Original author: Stacy Muur
Original translation: Deep Tide TechFlow
In just 30 days, 89 projects distributed across 9 blockchains completed over 2 million gasless transactions, saving up to $117,000 in gas fees.
This wave of gasless transactions indicates that solutions like the Paymaster in ERC-4337 smart wallets can rapidly enhance on-chain activity by covering costs for users.
Paymaster-driven usage may obscure real user demand
The surge in transaction volume does not necessarily reflect genuine user interest, especially when a small number of wallets (such as traders and bots) repeatedly call contracts.
For instance, one-time airdrops, free minting, or claiming activities can lead to a spike in wallet numbers in the short term, but subsequent usage may be minimal.
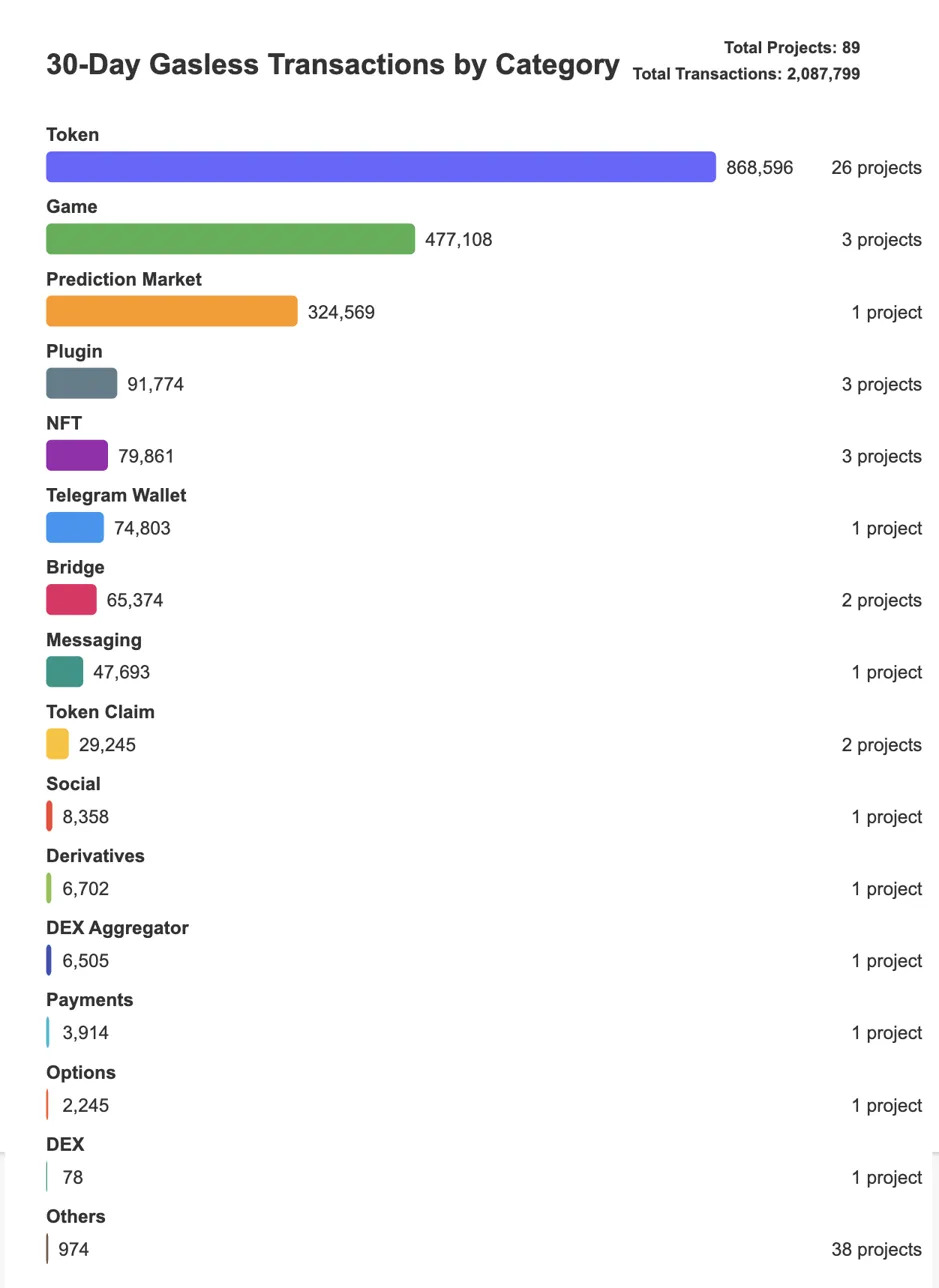
Currently, NFT, gaming, and token-related projects have indeed attracted a large number of new wallets, but many are only used for one-time operations (like minting or claiming rewards) without sustained user engagement.
