Core Summary
- Although cross-chain bridges can achieve asset transfers across chains, they always face security threats. Orbiter Finance has been operating steadily since 2021, earning user trust.
- With the rise of new public chains and the expansion of the DeFi landscape, the cross-chain bridge market is experiencing explosive growth, with an expected annual asset cross-chain scale of $510.7 billion by 2027. Rapid access capability, technical stability, and low fees will become the core factors for seizing market share.
- Relying on a solid product foundation, Orbiter Finance is breaking through the traditional boundaries of cross-chain bridges through the "Vizing" program, aiming to create a full-chain infrastructure that fundamentally revolutionizes the way assets and data are transmitted across chains.
I. Cross-Chain Bridge Market Landscape
The cryptocurrency market has experienced ups and downs, and the cross-chain bridge field is no exception. As a key component of the ecosystem, cross-chain bridges bear the fundamental function of connecting different blockchain networks and enabling asset transfers across chains.
Cross-chain bridges are essentially specialized protocols that connect two independent blockchains through economic, technical, and conceptual dimensions. Analogous to physical bridges, their value lies not only in simple connectivity but also in the rapid and efficient transfer of assets between networks. With the continuous emergence of Layer 2 (L2) solutions, cross-chain bridges have become essential tools for integrating fragmented ecosystems.
However, in stark contrast to their importance, cross-chain bridges are frequently exposed to significant security risks. A typical case is the Wormhole Bridge hack: attackers exploited a vulnerability in the Wormhole Solana smart contract to forge signatures, illegally minting 120,000 wETH, which were then exchanged for real wETH on the Ethereum network, leading to massive losses. Just as the collapse of a physical bridge affects two interconnected cities, a breached cross-chain bridge can also impact multiple networks.
There are three reasons why cross-chain bridges have become prime targets for hackers: first, the accumulation of large amounts of funds; second, the trust mechanism relying on smart contract coding; and third, potential vulnerabilities arising from the coordination of different blockchain rules. Even in decentralized environments aimed at minimizing trust dependencies, the risk of key theft from limited validating nodes and human regulatory loopholes remains a significant security concern.
