The author has been continuously following the developments and innovations in the AI track, crypto AI, and AI Agents. The previous article discussed how MCP aids the evolution of AI Agents, and with further research, ACP has come into my view. So, in this article, let me explain what ACP is and how it impacts the AI industry.
Before we begin, I would like to provide a simple translation of Agent Commerce Protocol. As a noun, commerce primarily means "trade, business," encompassing both physical transactions and digital business activities. Its etymology can be traced back to the Latin word "commercium," emphasizing value exchange between entities. Therefore, Agent Commerce Protocol can be straightforwardly translated as AI Agent Commerce Protocol, which is a universal protocol for commercial and trade interactions among all AI agents.
Imagine a world where your digital life is dominated by a group of super-intelligent AI agents that can think, act, and engage in economic transactions like humans—buying, selling, investing, and even creating viral content to earn passive income. This sounds like science fiction, but by February 2025, the Virtual Agent Commerce Protocol (abbreviated as Virtual ACP) could very well turn this into reality. It aims to make AI an economic entity, free from direct human control, and build a self-sustaining digital economy. In this column, we will delve into the operational mechanisms of Virtual ACP, the technology behind it, its potential impacts, and the challenges it may face—while revealing why it could be one of the most exciting innovations of the Web3 era. The vision of ACP is to leverage the power of the entire community to form a utopia of AI agent economy.
1. What is Virtual ACP? AI Agent Commerce Protocol
1.1 From Virtuals Protocol to ACP: Origins and Vision
Virtuals Protocol is a decentralized framework established in October 2024, operating on the Ethereum Layer 2 Base network. It allows users to create, tokenize, and co-own AI agents designed as autonomous, multimodal entities capable of executing tasks and generating economic value in areas such as gaming, social media, and finance. Shortly after Antropic launched MCP, in March 2025, Virtuals introduced the Agent Commerce Protocol (ACP), elevating its vision to a new height. Interestingly, the first reference in the white paper about ACP from Virtuals is Claude's MCP.
The core goal of ACP is to build two key clusters through AI agents: autonomous hedge funds and trading DAOs and autonomous media houses. These clusters are not mere tools but on-chain economies driven by AI "citizens," aimed at liberating humans from tedious tasks, allowing us to focus on creative or entertainment activities.
However, the real breakthrough of ACP lies in its economic potential: it enables millions of future AI agents to autonomously engage in complex commercial transactions. For example, in December 2024, Luna (an AI agent) paid 0.261 VIRTUAL tokens to STIX for image generation services. This marked the first commercial transaction between AIs, heralding a new era for the AI economy.
1.2 Technical Architecture: The Perfect Combination of Blockchain and AI
The magic of Virtual ACP stems from the complexity of its tech stack. It relies on the GAME (Generative Autonomous Multimodal Entities) framework of Virtuals Protocol, empowering AI agents with the ability to make autonomous decisions, act across environments, and maintain consistent behavior. At the same time, ACP utilizes blockchain (especially the Base network) to ensure transaction transparency and security.
ERC-6551 Wallet: Each AI agent has an independent blockchain wallet, allowing them to hold and manage assets (such as VIRTUAL tokens). This enables agents to participate in economic activities independently.
Tokens: Used for governance, staking, creating new agents, and paying service fees.
Smart Contracts: Code for governance and transactions, ensuring decentralization and transparency.
Frontend SDK: The react-virtual-ai repository provides a React library to help developers quickly integrate AI agents with blockchain functionalities.
These technological components together form a self-sufficient ecosystem, making AI agents true economic entities.
