I. Outlook
1. Summary of Macroeconomic Aspects and Future Predictions
The Trump administration announced details of a new tariff policy, triggering market panic and escalating global trade tensions. The policy will raise the prices of imported goods, prompting countermeasures from multiple countries and exacerbating the turmoil. U.S. stocks plummeted as a result, undermining investor confidence. Predictions indicate that if the trade dispute escalates, global supply chains will be under pressure, U.S. exports may be impacted, inflation risks will rise, and stock market volatility will increase. This policy could reshape the trade landscape, casting a shadow over economic prospects.
In the long term, if diplomatic avenues cannot ease tensions, this policy may reshape the global trade landscape, forcing countries to reassess their economic strategies, and the prospects for international cooperation will become increasingly uncertain. Investors need to remain vigilant about potential developments in the tariff war.
2. Market Movements in the Cryptocurrency Industry and Warnings
Although the cryptocurrency market showed some independence during the week and did not follow the U.S. stock market's plunge, panic and insufficient liquidity over the weekend led to another significant drop in the cryptocurrency market, with Bitcoin nearing previous lows and Ethereum falling below $1600.
If signs of easing in the global economic environment emerge or regulatory policies signal positivity, the cryptocurrency market may find a breathing space and could gradually stabilize under the influence of long-term capital. However, at the current stage, the fragility of market sentiment and the accumulation of external pressures make the path to future rebounds fraught with challenges. Investors should closely monitor the subsequent developments of the Trump administration's tariff policy, as it may further impact the global economy and market sentiment.
3. Industry and Sector Hotspots
Stabble is a decentralized exchange (DEX) native to Solana. Its uniqueness lies in allowing liquidity providers (LPs) to participate in both internal and external arbitrage trading, achieving automated liquidity provision through smart liquidity routing. Amnis Finance, a native LST protocol on Aptos, led by OKX and followed by Gate, releases the value of APT. Fhenix, a platform empowering public chain protocols with fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) technology, has raised over $20 million.
II. Market Hotspot Sectors and Potential Projects of the Week
1. Performance of Potential Sectors
1.1. Analysis of Stabble, a Native DEX Built on Solana, Introducing Innovative Yield Mechanisms for LPs
Stabble is a decentralized exchange (DEX) native to Solana, built on the automated market maker (AMM) conversion function initially introduced by the Uniswap protocol.
Stabble's uniqueness lies in allowing liquidity providers (LPs) to participate in internal and external arbitrage trading and achieving automated liquidity provision through smart liquidity routing. Additionally, Stabble supports virtual margin liquidity, enhancing capital efficiency, allowing liquidity providers to take on higher risks while attracting risk-averse investors into the AMM protocol.
Stabble shares similarities with Balancer and Curve protocols. Like Balancer, it supports weighted pools and composable stable pools, but compared to its competitors, Stabble's liquidity pools require significantly less liquidity (up to 97% reduction) while achieving similar trading volumes. This mechanism enhances capital utilization and annualized yield (APY) for liquidity providers.
Innovative Details

Smart Liquidity Routing (SLR)
Smart Liquidity Routing (SLR) aims to help liquidity providers (LPs) automate, decentralize, and optimize liquidity provision. Users can deposit a single asset, and the system will automatically allocate it to multiple liquidity pools, thereby diversifying liquidity risk. SLR compares the expected returns (APY) of different liquidity pools and automatically directs funds to the pool with the highest yield while maintaining diversification of liquidity positions.
SLR enables users to automate long-term liquidity deposits, as it continuously reallocates funds to maximize profits in liquidity pools. By diversifying, SLR can reduce divergence loss by up to 80% and improve the risk-return ratio for liquidity providers.
Smart Liquidity Arbitrage (SLA)
In AMM decentralized exchanges (DEXs), arbitrage trading accounts for up to 95%. Stabble's research found that in similar DEXs, arbitrage trading consumes 18-34% of total liquidity pool funds annually, leading to divergence losses for liquidity providers. Arbitrageurs profit from price differences between exchanges or within the same exchange while promoting market price convergence.
Stabble has dedicated arbitrage pools, where liquidity providers can receive additional compensation generated by Stabble's internal cross-exchange arbitrage bots. These bots trade internally within Stabble without fees and only execute trades when the arbitrage price difference exceeds a threshold set by Stabble token holders.