Despite the numerous risks, cross-chain bridges are still an indispensable part of the crypto market. In this context, selecting projects with sustained stability is crucial for maintaining the healthy development of the ecosystem. For example, Orbiter Finance has been continuously operating its cross-chain bridge service since 2021—this is rare in the Web3 field. The platform has achieved steady growth through operational resilience, gradually establishing a barrier of user trust.
Orbiter Finance received early support from top investment institutions such as Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin and OKX Ventures. This report will deeply analyze how Orbiter Finance builds competitive advantages in the cross-chain bridge market and look forward to its future development prospects.
II. Core Drivers of Growth in the Cross-Chain Bridge Market
The blockchain ecosystem continues to expand, with new public chains emerging constantly. In this process, the cross-chain bridge market benefits from the ongoing regularity of chain ecosystem development:
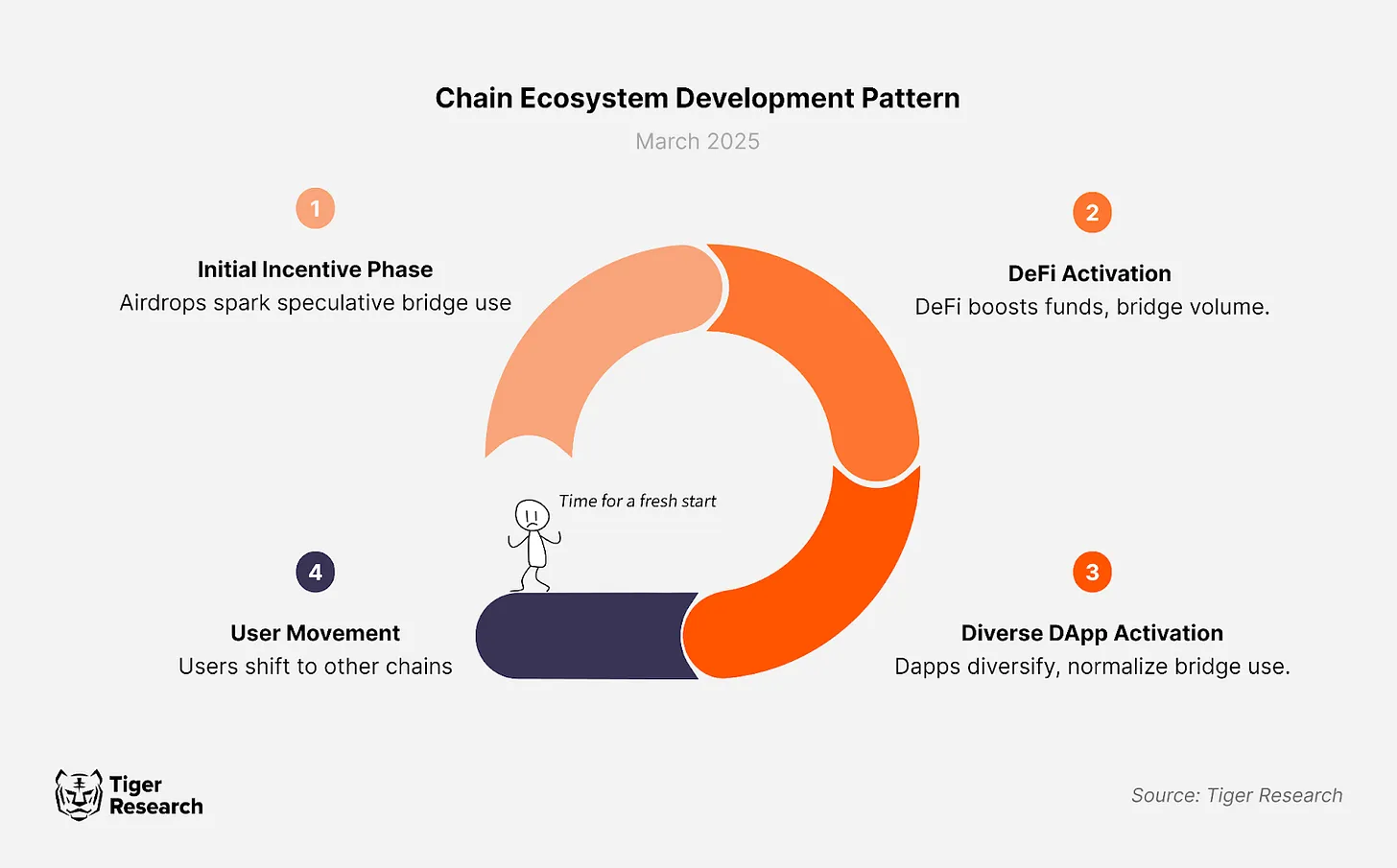
1. Initial Incentive Stage
When a new chain is launched, incentive measures such as airdrops attract investor attention. Reward expectations drive investors to transfer assets to the new chain through cross-chain bridge protocols, initiating the usage cycle of the cross-chain bridge.
2. DeFi Activation Stage
Beyond participating in airdrops, on-chain DeFi services begin to gain momentum. Early capital inflows achieve multiple utilities such as lending, staking, and liquidity provision across various DeFi protocols, attracting incremental funds into the market. As cross-chain asset flows intensify, cross-chain bridge transaction volumes significantly rise.
3. Diverse DApp Prosperity Stage
With ecosystem development, new types of DApps such as gaming platforms and NFT markets emerge, driving continuous capital inflow. At this stage, the use of cross-chain bridges has become a regular component of the ecosystem.
It is worth noting that as new chains continue to emerge, market attention will consistently shift towards new ecosystems, leading to periodic rebounds in cross-chain demand. In short, the scale of the cross-chain bridge market exhibits a spiral growth pattern alongside the birth of new chains and the maturation of ecosystems.
This process is akin to merchants migrating from mature commercial districts to emerging development zones: when the old area becomes saturated and profit margins narrow, the new area attracts early settlers with low rental costs, first-mover advantages, and long-term appreciation potential, offering them franchise opportunities and other future prospects. Driven by compound incentives, the retail migration forms a continuous cycle—this is a microcosmic reflection of capital flows between blockchain ecosystems.