On the other hand, some applications demonstrate deeper levels of repeat usage, often due to more engaging gameplay loops, regular DeFi operations, or infrastructure-level services.
These findings suggest that ERC-4337 smart wallets are reshaping on-chain activity. On one hand, the sponsorship of gas fees effectively attracts users; on the other hand, only applications that are appealing and encourage repeat usage can truly retain them.
@0xKofi has created an authoritative dashboard tracking this growth, supported by @base:
https://www.gogasless.io/leaderboard/all
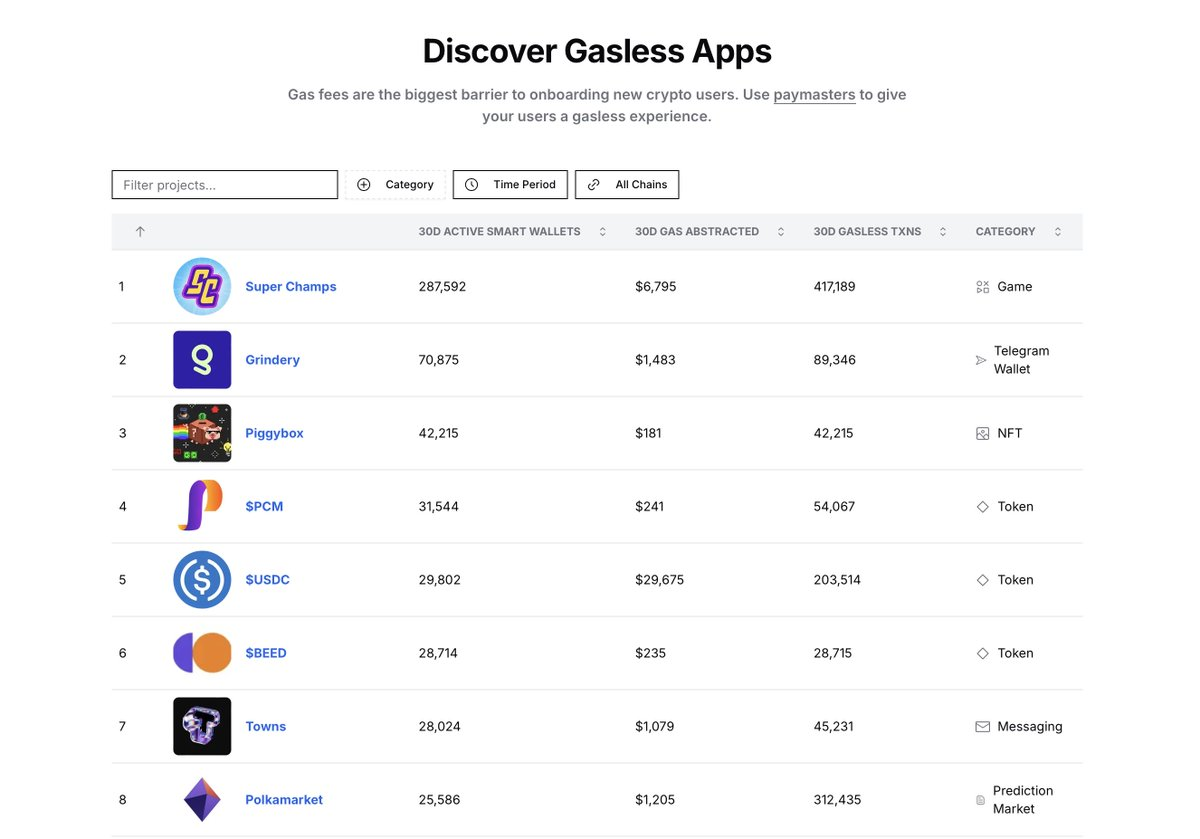
Core Data
89 independent applications/protocols
Approximately 724,000 active smart wallets
Approximately $117,000 in gas fees abstracted
Approximately 2.08 million gasless transactions
The bigger picture of ERC-4337 evolution
The rapid growth of gasless transactions is part of a larger trend. In 2024, user operations (UserOps) executed through ERC-4337 accounts exceeded 103 million, growing more than tenfold from 8.3 million in 2023. Among these, 87% of transactions were paid for by Paymaster, providing a gasless experience.