Additionally, Stabble replaces the flash loan mechanism designed by Balancer with internal arbitrage. Traditional flash loans support arbitrage between different pools within a DEX, benefiting arbitrageurs, while Stabble believes that arbitrage profits should belong to liquidity providers.
- Internal Arbitrage: Automatically allocates arbitrage profits to liquidity providers instead of external arbitrageurs.
- External Arbitrage: Stabble supports off-chain arbitrage, ensuring efficient liquidity flow between Stabble and other exchanges.
By combining internal and external arbitrage, Stabble allows liquidity providers to earn additional profits while enabling traders to benefit from more accurate price matching and lower slippage. Stabble's arbitrage pools are particularly suitable for large traders and liquidity providers and plan to connect more decentralized and centralized exchanges to build a seamless and robust DeFi ecosystem.
Margin Liquidity and Virtual Margin Liquidity
Margin Liquidity
Although arbitrage trading can provide additional compensation, providing liquidity still carries risks during periods of high market volatility. Generally, liquidity providers need to possess risk-neutral or risk-seeking attributes. Stabble aims to attract risk-averse liquidity providers and promote broader liquidity supply in the DeFi ecosystem, thus developing a margin liquidity mechanism.
Stabble's margin liquidity offers 8000 times the capital efficiency compared to concentrated liquidity (Uniswap V3).
- Traditional liquidity providers need to provide liquidity directly, while margin liquidity introduces lenders and margin liquidity providers (MLPs).
- Margin liquidity providers obtain capital from lenders and provide it to liquidity pools while needing to provide collateral.
- Revenue model: Margin liquidity providers must pay interest to lenders, and their liquidity is limited to specific price ranges, similar to concentrated liquidity in Uniswap V3.
This mechanism enhances the flexibility and capital efficiency of liquidity provision:
- Risk-averse liquidity providers can choose to act as lenders without bearing divergence losses.
- Risk-seeking liquidity providers can open margin liquidity positions to earn higher returns while assuming liquidation risks.
Virtual Margin Liquidity
The main difference between virtual margin liquidity and traditional margin liquidity lies in the role of the lender:
- Margin Liquidity: Lenders are third-party users who provide funds and earn interest.
- Virtual Margin Liquidity: The lender is the liquidity pool itself, meaning the liquidity pool acts as the counterparty, providing funds to margin liquidity providers.
Advantages:
- Reduced Divergence Loss Risk: Virtual margin liquidity providers do not suffer from divergence losses during the borrowing period.
- Increased Earnings for Liquidity Providers: Liquidity providers can receive higher trading fee compensation.
Virtual margin liquidity expands Stabble's capital efficiency, allowing liquidity providers to earn more under safer conditions.
Commentary

Overall, Stabble enhances the earnings of liquidity providers through smart liquidity management, arbitrage profit sharing, and margin liquidity, while also improving the overall capital efficiency of the DeFi ecosystem. However, it still needs to address challenges such as user understanding costs, sustainability of arbitrage profits, liquidation risks of leverage, and market competition pressure to ensure long-term competitiveness and user growth.
1.2. How does Amnis Finance, led by OKX and followed by Gate, release the value of APT on Aptos?
Amnis Finance - a pioneering liquid staking protocol on Aptos.
As a foundational component of the Aptos ecosystem, Amnis Finance has launched a secure, user-friendly, and innovative liquid staking protocol that allows users to easily maximize the yield of APT tokens while unlocking their liquidity.
Architecture Overview
amAPT & stAPT
- amAPT
amAPT (Amnis Aptos Token) is a stablecoin loosely pegged to APT, ensuring that 1 amAPT always represents 1 APT, and the circulating supply of amAPT matches the amount of APT in Amnis Finance. When APT is deposited into Amnis Finance, amAPT is minted in equal amounts.
amAPT/APT Liquidity Pool
The amAPT/APT liquidity pool provides users with a quick and convenient way to instantly withdraw amAPT without waiting for the standard 14-day settlement period. With the 1:1 peg between amAPT and APT and deep liquidity across multiple DEXs, users can easily swap between the two.
In response to significant fluctuations in market demand for amAPT or APT, Amnis has established a reserve mechanism. When necessary, the protocol will repurchase amAPT from the market to stabilize its price. Any profits generated by this mechanism will be directly transferred to the Amnis treasury. Additionally, Amnis has developed a robust system equipped with monitoring alerts and AI algorithms to ensure the stability and effective management of amAPT prices.