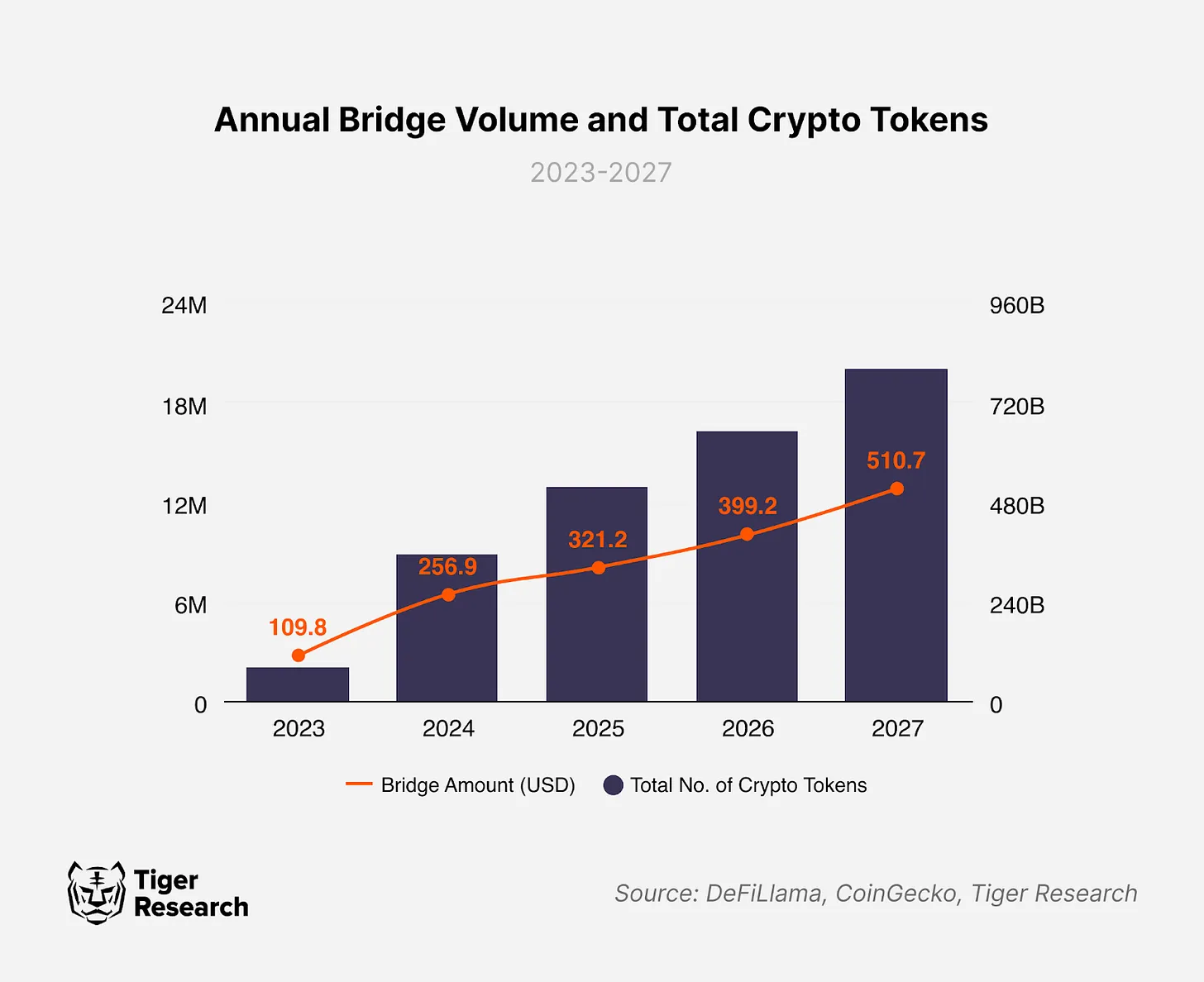
According to DeFiLlama data, the asset cross-chain scale reached $256.9 billion in 2024, doubling from 2023 (Note: this data does not cover all on-chain cross-chain activities, and the actual scale may be higher).
With the expansion of market scale, the industry is undergoing profound changes: blockchain ecosystems are maturing, regulatory frameworks are accelerating improvement, and meme coin launchpads are driving a surge in token projects (although the proportion of quality projects remains relatively limited). In this context, it is conservatively estimated that by 2027, the annual cross-chain asset scale will reach $510.7 billion.
In this continuously expanding market, obtaining stable fee income and a strong market position depends on three key factors:
Rapidly establishing connections with emerging chains
Ensuring robust and secure technical services
Providing competitive transaction speeds and low fees
Source: Orbiter Finance
In this market environment, Orbiter Finance stands out with its decentralized cross-chain bridge positioning, supporting asset flows between multiple networks. Its rapid access capability to mainstream projects like Solana and emerging projects like Abstract and Story, combined with 10-20 second rapid transfers and low fees, are key factors for continuous user inflow.
With excellent technology and scalability, Orbiter Finance has successfully simplified blockchain asset transfers to the level of everyday online transactions, perfectly fulfilling the role of a "bridge between Web2 and Web3," further solidifying its unique position in the rapidly evolving blockchain market.