From the monthly Paymaster gas expenditure chart, we can see an interesting trajectory of this evolution:
Early adoption phase (2023): Spending was low before mid-2023, with Optimism being the first to adopt.
Growth phase (end of 2023): By October 2023, monthly spending steadily increased to about $400,000.
Peak activity (April 2024): Spending surged to about $700,000, primarily driven by Base.
Recent trends (late 2024 to early 2025): New highs were reached in November to December 2024 (around $630,000), but spending significantly dropped in early 2025, down to about $150,000 in February 2025.
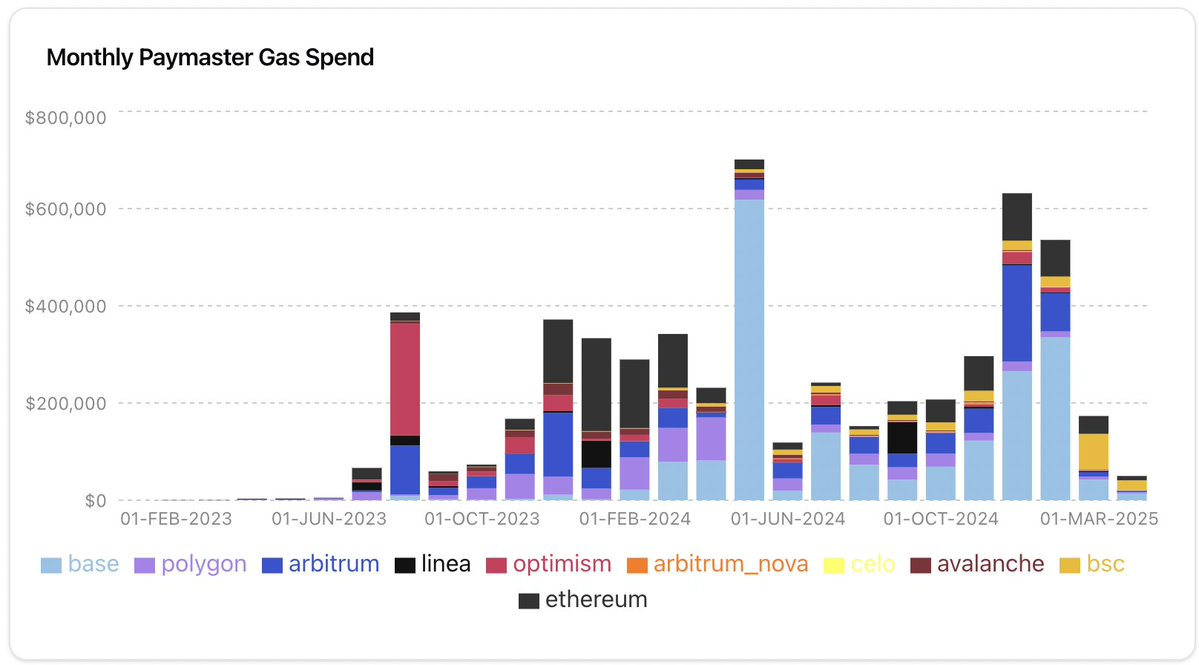
The UserOps fees paid through Paymaster have exceeded $3.4 million, with major providers including @biconomy, @pimlicoHQ, @coinbase, and @Alchemy. Despite market contraction, total spending in the first quarter of 2025 showed a downward trend, but @base ($391,000), @ethereum ($121,000), and @BNBCHAIN (about $112,000) remained dominant.