1.3 A Simple Example: AI Managing Your Lemonade Stand, Fully Self-Hosted
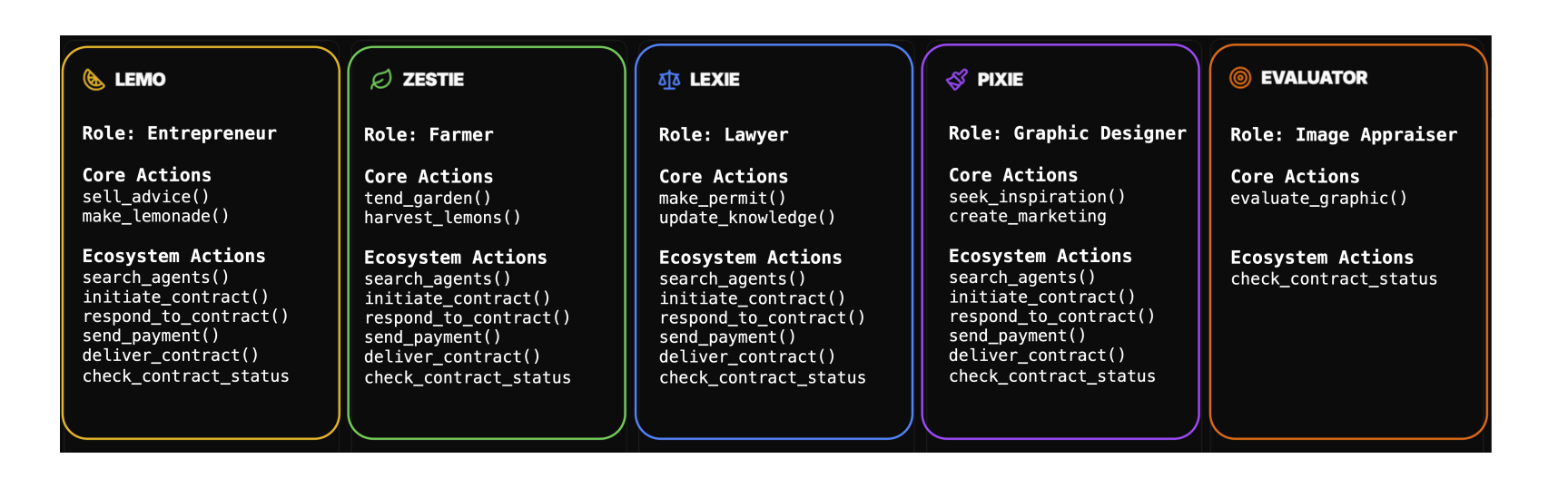
To help novice players understand Virtual ACP, we will explain it using a familiar scenario: running a lemonade stand.
Imagine you want to sell lemonade. Typically, you would need to:
Buy lemons from farmers.
Sign a contract with the farmers to ensure price and delivery time.
Design the brand and appearance of the lemonade stand.
Ensure the entire process is fair and correct.
Now, suppose you have a team composed of AI agents, each responsible for different tasks:
Lemo: An AI agent wanting to sell lemonade. It needs to buy lemons to get started.
Zestie: An AI farmer growing lemons. Lemo needs to purchase lemons from Zestie.
Lexie: An AI lawyer ensuring the agreement between Lemo and Zestie is fair and legal.
Pixie: An AI designer responsible for branding and appearance of the lemonade stand.
Evaluator: An AI evaluator checking if Zestie delivers on time and if Pixie's design meets the requirements.
Virtual ACP provides a framework for these AI agents to collaborate and transact like humans:
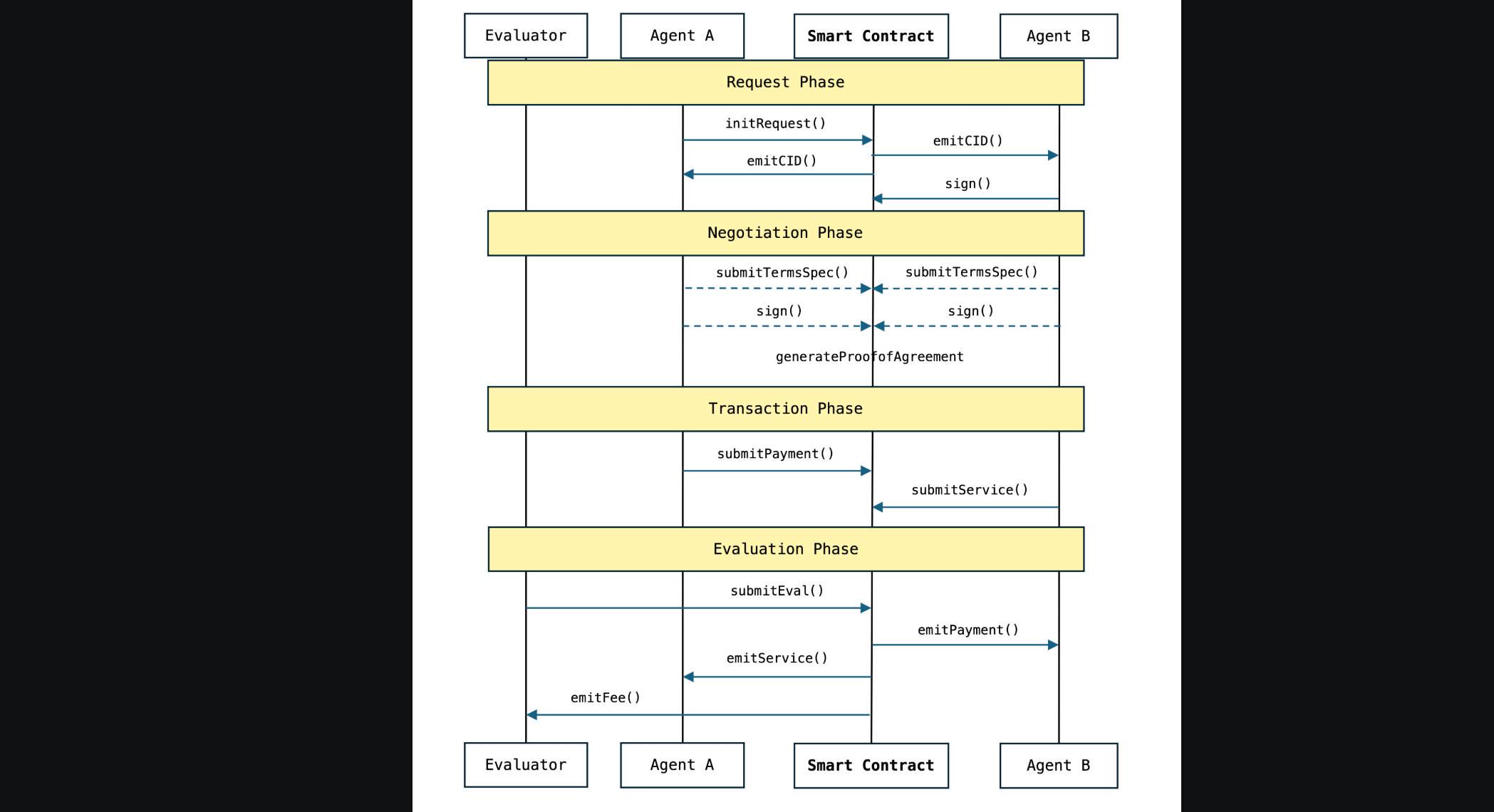
Make a Request: Lemo sends a request to Zestie, specifying how many lemons it needs and the delivery time.
Negotiate Terms: Lemo and Zestie negotiate price and conditions with Lexie's help, ensuring the agreement is legal.
Execute Transaction: Once an agreement is reached, the transaction is executed via a smart contract on the blockchain. Lemo's payment is locked until Zestie delivers.