2.1 Orbiter Finance's New Chain Connection Trends
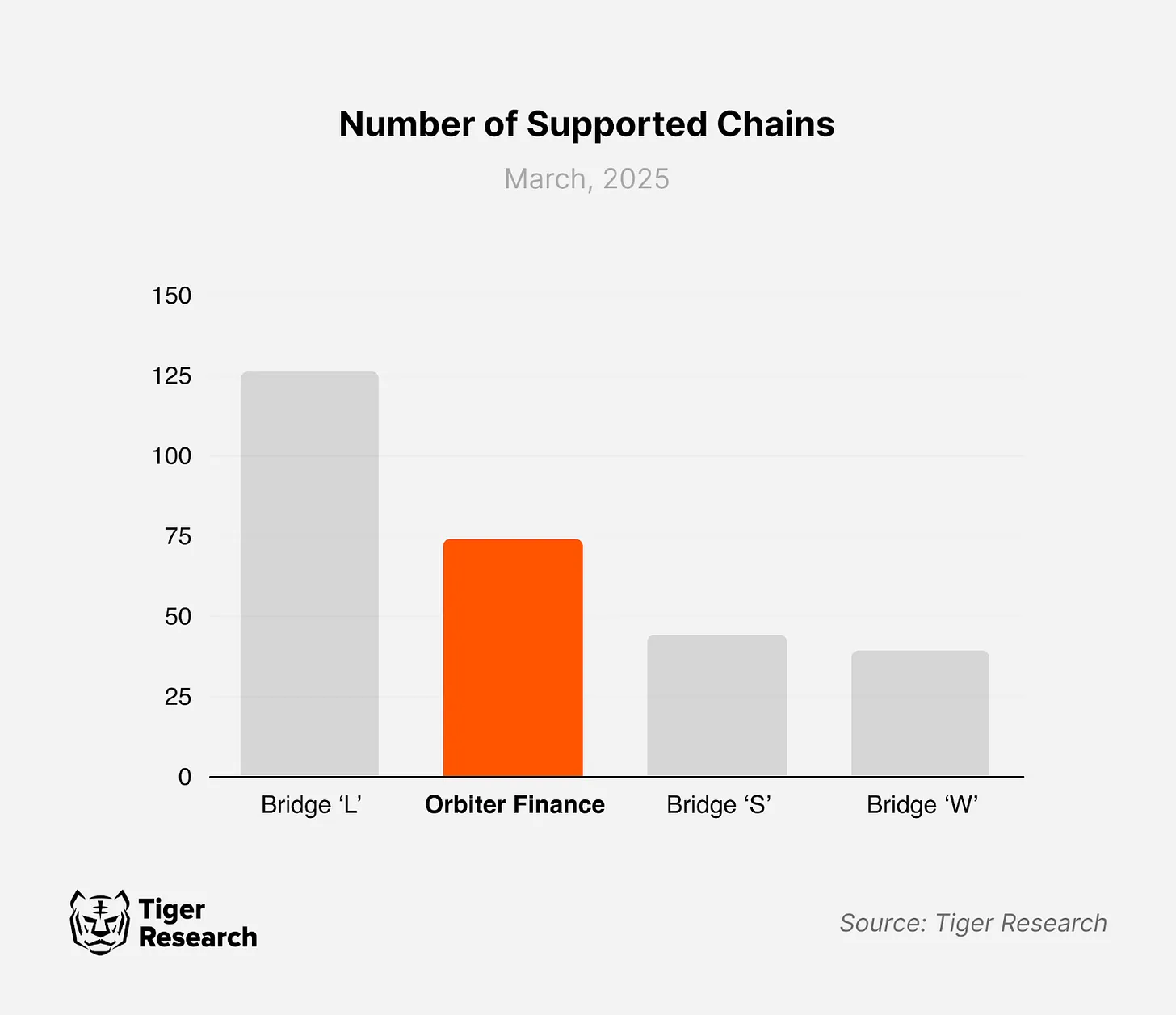
Orbiter Finance has supported over 70 blockchains and continues to expand its coverage by integrating highly scalable new chains. Its most significant advantage lies in its rapid adaptation to the latest Ethereum L2 solutions. Among the many L2 scaling solutions aimed at solving Ethereum's scalability issues, Orbiter Finance is particularly proactive in integrating ZK technology-based Rollups.
By integrating ZKFair, zkLink Nova, and Proof of Play Apex, among other ZK-based public chains, Orbiter Finance continues to strengthen its layout in the ZK ecosystem. At the same time, it expands the Ethereum ecosystem through its self-developed ZK-based L2 network Vizing and supports diverse L2 solutions like Arbitrum and Optimism, achieving seamless interoperability between Ethereum-based L2 networks.
Another differentiated advantage is its early support for Bitcoin Layer 2 solutions. While most cross-chain bridge services have yet to be compatible with Bitcoin-based public chains, Orbiter Finance has taken the lead in integrating networks like BEVM, Bitlayer, and B² Network. This move demonstrates its strategic ambition to break through the boundaries of the Ethereum ecosystem and reach established ecosystems like Bitcoin, providing users with more flexible asset transfer options.
These strategies enable Orbiter Finance to capture the benefits of the rapid expansion of the Ethereum L2 ecosystem while maintaining flexible interoperability between multiple Layer 1 (L1) blockchains. As the adoption rate of Ethereum L2 accelerates, Orbiter Finance is expected to play a more significant role in the field of cross-chain connectivity.