Data source: https://www.bundlebear.com/
Developer: @0xKofi
On-chain activity ranking
Base (43.2%): Entertainment and social hub, dominating the gaming sector (76.8%).
Polygon (21.4%): Community interaction layer, focusing on NFTs (50.7%) and Telegram wallets (42.3%).
Optimism (8.5%): Emphasizing security and recovery infrastructure.
Celo (7.4%): Niche expert, focusing on prediction markets.
BSC (4.2%): Value transfer layer, with the highest gas costs, focusing on token trading.
Key insights from the data
Before delving into the data analysis, two key metrics need to be understood:
1️⃣ Tx/Wallet (transactions per wallet) – Measures the average number of transactions per wallet. A low value (e.g., 1.0) indicates one-time use, such as minting an NFT or claiming an airdrop. A high value (e.g., 25) indicates repeat participation, such as active trading, gameplay, or bot operations.
2️⃣ Cost/Tx (cost per transaction) – Represents the average cost per transaction. In a gasless system, it reflects the abstracted fees per transaction rather than what users actually pay.
1. NFT projects: A large number of wallets often indicates one-time accounts
Piggybox: Approximately 1 transaction/wallet, about $0.004/transaction.
Somon Badge: Approximately 1.4 transactions/wallet, about $0.007/transaction.
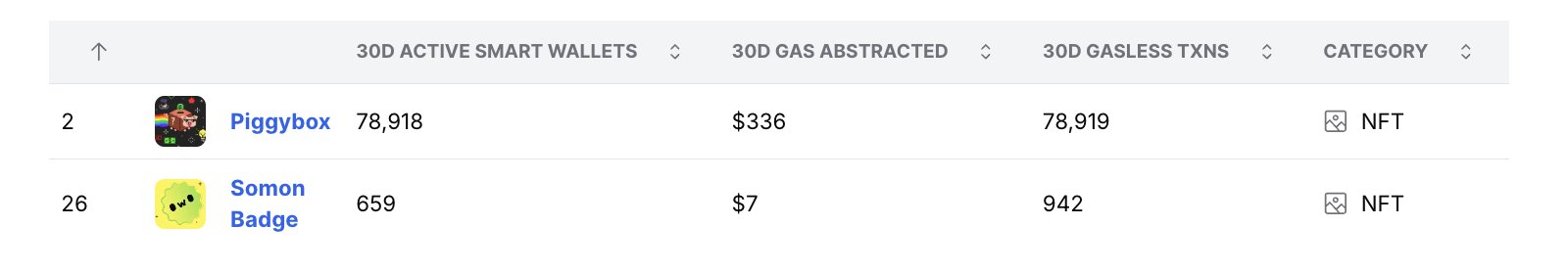
Interpretation: The 1:1 ratio of wallets to transactions for Piggybox strongly indicates that it is primarily driven by minting or claiming activities. Piggybox is an NFT obtained when users register for EARN’M, along with a lottery box that may contain EARNM tokens.
One-time spike: Many wallets only perform one transaction (initial minting or claiming) and then cease usage, resulting in an almost perfect 1:1 ratio.