- stAPT
stAPT (Amnis Staked Aptos Token) is a treasury used to accumulate staking rewards from Amnis APT validators. Users can exchange amAPT for stAPT at any time by depositing amAPT into the stAPT treasury, thereby earning staking rewards on amAPT. Over time, as validators accumulate staking rewards, the protocol will mint an equivalent amount of amAPT and add it to the treasury, allowing users to redeem more amAPT with stAPT than they initially deposited.
The amAPT exchange rate for stAPT will increase over time as staking rewards are continuously added to the treasury. Holding stAPT means that users hold a certain percentage share of the amAPT assets in the treasury, and staking rewards will be distributed based on the proportion held by stAPT holders. This mechanism is similar to other auto-compounding tokens, such as Aave's aUSDC and Compound's cUSDC.
Smart Contract Architecture

Amnis Finance allows users to earn staking rewards on their APT holdings without locking up funds or maintaining validator nodes. The Amnis protocol consists of several core components:
- Dual Token Model: amAPT and stAPT
- Depositing or Withdrawing APT to Whitelisted Validator Nodes
- Performance Scoring Calculation for Whitelisted Validator Nodes (Automated Portfolio Management) to Optimize Rewards
- Reward Distribution Every 2 Hours (As Network Rewards Are Generated)
- Two Withdrawal Methods: Slow Withdrawal and Fast Withdrawal
APT Staking Process
Users send APT to the Amnis Finance smart contract and receive amAPT tokens in return. Holders of amAPT can choose to:
- Directly Participate in the Aptos DeFi Ecosystem, such as providing amAPT-APT liquidity to decentralized exchanges (DEX) in exchange for an annual percentage rate (APR). Holding amAPT does not earn staking rewards.
- Use Amnis for Secondary Staking, exchanging for stAPT tokens. stAPT represents all staking rewards generated from APT staked in the Amnis protocol and can be held, traded, or sold. The exchange rate of stAPT is based on the total amount of staked APT and accumulated staking rewards.
All fund flows are automatically managed by smart contracts (modules), as illustrated. Additionally, the design of the Amnis protocol features the following characteristics:
- Priority on Security: The minting amount of amAPT (and the value of stAPT) is always equal to the amount of APT deposited. This is ensured by formal verification of the smart contract, guaranteeing that amAPT always maintains a 1:1 exchange with APT, while the value of stAPT continuously increases with the accumulation of staking rewards, preventing any loss of value.
- Arbitrage Prevention: A small deposit fee (always below 0.0008%) is charged when depositing APT to mint amAPT. This fee is refunded at the end of the current 2-hour network cycle, ensuring that depositors are not harmed. This mechanism prevents arbitrageurs from depositing APT at the last moment before reward settlement to gain rewards.
- Decentralized Performance Optimization: The performance scores of validators are calculated and recorded on-chain in each cycle. Based on factors such as overall operating fee rates and total amounts deposited, each validator will receive an overall score to determine fund allocation for the next cycle. The system may automatically reallocate staking funds based on scores to optimize returns.
- Composability: The Amnis protocol is designed for composability, allowing more DeFi protocols and other applications to easily integrate and build upon it.
User Flow

Commentary
Advantages
Liquidity Release: By tokenizing APT staking with amAPT, users can utilize amAPT in the Aptos DeFi ecosystem without affecting their earnings.
Automatic Yield Optimization: stAPT represents APT staking rewards, and its exchange rate automatically increases over time, similar to Aave's aUSDC, achieving auto-compounding.
Dual Token Model: amAPT (liquidity) + stAPT (rewards) separation improves capital utilization, allowing users to freely choose strategies.
Fast Withdrawals: Provides amAPT/APT liquidity pools, supporting instant redemption of amAPT, bypassing the 14-day staking release period, while also having a repurchase stabilization mechanism to ensure amAPT price anchoring.
Decentralized Optimization: Utilizes smart contracts to manage validator performance scores, dynamically adjusting fund allocation based on yield to enhance overall returns.
Security Assurance: Through formal verification, ensures that the value of amAPT is always 1:1 pegged to APT, with stAPT value only increasing, eliminating capital loss risks.
Composability: Open protocol design allows integration with the DeFi ecosystem, such as DEX trading, lending, liquidity mining, etc.
Disadvantages
Dependence on Secondary Market Liquidity: The exchange of amAPT relies on the depth of liquidity pools; insufficient liquidity may lead to premium or discount trading.