2.2 A Reliable Service Foundation
Since 2021, Orbiter Finance has maintained a zero-security-incident record for its cross-chain bridge services. As a cross-chain bridge that combines a decentralized market maker network with a smart contract liquidity pool, it achieves dual guarantees of security and efficiency through ZK-SPV technology and the O-Pool system.
The operational mechanism of Orbiter Finance is simple and efficient: when users deposit cross-chain assets into the source chain O-Pool contract, market maker nodes detect the transaction and execute an equivalent asset transfer on the target chain. In this process, market makers earn fee income, while ZK-SPV technology cryptographically verifies the legitimacy of the transaction, ensuring secure and minimized trust cross-chain transfers.
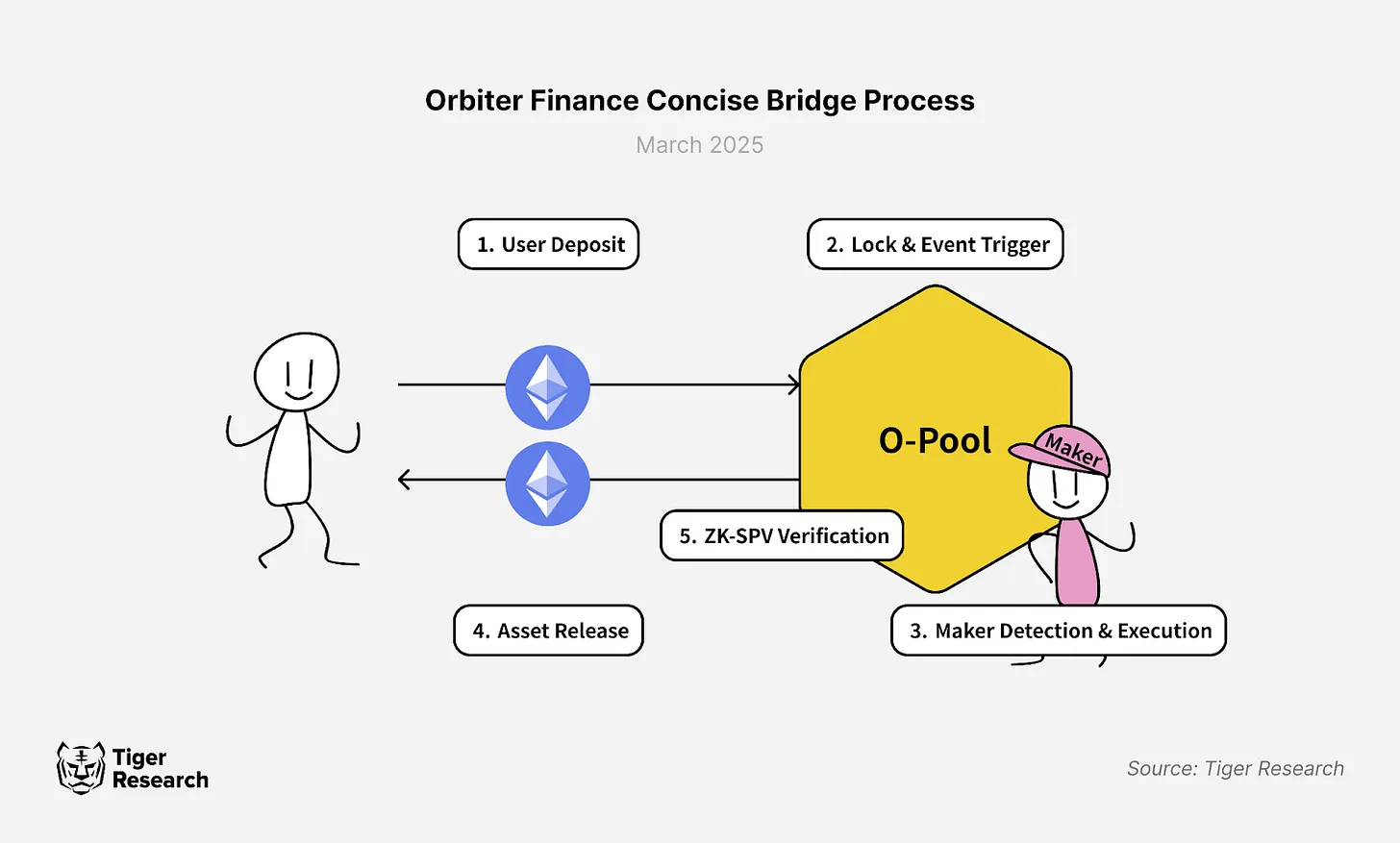
This system operates similarly to a multinational banking network: when a user deposits funds in a bank in one country (source chain), the bank representative (market maker) notifies the branch in another country (target chain) to provide an equivalent amount of funds. All transactions are reinforced by non-falsifiable credentials (ZK proofs), ensuring security and trustworthiness.