Leaderboard distortion: Due to a large number of new wallets participating in minting, Piggybox ranks high in the wallet count/transaction volume leaderboard. However, if one-time wallets are filtered out, its ranking may drop from the top five, and user retention is also very low.
2. Token trading: A few projects dominate
- Data analysis: The total volume of token trades (868,000 transactions) seems to dominate, but there are 26 token projects listed, far more than other categories. However, only two tokens ($BVRP and $USDC) have transaction volumes exceeding 667,000, accounting for the vast majority of trading volume.

$BVRP: Approximately 25 transactions per wallet, cost per transaction $0.012.
$USDC: Approximately 4.6 transactions per wallet, cost per transaction $0.21.
Interpretation:
This concentration of trading volume indicates that not all token projects are equally active, but rather that a few leading projects are driving the overall increase in trading volume.
$BVRP shows extremely high trading activity relative to wallet numbers, which may indicate high user engagement on its platform, frequent trading, and possibly automated or repeat operations.
3. Gaming: A "hit" and the disparity in wallet/transaction ratios
Data analysis:
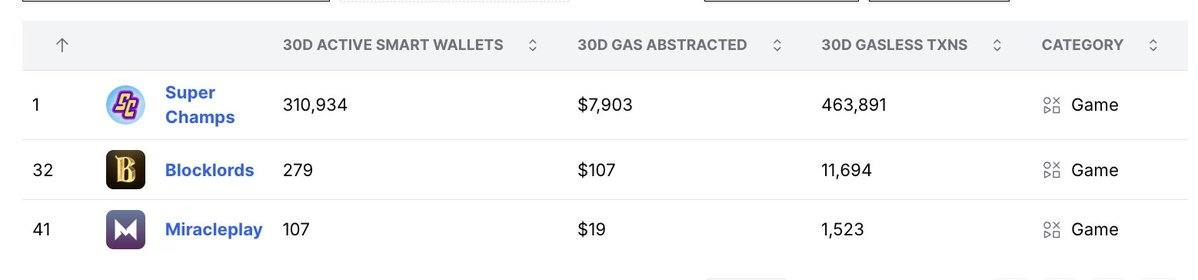
@SuperChampsHQ: Approximately 1.49 transactions per wallet, cost per transaction $0.017.
@BLOCKLORDS: Approximately 42 transactions per wallet, cost per transaction $0.009.
@miracleplay_cn: Approximately 14 transactions per wallet, cost per transaction $0.012.
Interpretation:
Although Super Champs has a total transaction volume (463,000 transactions) far exceeding other games (approximately 13,000 transactions combined), each wallet only completes about 1-2 transactions, indicating low user engagement.
Blocklords, while having fewer wallets, has a very high transaction volume per wallet (about 42 transactions), which is often associated with repeat behaviors that may be driven by bots. As David Johansson from Blocklords stated, "They are fighting against bots."