Smart Contract Risks: Despite security mechanisms, inherent risks in DeFi such as code vulnerabilities and hacking attacks still need to be addressed.
Market Arbitrage Risks: Although there is a deposit fee mechanism to prevent short-term arbitrage, excessively high yields may still attract arbitrageurs, affecting fund flows.
Complexity of Validator Management: Amnis needs to continuously optimize the validator allocation algorithm to ensure optimal returns, which relies on the effectiveness of the Aptos ecosystem and Amnis's own strategies.
Intense Competition: Faces competition from other liquid staking protocols in the Aptos ecosystem, necessitating continuous product and user experience optimization.
1.3. Analysis of Fhenix, a Platform Empowering Public Chain Protocols with Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) Technology, Raising Over $20 Million
Fhenix is a blockchain platform that is the first to adopt Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) technology, enabling confidential smart contracts on public blockchains like Ethereum. FHE, as a cutting-edge encryption technology, allows computations to be performed directly on encrypted data without the need for decryption, ensuring that transaction inputs and states remain encrypted throughout the process, enhancing privacy protection.
Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE) is a technology that processes data without the need for decryption. Since data remains encrypted during transmission and processing, FHE makes end-to-end encryption applicable not only to digital communications but also extendable to all online operations!
This means that businesses can provide various services without exposing user data, including computations and processing of user data, thereby ensuring user privacy. At the same time, users will not notice any functional differences when using these services, but their data remains confidential.
In the blockchain field, FHE makes confidential smart contracts possible, ensuring that on-chain data remains encrypted. This allows blockchains to maintain decentralization and auditability without permission while preventing external observers from accessing sensitive information, achieving true privacy protection.
Architecture Analysis
Fhenix aims not only to provide the first L2 solution based on FHE (Fully Homomorphic Encryption) but also to create a modular and flexible platform that can be easily adjusted, scaled, and optimized as traffic, use cases, and demands evolve.
The Fhenix protocol consists of several core components that together build a secure and private smart contract environment. The main components include:
- Core Chain: Built on Arbitrum Nitro
- FheOS
- Warp-Drive
These components combine in a layered architecture, providing a modular design that offers high flexibility to adapt to different application scenarios and future development needs.

Core Chain
The core blockchain is the foundational layer of the Fhenix protocol, built on Arbitrum Nitro. Arbitrum Nitro is a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum that provides a scalable and secure operating environment for smart contracts through a combination of Fraud Proofs and Optimistic Rollups.
The main responsibilities of the core blockchain include:
- Processing Transactions
- Executing Smart Contracts
- Maintaining Blockchain State
FheOS
FheOS is the core of the Fhenix protocol, specifically responsible for operations related to Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE). Its goal is to become a modular and scalable component that can seamlessly integrate into the underlying blockchain, providing FHE support for smart contracts.
FheOS includes:
- FHE Precompiled Functions
- Solidity-related Functions
- Ciphertext Management for interactions at the FHE layer of smart contracts
Warp-Drive
Warp-Drive is responsible for managing FHE keys and executing FHE computations, with core components including:
- Key Management
- FHE Operation Interfaces
- Encryption/Decryption Functions
As an independent component, Warp-Drive brings the advantage of separation of responsibilities:
- The blockchain itself does not need to directly handle FHE computations or rely on specific functionalities.
- Supports various FHE schemes, allowing developers to choose suitable encryption methods based on their needs.
Warp-Drive consists of multiple subcomponents that work together through shared interfaces, ensuring ease of use and scalability.

Commentary
Advantages
True Web3 Privacy Protection: Data is encrypted throughout the process, with no plaintext storage on-chain, suitable for scenarios such as finance, healthcare, and identity management.
Strong Composability: The modular design facilitates integration, allowing seamless combination with existing DeFi, DAO, and NFT applications.
High Scalability: Leveraging Arbitrum Nitro, it achieves low cost & high throughput, making it suitable for large-scale applications.
Support for Multiple FHE Schemes: The Warp-Drive component allows developers to choose suitable encryption methods based on specific needs.
Potential Challenges
High Cost of FHE Computation: FHE computation incurs higher performance overhead compared to traditional computation, making optimization algorithms and hardware acceleration crucial.
High Development Difficulty: FHE is still in its early stages, and the developer ecosystem needs further maturation, along with improvements in the toolchain.
User Experience Needs Optimization: Applications with complete privacy protection may introduce additional complexities in certain scenarios, such as key management and the verifiability of privacy computations.