On the technical level, Orbiter Finance integrates two core components:
O-Pool System: Manages liquidity through smart contracts deployed across multiple chains. Users deposit assets into the O-Pool from the source chain, and market maker nodes detect and execute withdrawals on the target chain.
ZK-SPV Technology: Utilizes zero-knowledge proofs to achieve mathematical verification of cross-chain transactions, allowing for instant verification without long waits, overcoming the latency issues of Optimistic Verification.
This model marks a significant advancement in cross-chain infrastructure. Orbiter Finance abandons centralized mechanisms (such as wrapped token issuance or multi-signature validators) and adopts a decentralized market maker model that does not rely on complex wrapping processes, enhancing security with ZK-SPV technology and establishing a minimal trust and scalable framework for cross-blockchain asset transfers.
2.3 Competitive Advantages in Speed and Fees
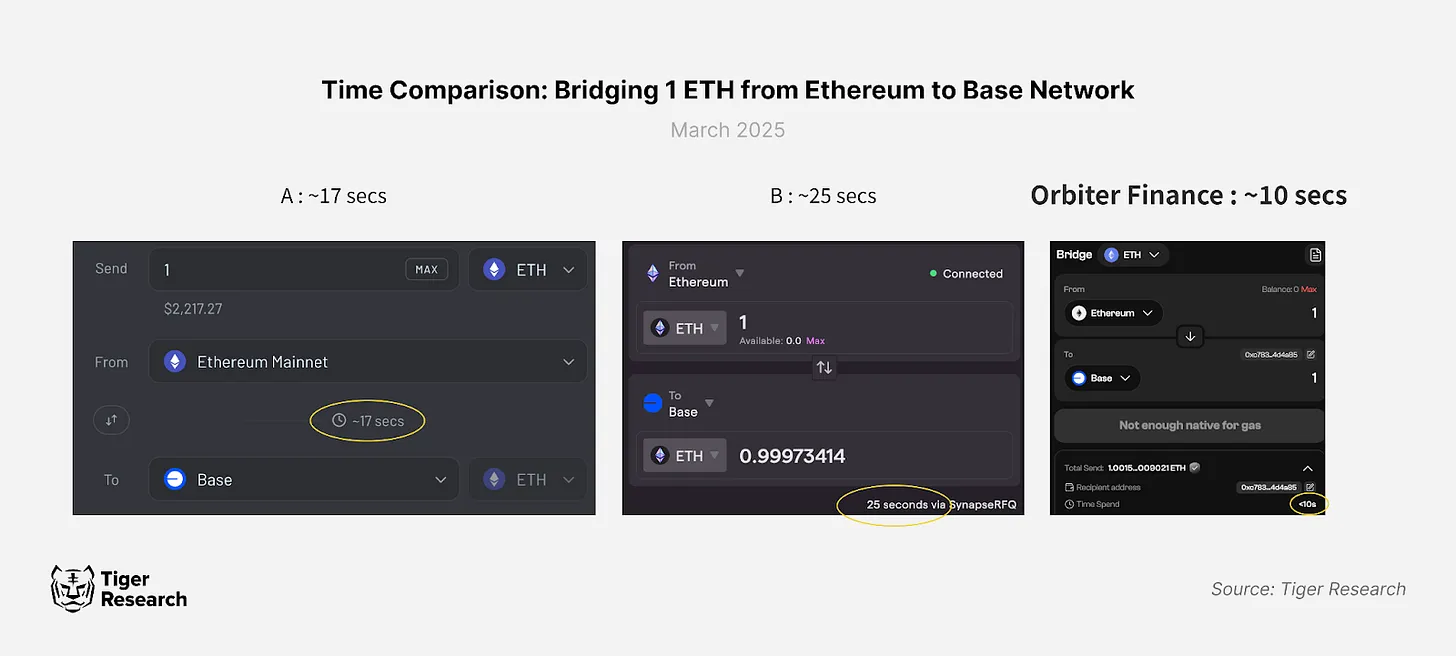
Orbiter Finance offers industry-leading transaction speeds, with cross-chain transfers typically completed within 10-20 seconds—significantly better than other cross-chain bridges. This speed advantage primarily stems from ZK-SPV technology and a streamlined transmission mechanism, minimizing blockchain confirmation requirements.