https://www.blockchaingamer.biz/features/interviews/33860/blocklords-david-johansson-podcast/
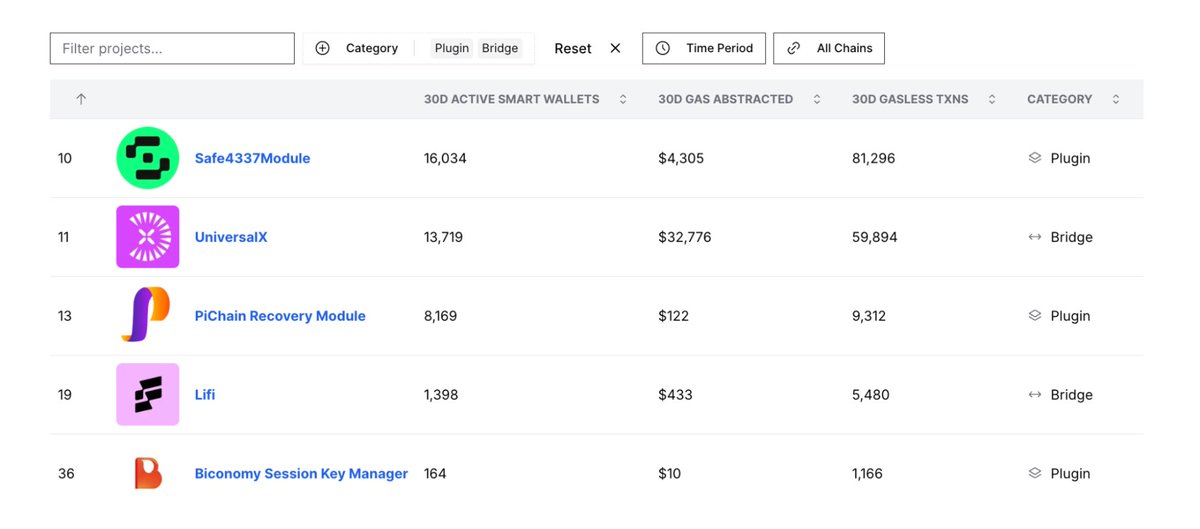
4. Cross-chain bridges and plugins: Stable usage with higher gas costs
UniversalX: Approximately 4.4 transactions per wallet, cost per transaction $0.55.
Safe4337Module: Approximately 5.1 transactions per wallet, cost per transaction $0.053.
Interpretation:
Behind-the-scenes tools: Cross-chain bridges and plugins may not be as eye-catching as tokens or games, but their usage remains stable due to reliance from multiple dApps.
Ecosystem health indicators: The sustained moderate usage of infrastructure services indicates that they provide real utility rather than hype-driven short-term spikes.
5. The specialization trend of on-chain activity
@base: 99.5% of gaming wallet activity (312,361 out of 310,934 wallets).
@0xPolygon: Dominates NFT and social activities, accounting for 87% of ecosystem NFT wallets.
@BNBCHAIN: Leads in high-value cross-chain bridge transactions, accounting for 23.2% of all gas abstracted transactions.
@Celo: Strong performance in prediction markets (25,574 wallets, averaging 12.7 transactions per wallet).
6. Cost differences between chains
The cost of gasless transactions varies by up to 100 times across different chains, driving different application categories to choose specific chains:
Ethereum: $2.41 per gasless transaction (highest).
BSC: $0.50 per gasless transaction.
Base: $0.02 per gasless transaction (lowest among major chains).
Polygon: $0.03 per gasless transaction.
Conclusion: This significant difference in cost structure will drive specific application categories to choose particular blockchains, regardless of technical similarities. For example, high-cost chains are unsuitable for economically demanding games and social applications.
Overall Observations
NFT adoption: Although NFT activity may show tens of thousands of wallets minting once (like Piggybox), subsequent usage rates are extremely low.
Infrastructure: The usage of cross-chain bridges and plugins remains stable, with higher transaction costs (cross-chain bridges) or lower volatility as backend tools (plugins).
Transaction pattern differences: There are significant differences in transaction volumes per wallet across different categories, with some being highly repetitive operations and others being "one-time completions."
Project long-tail effect: Many projects have almost no user engagement, indicating that free gas alone is insufficient to stimulate demand; dApps need to provide a genuine value proposition to retain users.
Key Takeaways
Account abstraction and gas sponsorship can indeed boost transaction volumes and user registrations, but the real test lies in user repeat engagement. Analyzing the data on wallet numbers, gas abstraction, and gasless transaction volumes reveals that usage across categories is often concentrated in a few star dApps or large-scale one-time activities. Projects like Piggybox can quickly rise to the top of the leaderboard with an almost 1:1 wallet-to-transaction ratio, but their ranking will quickly drop when one-time accounts are filtered out. In contrast, cross-chain bridges and plugin solutions demonstrate more stable moderate usage, reflecting the actual needs of the ecosystem rather than short-term hype.
The Role of ERC-4337 Smart Wallets
All these trends—gasless gaming, seamless DeFi, on-chain specialization—are driven by ERC-4337 smart wallets.
