector has the capacity to routinely support large-scale trading and risk exposure. Leading platforms still occupy the core mindset of "depth and risk control," but the logic of competition underwent substantial changes in 2025: the battle for market share no longer primarily relies on subsidies and the speed of listing but shifts more towards depth, open interest accumulation, and the stability of clearing orders during extreme market conditions. For example, Hyperliquid had an open interest of about $6.88 billion and a 30-day trading volume of approximately $180.4 billion, reflecting "stronger risk exposure accumulation + relatively stable trading volume."
More encouragingly, new entrants in the second half of 2025 are no longer just conceptual challengers but are joining the competition with quantifiable data and rewriting the share structure: Lighter had a 30-day trading volume of about $233.2 billion, a cumulative trading volume of about $1.272 trillion, and an open interest of about $1.65 billion; Aster had a 30-day trading volume of about $194.4 billion, a cumulative trading volume of about $811.7 billion, and an open interest of about $2.45 billion. According to open interest rankings, Hyperliquid, Aster, and Lighter are now in the top three (approximately $6.88 billion / $2.41 billion / $1.60 billion), indicating that the sector has entered a mature stage of "multi-platform parallel competition."
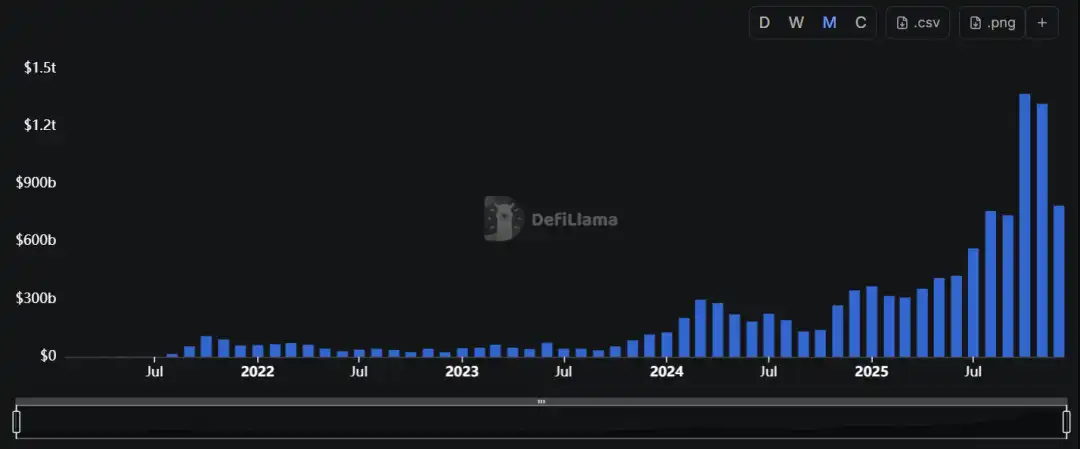
Source: DeFiLlama / On-Chain Perpetual Contract Trading Volume
For the industry, the competition of on-chain perpetual contracts in 2025 has entered the "quality and resilience pricing" stage — trading volume can be amplified by short-term incentives, but the scale of open interest, the sustainability of fees/income, and risk control performance during extreme market conditions better reflect the real capital residence and platform stickiness.
Looking ahead to 2026, the sector is likely to evolve along two lines simultaneously:
The penetration rate of on-chain derivatives continues to rise;
Under fee compression and elevated risk control thresholds, the market further concentrates towards a few platforms that can maintain depth and clearing order in the long term.
Whether new platforms can transition from scale sprinting to stable retention depends critically on their capital efficiency and risk framework under stress tests, rather than on the trading volume performance of a single phase.
Prediction Markets Transitioning from Crypto-Native to Event Contract Markets
In 2025, prediction markets completed an upgrade from phase-specific spikes to more independent, sustainable trading scenarios based on the validated "event contracts (probability pricing)" during the 2024 U.S. presidential election: they no longer primarily rely on short-term traffic brought by a single political event but instead establish "probability trading" as a more stable trading demand and user habit through high-frequency/reusable contract categories such as sports, macro, and policy nodes. Due to the inherently externalized nature of event contract subjects (macro data, regulatory bills, elections, and sports schedules), the activity level of prediction markets significantly increased, enhancing the linkage with the risk appetite and interest rate expectation shifts in the U.S. stock market, and the rhythm of industry applications further shifted from the "internal narrative cycle of crypto" to a function of "macro uncertainty × event density × risk budget."
On the data front, the prediction market sector experienced exponential expansion in 2025: the total trading volume for the year was approximately $44 billion, with Polymarket accounting for about $21.5 billion and Kalshi around $17.1 billion. The scale of leading platforms is now sufficient to support stable market making and category expansion. Growth exhibited clear event-driven peaks throughout the year: monthly nominal trading volume surged from less than $10 million in early 2024 to over $13 billion in a single month in 2025 (with November as a representative month), demonstrating strong resilience during high-attention event windows. Structurally, the prediction market evolved from being "driven by political spikes" to "high-frequency retention in sports + multi-category expansion of events": Kalshi's trading volume in November 2025 was approximately $5.8 billion, with about 91% coming from sports; the platform disclosed that its trading volume had reached over $1 billion per week, claiming a growth of over 1000% compared to 2024, reflecting a certain normalization of trading activity.