In addition to speed, Orbiter Finance demonstrates a strong cost advantage in L2 transfer scenarios. By minimizing smart contract calls, its ETH cross-chain gas consumption is reduced to approximately 21,000 gas, significantly lower than competitors' 120,000-450,000 gas. However, it should be noted that Orbiter Finance does not maintain a cost advantage across all transfer paths; under specific market conditions and transfer routes, its fees may exceed those of competitors.
III. Orbiter Finance's Stellar Vision—Vizing
Source: Vizing
Orbiter Finance's vision goes beyond basic cross-chain bridge services, aiming to expand interoperability in an L2-dominated environment. Traditional cross-chain solutions focus on asset transfers, but as the blockchain ecosystem evolves, the market's demand for cross-chain messaging and data transmission is increasing.
This shift resembles the development trajectory of urban infrastructure—expanding from road construction to communication networks and public facility systems. For example, a DeFi application on one chain may need to call a price oracle from another chain or execute transactions based on specific cross-chain events. However, existing cross-bridge systems exhibit clear limitations in efficiently handling such data interactions.
To address this, Orbiter Finance has developed Vizing: a ZK-based Ethereum L2 network designed to support on-chain messaging and cross-chain data transmission. By utilizing zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) for data verification, Vizing enables rapid and efficient cross-chain flow of assets and data.
Vizing has two core advantages: Vizing Account Abstraction (VAA): allows users to manage multiple L2 networks through a single account, significantly enhancing usability. Vizing Environment Layer (VEL): provides a unified execution environment across L2s, enabling developers to achieve multi-chain application coverage with a single deployment.
Source: Likwid
Vizing currently focuses on addressing key challenges in L2 interoperability. To support ecosystem development, Vizing launched a funding program last year, taking the first step towards practical adoption.
A typical case is the AMM service Likwid, based on Vizing technology. This platform achieves fully decentralized derivatives trading without relying on centralized intermediaries or oracles, and has been recognized by Uniswap as a DeFi innovation champion, creating a new paradigm for counterparty-free derivatives trading.
By enabling cross-chain communication and data sharing that goes beyond simple asset transfers, Vizing effectively addresses the fragmentation issue in the L2 ecosystem, enhancing the efficiency and usability of blockchain infrastructure and laying the groundwork for broader real-world applications.
IV. Orbiter Finance: Building a Faster and Stronger Ecosystem
The challenges facing Ethereum extend far beyond liquidity fragmentation. While L2 solutions continue to increase, progress in scalability and performance improvements at the Ethereum base layer has been slow. The network's transaction processing capacity remains limited, creating a demand for auxiliary network construction, but these efforts have yet to yield fundamental throughput improvements.
For example, when user A on the Base chain transfers 1 ETH to user B on the Arbitrum chain, the current Ethereum L2 environment still needs to read data from L1 and update the Ethereum state on the Beacon Chain. As the core ledger of Ethereum 2.0, the Beacon Chain manages the final records and validations of all transactions. This architecture constrains L2 scalability to L1 performance, creating a systemic bottleneck.
This situation is akin to remitting money from Seoul to Busan requiring central bank processing: even if the number of local banks (L2) increases, if the central bank (L1) processes transactions slowly, the entire system will remain constrained.
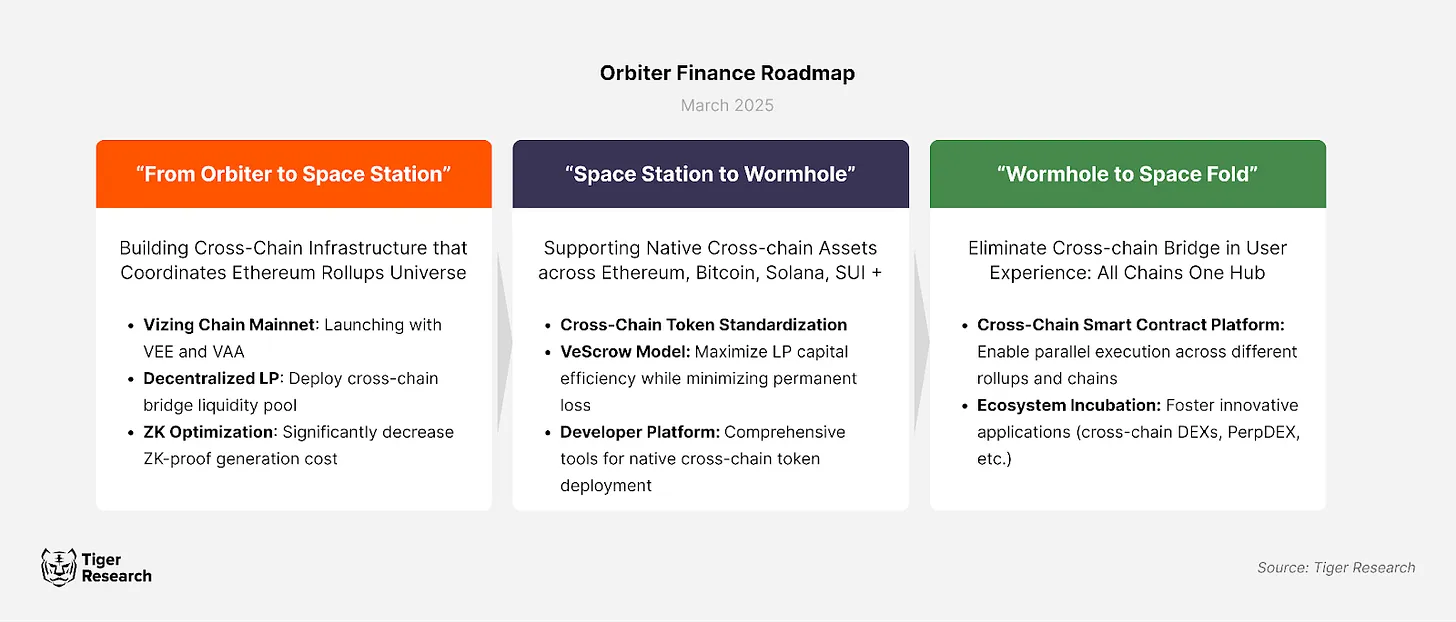