Unlike traditional externally owned accounts (EOAs), smart wallets significantly improve user experience through automation, security, and flexibility.
What is an ERC-4337 Smart Wallet?
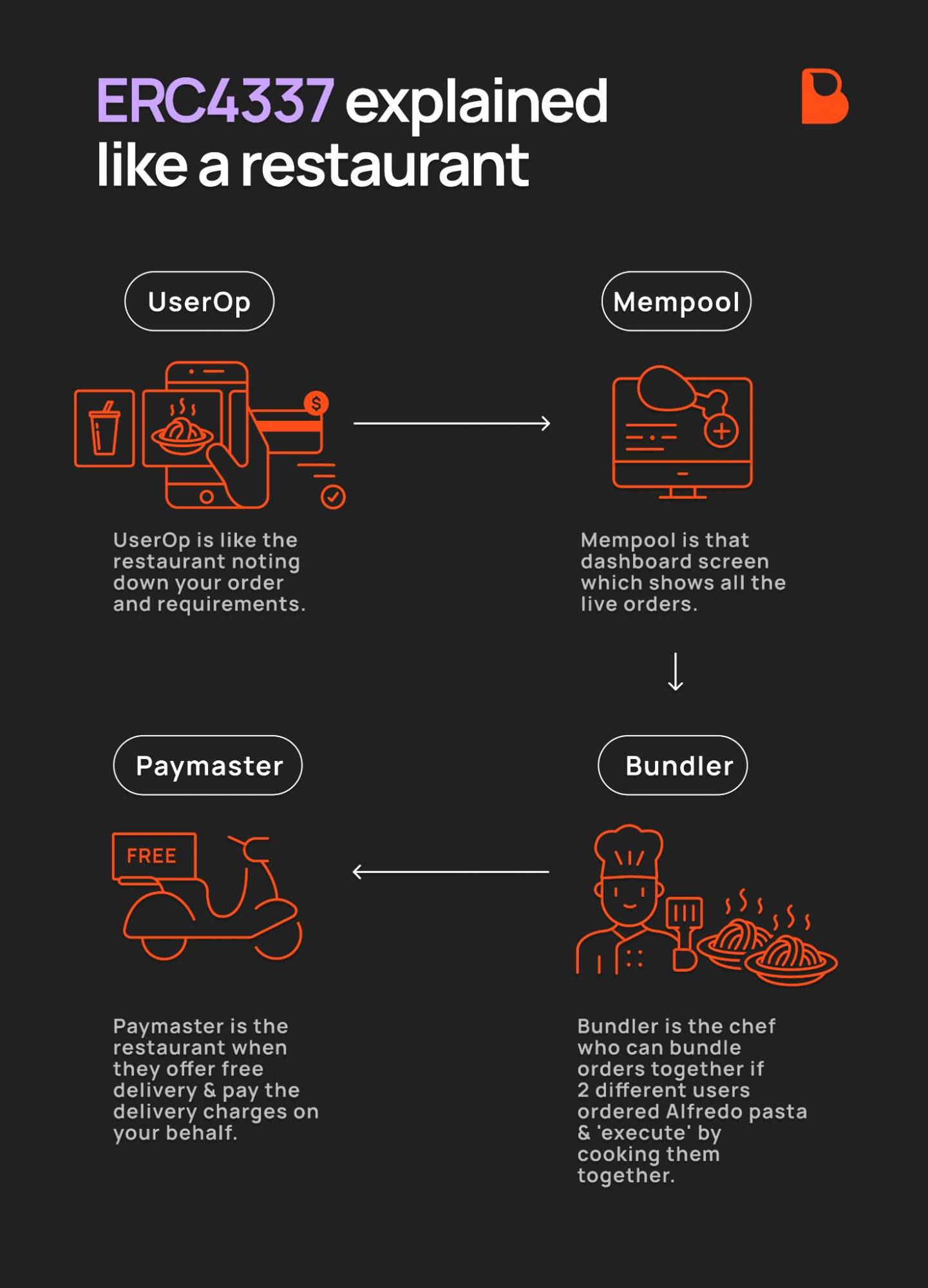
Smart contract wallets (or smart wallets) are programmable Ethereum accounts that offer the following features:
✅ Batch transactions: Users can combine multiple operations (e.g., authorizing + trading on a DEX) into a single transaction.