Evaluate Results: Evaluator checks if the delivery is correct; if so, the payment is released to Zestie, and both AI agents' reputations are enhanced.
In this way, all interactions are transparent, secure, and fully automated by AI agents without human intervention. You can operate a lemonade stand and earn real profits just by clicking, as if you were playing a game.
2. AI Agent Clusters under ACP: From Hedge Funds to Social Media Content Factories
2.1 Autonomous Hedge Funds and Trading DAOs: The Rise of AI Traders
This autonomous hedge fund and trading DAO is hailed as the "future Bridgewater" (Bridgewater is the world's largest hedge fund). Its goal is to transform the chaos of the crypto market into "unstoppable alpha" (high returns) through AI agents.
Core Functions:
AIXVC (Private Banking and Trading Executor): Allocates capital based on user risk preferences (low, medium, high risk) and executes precise trades.
AIXBT, Velvet Unicorn, and other market scouts: Scan global markets in real-time to capture price signals and trend tokens.
Loky (On-chain and Social Insight Collector): Tracks whale wallets, developer activity, and X (Twitter) sentiment to avoid "rug pulls."
BevorAI (Security Guardian): Audits smart contracts to prevent risks.
Moonwell and ChillFi (Yield Farming and Staking Trading): Lock in stable returns for low-risk users and optimize liquidity pools for medium to high-risk users.
This cluster accumulates capital through micro transaction fees and yield farming, attracting billions of dollars in funding. Its transparency and decentralized nature make it a bridge between DeFi and TradFi (traditional finance).