2. Detailed Analysis of Projects to Watch This Week
2.1. Detailed Mechanism of the Native Decentralized CDP Protocol Beraborrow Backed by Berachain's Huge Traffic
Introduction
Beraborrow unlocks instant liquidity based on Berachain assets through the first PoL-supported stablecoin, Nectar ($NECT). The core design philosophy of Beraborrow is simplicity and flexibility, aimed at maximizing user opportunities without forcing them to sacrifice returns.
The protocol allows users to deposit collateral assets into Dens, thereby minting over-collateralized stablecoins $NECT. Subsequently, $NECT can be used within the Berachain DeFi ecosystem, unlocking more opportunities while maintaining exposure to the original assets. Initially built around $iBGT, the protocol has evolved into a multi-collateral platform supporting Bera native tokens, liquid staking derivatives, or LP positions as collateral to mint $NECT.
Beraborrow enables users to unlock liquidity while retaining price exposure to their assets. The protocol utilizes Proof of Liquidity (PoL) to enhance key features and guide liquidity, allowing users to gain leverage on collateral assets while increasing their generated returns.
Technical Analysis
- Dens (Lending Module)
Dens is the core collateral management system of Beraborrow, providing users with a way to deposit assets, earn returns, and mint $NECT while maintaining exposure to the original collateral assets. This flexibility allows users to unlock liquidity without selling or giving up their positions in valuable assets.
- How Dens Operates
When users deposit assets into a Den, they are effectively locking their collateral assets within the protocol. This allows users to mint $NECT, which is Beraborrow's over-collateralized stablecoin, and can subsequently be used within the Berachain DeFi ecosystem. The amount of $NECT that users can mint is determined by the asset's Minimum Collateral Ratio.
Beraborrow's Dens support various types of collateral assets, including liquid staking tokens like $iBGT and $iBERA, as well as other whitelisted assets such as LP positions from Bex and Berps. Once collateral assets are deposited into a Den, users can still be fully exposed to the price fluctuations or returns of that asset, allowing them to benefit from asset appreciation.
- Automatic Reinvestment Feature
A key innovation in Beraborrow's Dens is the automatic reinvestment feature. Dens are designed to maximize returns by automatically reinvesting rewards earned from collateral assets back into the same asset. For example, if you deposit a USDC:HONEY BEX LP position into a Den, the protocol will deposit that LP into the Infrared treasury and re-stake any $iBGT tokens earned.
This automatic reinvestment process increases the amount of collateral assets over time, allowing users to steadily improve their collateral ratios without manual intervention, thereby reducing the risk of liquidation. As collateral assets grow, users can borrow more $NECT, providing additional liquidity and yield opportunities.
- Brime Den
Brime Den is a reserve pool managed by the protocol, designed to protect Beraborrow users from the direct impact of $NECT redemptions. All redemptions are first processed through this protocol-owned Den, ensuring that users are initially unaffected. Once the Brime Den is depleted, redemptions will be processed through Dens that pay the minimum interest rate.
- NECT (Stablecoin)
Nectar ($NECT) is the first native collateralized stablecoin of Berachain. Beraborrow aims to establish $NECT as the preferred stablecoin on Berachain, utilizing various native collateral assets and will announce more assets soon. $NECT is positioned as the foundational stablecoin within the Berachain ecosystem, driving growth and innovation across the entire chain. The utility of $NECT is further enhanced through strategic partnerships with key projects within the Berachain ecosystem.
As the Beraborrow protocol operates as a unilateral money market, borrowers do not need to pay market-leading interest rates. This means that interest rates are used to incentivize the growth and stability of $NECT. The primary beneficiaries are any LPs or protocols that drive demand for $NECT. For the Beraborrow protocol itself, this has already been achieved through the liquidity stabilization pool and early guidance of the $NECT-$HONEY LP trading pair. It can also be a trading protocol that uses $NECT as a quote asset, a game that trades using $NECT, or simply a new token launch that pairs its initial liquidity with $NECT.
This means that $NECT will be temporarily locked or pooled, reducing selling pressure, which also allows Beraborrow to handle more leverage.
- POLLEN (Governance Token)
POLLEN is a governance token designed to support the stability and growth of the Beraborrow protocol by incentivizing the adoption and liquidity of NECT. POLLEN holders can participate in protocol decision-making and drive governance-driven incentives to enhance the Beraborrow ecosystem.