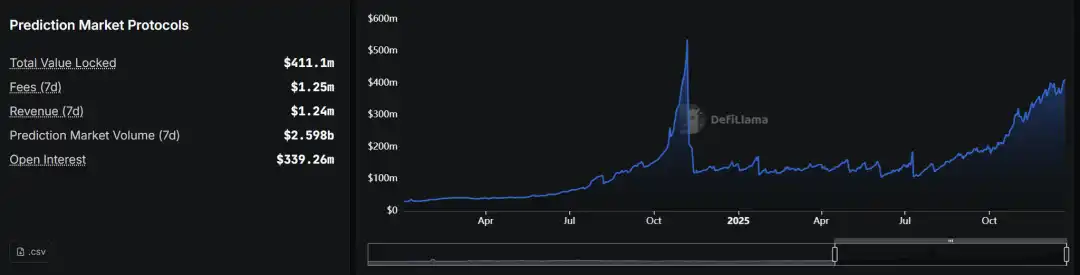
Source: DeFiLlama / Overview of Prediction Market Data
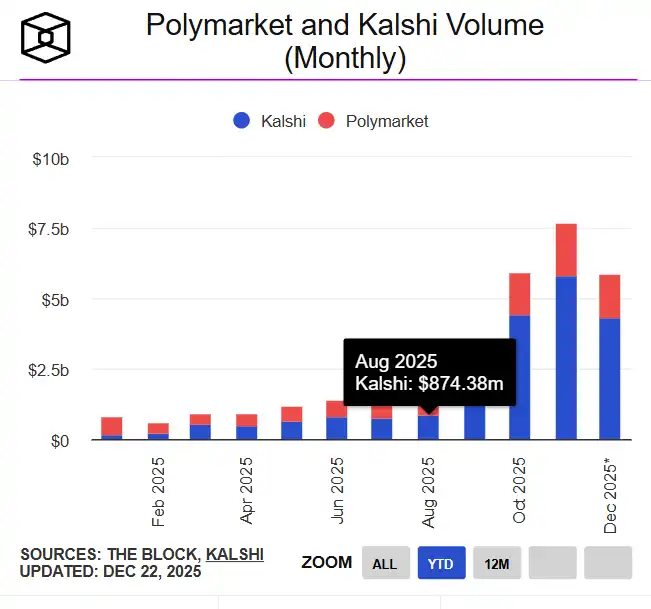
Source: theblock.co / Trading volume of Polymarket and Kalshi markets
In addition to the capital structure changes mentioned earlier and the industry shifts brought about by crypto company IPOs, the prediction market sector rapidly upgraded from "crypto entrepreneurship" to "financial infrastructure/data assets": Kalshi completed a $1 billion financing in December, with a valuation of approximately $11 billion, and had previously raised $300 million at a valuation of about $5 billion two months prior; at the same time, traditional market infrastructure players began to enter with heavy capital, with reports indicating that ICE (the parent company of the New York Stock Exchange) plans to invest up to $2 billion in Polymarket, giving it a pre-investment valuation of about $8 billion. The common implication of these transactions is that event contracts are viewed not only as "trading products" but also as integrable market data, sentiment indicators, and risk pricing interfaces.
Looking ahead to 2026, prediction markets are more likely to become one of the "more certain" structural increments in the crypto application layer: growth drivers will stem from event density and information uncertainty, with commercialization moving closer to a combination of "transaction fees + data products + distribution channels." If compliance pathways, distribution entry points, and dispute resolution standards become clearer, prediction markets are expected to transition from phase-specific hits to more normalized event risk trading and hedging tools; their long-term ceiling will primarily depend on three hard indicators: real depth (capable of supporting large amounts), reliable settlement and dispute governance, and controllable compliance boundaries.
Conclusion
Reflecting on 2025, the core characteristic of the crypto market is the externalization of pricing frameworks and the deepening of channel competition: funding entry shifted from an endogenous cycle driven by on-chain leverage and narratives to a multi-channel system composed of ETFs, stablecoin USD bases, corporate treasuries, and equity channels (crypto company IPOs in the U.S.). The expansion of channels enhanced asset configurability and reinforced macro boundary conditions — market movements became more reliant on net inflows and financing windows, while pullbacks were more easily concentrated and released in deleveraging and clearing chains.
The internal structural evolution of the industry further corroborated this shift: stablecoins completed their layering between "cash layers" and "efficiency tools," on-chain derivatives entered the stage of scalable capacity and market share competition, and prediction markets and event contracts formed more independent trading scenarios. More importantly, the return of IPOs "securitized" crypto financial infrastructure into auditable, comparable, and exit-able equity assets, allowing mainstream funds to participate in a more familiar manner and pushing the valuation system towards "compliance moats, risk control governance, income quality, and capital efficiency" — this is the core basis for our optimism in this direction.
Looking ahead to 2026, the industry's slope is more likely to depend on three variables: whether institutional channels can continue, whether capital retention is sustainable, and the resilience of leverage and risk control under stress scenarios. Among these, if crypto company IPOs in the U.S. can maintain a more continuous push and stable reception, they will continue to provide valuation anchors and financing flexibility, reinforcing the industry's shift towards sustainable pricing in the public market.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。