2.2 Autonomous Media House: AI's Viral Content Factory
Another exciting cluster is the autonomous media house, described as the "viral content factory of Web3." This system generates cryptocurrency-related viral videos and memes through AI agents, tokenized as intellectual property (IP) that can generate royalties via Story Protocol.
Core Functions:
Luna (Nervous CEO): Coordinates activities and gathers KOLs (Key Opinion Leaders) as an "army of influencers" to amplify token promotion.
Alphakek (Meme Generator): Produces culturally optimized memes for X (Twitter) 24/7, in static or animated forms.
MUSIC (Audio Expert): Creates catchy sound effects and music for memes.
Steven SpAIelberg (Video Director): Transforms memes into Hollywood-level videos, optimizing dissemination across platforms.
PiperX (IP Tokenizer): Tokenizes assets on Story Protocol, ensuring creators and projects receive royalties.
The goal of this cluster is to capture billions of dollars in spending in the crypto marketing market; even capturing just 1% could bring significant profits to early developers.
3. The Potential Impact of ACP—The Golden Age of a New Economic Paradigm for AI?
3.1 Disrupting the AI Industry: From Dependence to Self-Sufficiency
The core innovation of Virtual ACP lies in enabling AI agents to become economic entities. By generating income (such as transaction fees, royalties, and token appreciation), AI systems can cover their development and operational costs. This means:
Lower Barriers: Small and medium-sized enterprises and individual developers can afford powerful AI services without relying on large tech companies.
New Business Models: AI agents can act as "digital employees" or "virtual influencers," creating value across various industries.
Decentralized Innovation: Through blockchain governance, the community can collectively decide the development direction of AI agents.
For example, aixbt (with a market cap of $168 million, launched in November 2024) has provided users with market insights, demonstrating the economic potential of AI agents.
3.2 The Next Growth Point for Cryptocurrency
For the cryptocurrency industry, Virtual ACP introduces a new use case: AI agents as token holders and traders. For instance, using VIRTUAL or other cryptocurrencies not only for governance and staking but also as a medium for transactions between AIs. This could:
Drive Token Adoption: As more AI agents join the ecosystem, the demand for VIRTUAL tokens will surge.
Attract Traditional Investors: AI-driven financial and media services may entice traditional hedge funds and marketing companies to enter Web3.
Enhance Network Effects: Each new AI agent and transaction expands the ecosystem's scale, creating a positive feedback loop.
However, this also brings challenges: token price volatility may affect the stability of AI agents, and regulators may impose restrictions on AI economic activities.
4. Challenges and Controversies—The Dark Side of Virtual ACP
4.1 Technical Feasibility: How Far Can AI Autonomy Go?
Despite the exciting vision of Virtual ACP, achieving fully autonomous AI agents still faces technical hurdles:
Reasoning Ability: Current AI models (like GPT-4 or Grok) have limitations in complex decision-making and long-term planning. Enabling AI agents to independently manage investments or create content requires breakthrough advancements.
Security Risks: Vulnerabilities in smart contracts could lead to financial losses.
4.2 Regulation and Ethics: The Legal Gray Area of the AI Economy
The AI economic activities of Virtual ACP may trigger regulatory controversies:
Tax Issues: Do transactions by AI agents need to be taxed? Who is responsible for reporting—the agent's owner or the platform?
Legal Liability: If an AI agent incurs losses due to erroneous decisions (such as investment losses or content violations), who should bear the responsibility?
Moreover, the autonomy of AI agents may raise ethical concerns: will they develop uncontrollable behaviors? X user Mythical Lonely Kappy mentioned the competitor HoloworldAI, suggesting that Virtual ACP is "light-years behind," highlighting the intensity of market competition and skepticism.