Initially, incentives will focus on liquidity stabilization pools and stablecoin liquidity. Once the stable exchange system establishes sufficient liquidity, incentives will be reallocated to enhance NECT's utility as a stablecoin through protocols and use cases, such as trading protocols that use NECT as a quote asset, games that trade using NECT, or a new token launch that pairs its initial liquidity with NECT.
- Protocol Interest Rate Distribution
Since Beraborrow has no lenders, all protocol interest income will be allocated to governance-driven initiatives to support the sustainability of the ecosystem:
- Berachain Reward Treasury: Governance participants can stake POLLEN to participate in ecosystem governance and decision-making, aligning incentive mechanisms with the long-term sustainability of Beraborrow.
- Protocol Liquidity Program: Governance participants allocate funds to enhance stablecoin liquidity, ensuring the stability of NECT as a decentralized stable asset.
This creates a positive feedback loop (flywheel effect), where the utility of NECT increases, attracting more users to leverage Beraborrow, thereby raising overall interest rates and protocol fees, which ultimately flow into the sPOLLEN Berachain reward treasury, allowing more value to be used to incentivize liquidity, and then the cycle continues to strengthen.

- Staking
POLLEN can be staked to mint sPOLLEN, allowing participation in governance and deeper ecosystem interaction. Staking does not guarantee financial returns but aligns long-term participants with protocol incentives. Additionally, through the Beraborrow interface, governance participants can direct protocol rewards towards initiatives that enhance NECT's utility within the Berachain ecosystem.
- Bonding
Users can provide liquidity through a bonding mechanism, such as sNECT, HONEY-NECT, POLLEN-BERA, or POLLEN-NECT LP tokens, in exchange for POLLEN allocations to gain governance rights. Bonding does not provide financial returns; its design goal is solely to support protocol sustainability and expand decentralized liquidity.
- aPOLLEN
aPOLLEN can be exchanged 1:1 for POLLEN at the TGE (Token Generation Event). It serves as a placeholder fundraising token on Arbitrum, as Arbitrum supports cross-chain purchases, allowing us to attract users from multiple chains and ultimately guide them to the Berachain ecosystem.
- cPOLLEN
cPOLLEN can be earned through NECT-related farming or usage before the TGE and will be exchanged 1:1 for POLLEN at the TGE. A portion can be claimed immediately, while the remaining portion will unlock after one month, with a light gamification mechanism to reward loyal holders.
Conclusion
Beraborrow, leveraging the PoL mechanism and the native stablecoin $NECT, has built a decentralized, auto-compounding, and efficient liquidity lending platform, empowering community decision-making through the governance token POLLEN. Its advantages include high capital efficiency, ecosystem integration, and stablecoin application growth, but it also faces potential issues such as reliance on Berachain's development, challenges in liquidity sustainability, and liquidation risks. Future success depends on key factors such as the growth of the Berachain ecosystem, increased adoption of $NECT, and optimization of governance mechanisms.
3. Industry Data Analysis
1. Overall Market Performance
1.1 Spot BTC & ETH ETF

Analysis:
In this week, the fund flows of BTC and ETH ETFs showed a clear divergence. Bitcoin ETFs quickly rebounded from outflows at the beginning of the week, experiencing strong net inflows, while Ethereum ETFs predominantly faced net outflows, although some individual products saw slight inflows. This difference may reflect institutional investors' more optimistic outlook on BTC while maintaining a wait-and-see attitude towards ETH.
Overall, the strong rebound of BTC ETFs indicates that market confidence is recovering, and institutions are reallocating funds to bet on BTC. The continued outflows suggest that there is still uncertainty in the market regarding ETH, which may be related to market volatility, upgrade progress, or regulatory policies.
As of November 1 (Eastern Time), the total net outflow of Ethereum spot ETFs was $10.9256 million.
1.2. Spot BTC vs ETH Price Trends
BTC

Analysis
As of this Monday, after struggling to stabilize above $80,000 last week, BTC was once again affected by global tariff countermeasures and quickly fell below the $80,000 mark this morning, temporarily stopping at this year's low near $76,600. From the short-term selling volume released, the intensity of this waterfall sell-off is much stronger than during the formation of the March low. Therefore, this week’s focus is on three key levels: the current support at $76,600. If it continues to decline but does not effectively break this level, the probability of forming a W-bottom and starting a rebound is relatively high. Conversely, if the fundamentals continue to deteriorate and break below this support level, attention should shift to the second support level at $74,000 (the top of the 2024 range), which may also become the starting point for the next upward trend. As for the first significant resistance for the rebound, it can be directly observed around $89,000. Only an effective breakthrough of this resistance would open the door for a long-term upward trend; otherwise, there is still a chance of entering a wide-ranging oscillation phase.