To break through these limitations, Orbiter Finance is developing infrastructure that supports direct communication between Rollups. This omnichain infrastructure breaks down barriers between blockchain networks, facilitating seamless transmission of assets and data while reducing reliance on Ethereum L1. By enabling L2 liquidity sharing, Orbiter Finance aims to enhance the overall efficiency of the Ethereum ecosystem.
This infrastructure consists of four core components:
Omnichain Wallet System: A unified account system similar to a universal bank account, minimizing L1 data access requirements. Users can access funds through a single account regardless of which local bank (L2) they interact with.
Relay Protocol: A cross-shard communication protocol that supports direct interaction between Rollups, avoiding L1 transaction routing. Similar to a direct connection network between local banks, allowing transactions between Busan and Daegu banks without going through the Seoul central bank.
Liquidity Aggregation Layer: A cross-chain asset pool management system. Similar to local banks sharing liquidity pools, ensuring that funds across different networks are dynamically allocated as needed, enhancing capital efficiency.
Parallel Execution Contracts: An omnichain smart contract system, similar to Vizing Dapp, enabling automatic deployment across Rollups. This model eliminates the need to develop financial products for each bank individually, achieving seamless deployment across the entire network.
By implementing this model, Ethereum L1 can focus on maintaining security, while L2 handles execution and transaction functions, eliminating bottlenecks while maintaining decentralization. This transformation is akin to financial system reform: central banks focus on policy stability, while local banks manage daily transactions independently.
Orbiter Finance's omnichain infrastructure does not replace L1 (the central bank) but alleviates existing bottlenecks by enabling direct connections between L2s. Ultimately, this creates an efficient financial network: local banks (L2) autonomously handle transactions, while the central bank (L1) intervenes only when necessary. This model promotes collaboration between Rollups, guiding the industry from TVL competition to a more decentralized and scalable ecosystem.
V. Future Blueprint Built on Solid Foundations
Orbiter Finance has established a solid foundation in its core business: by leveraging rapid differentiated chain connection capabilities, a technically stable infrastructure, and cost-effective transactions, it provides reliable cross-chain services to real users, building an active user moat.
At the same time, it demonstrates a rational and solid future vision. As the L2 ecosystem expands, Orbiter Finance accurately identifies key scalability challenges and systematically develops solutions.
Unlike competitors that merely talk about visions, Orbiter Finance expands Vizing based on actual operational services and an active user base, gradually broadening its business landscape. This strategy not only helps it maintain market share in the growing cross-chain bridge market but also creates incremental revenue opportunities in emerging markets.
As the L2 ecosystem matures and DeFi services expand, the roles of cross-chain bridges and omnichain infrastructure will become increasingly critical. Users will more frequently combine Arbitrum's high-yield lending services with Optimism's efficient trading, or stake assets on the Base chain for derivatives trading on the Scroll chain. Just as traditional finance evolves through complex financial products and strategies, cross-chain asset flows and multi-layer DeFi strategies will become the norm. In this accelerating trend, cross-chain bridge services and omnichain infrastructure like Orbiter Finance will become indispensable components of the blockchain ecosystem.
However, continuous attention must be paid to the stability of Vizing's ecosystem services. Although Likwid has launched, it is still in the early stages and requires more use cases to demonstrate its potential. Additionally, there is always a gap between vision and execution, making it crucial to closely monitor the progress of the roadmap implementation.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。