✅ Gas fee abstraction: Users do not need to hold ETH to pay gas fees; costs can be covered by sponsors or paid with other tokens.
✅ No mnemonic security: Users can authenticate through keys, social recovery, or multi-factor authentication instead of relying on high-risk mnemonics.
How do gasless transactions work?
When a user initiates a transaction, the Paymaster (a dedicated smart contract) can pay the gas fees on their behalf or allow users to pay with any ERC-20 token. This significantly lowers the entry barrier for new users, making blockchain applications as smooth as Web2 applications.
Challenges of ERC-4337 and Solutions from EIP-7702
While ERC-4337 promotes gasless transactions, it also faces significant adoption challenges, which directly lead to the aforementioned retention issues:
Technical barriers: Complex components (such as UserOperations, Bundlers, and EntryPoint contracts) set a high threshold for ordinary users and developers.
Cost issues: Although gasless transactions benefit users, the cost of implementing a complete tech stack is high, and the profitability of bundlers can be affected during gas fluctuations.
Reliability issues: Network congestion can lead to transaction delays, and complex validation logic increases potential security vulnerabilities.
User experience flaws: Multi-chain fragmentation leads to inconsistent wallet experiences, hindering seamless cross-chain management.
Key Takeaways
Account abstraction and gas fee sponsorship effectively increase transaction volumes and new wallet registrations, but the real challenge lies in maintaining ongoing user engagement. The data shows:
Many dApps only see usage spikes during one-time activities (like NFT minting or airdrops), with low long-term retention rates.
A few star projects drive most on-chain activity, while the majority of projects face a lack of actual user demand.
Cross-chain bridges and infrastructure solutions demonstrate more stable usage, indicating that they provide real utility rather than short-term hype.
Although ERC-4337 has driven gasless transactions and improved user experience, its complexity and cost barriers limit widespread adoption among mainstream users. EIP-7702 fills these gaps in the following ways:
Allow EOAs to support account abstraction
The core issue of ERC-4337 is that it excludes externally owned accounts (EOAs), requiring users to switch to smart contract wallets. EIP-7702 addresses this by allowing EOAs to temporarily adopt smart contract code, enabling them to use gas sponsorship (e.g., paying fees with ERC-20 tokens) and transaction batching (e.g., completing ERC-20 authorization and usage in a single transaction). For example, users can now batch process ERC-20 token authorizations and consumptions, a common operation flow in decentralized exchanges (DEXs), without switching to a smart contract wallet.
As mentioned in community posts, this is particularly beneficial for users who are fond of their external accounts (EOAs) and find migrating assets to a new account cumbersome.
Simplify complexity and reduce costs
Allowing EOAs to temporarily adopt smart contract functionalities reduces the need for permanent wallet contracts, lowering gas costs while decreasing reliance on EntryPoint or bundlers.
Enhance efficiency
Introduce transaction type 0x04 for batch processing EOA operations, providing a more streamlined alternative for ERC-4337's UserOps.
Optimize infrastructure
Limit smart contract code to the scope of transaction execution, reducing reliance on alternative memory pools (alt mempools) and bundlers, thereby simplifying infrastructure.
Empower developers
Integrate with ERC-4337 while providing a flexible, low-barrier upgrade path, enabling developers to more easily offer enhanced functionalities to users.
ERC-4337 lays the foundation, but EIP-7702 will make smart wallets cheaper, simpler, and easier to use, accelerating the next wave of Web3 adoption.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