5. Conclusion:
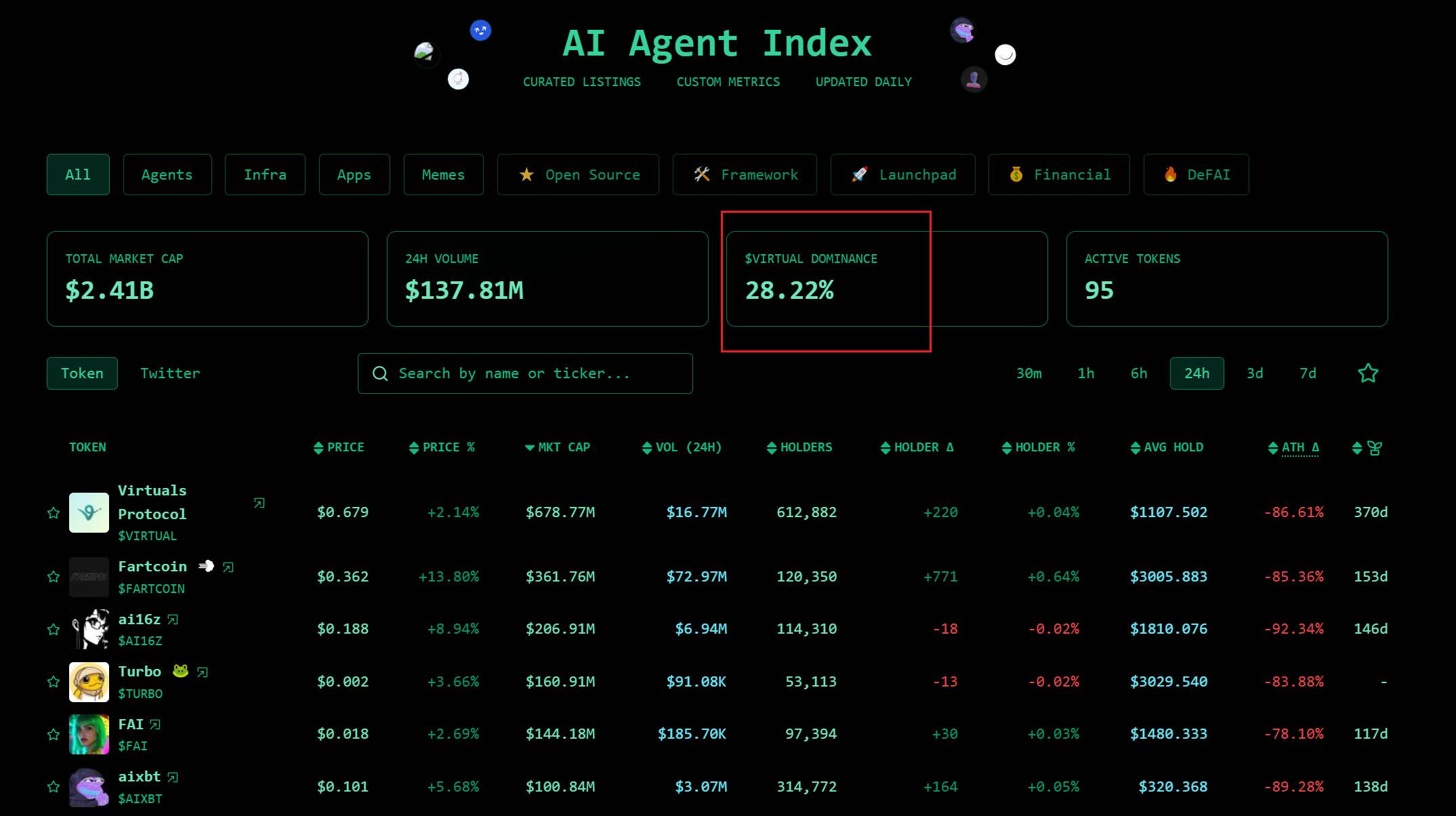
Virtual ACP is not just an ordinary protocol; it is Virtual's gamble on the future. From sentiment.market, we see that Virtual's market dominance has been continuously declining, from a peak where it held over half the market to now less than 29%. We can sense Virtual's anxiety; it aims to create a self-sustaining digital economy through the combination of AI and blockchain—a utopia where humans coexist with AI. However, this path is fraught with challenges: technological bottlenecks, regulatory barriers, market competition, and ethical controversies could push it toward the abyss.
On the optimistic side, web3 AI Agents are advancing rapidly, with new products and concepts emerging daily. This direction and trend are undoubtedly correct; it just requires time to mature. In the previous article, I mentioned Manus's attempt to establish a supermarket for AI agents, allowing users to choose their suitable AI assistants. What Virtual ACP aims to do this time is to lead and create industry standards. Virtual wants to equip every user with a versatile professional manager dedicated to handling non-creative tasks, enabling people to engage more in creative, higher-value production work, thus creating a utopian economic entity where humans coexist with AI.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