ETH
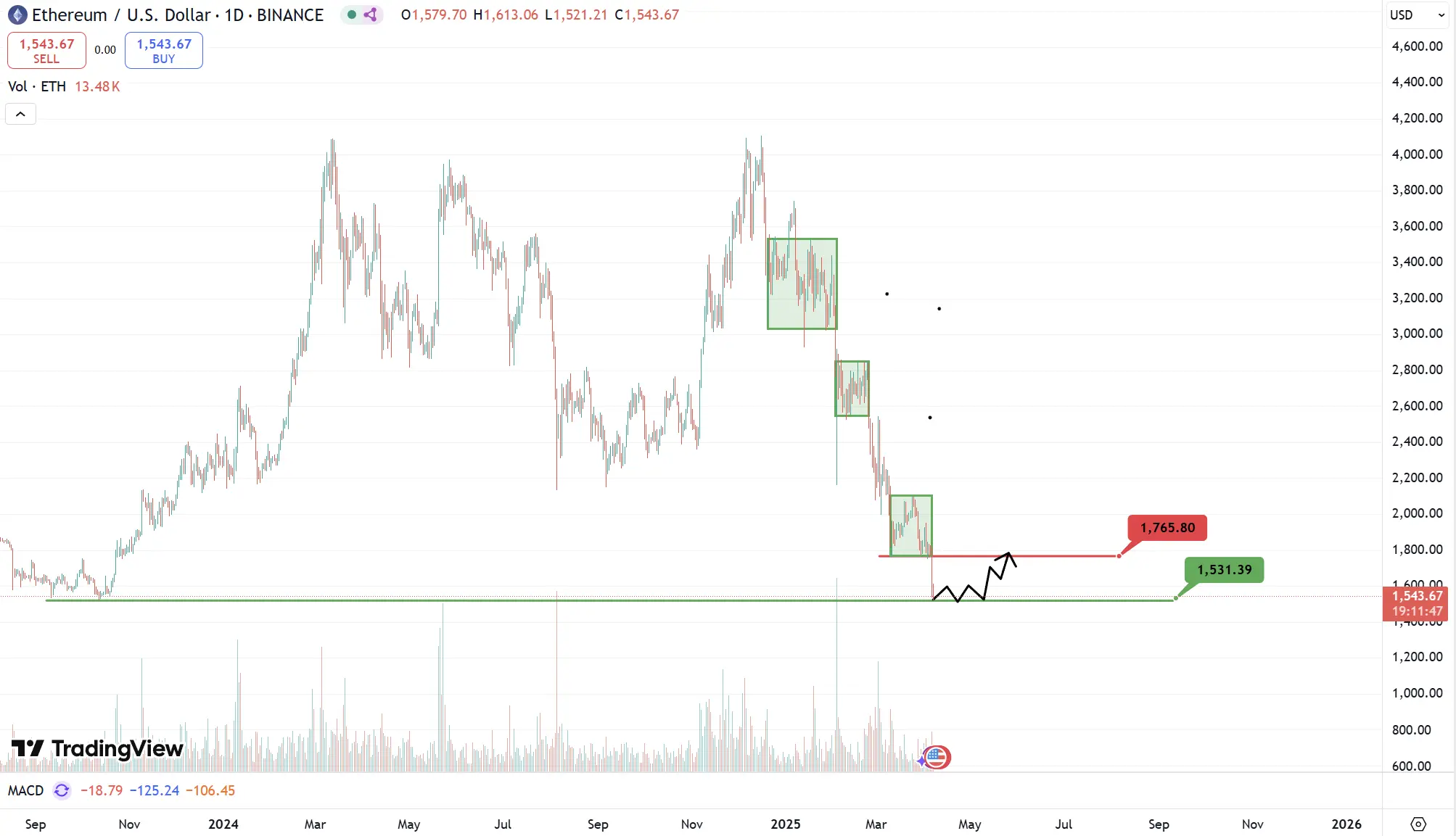
Analysis
For ETH, bullish momentum has not effectively erupted, leading to a continuous decline in the coin price since 2025, now even probing down to $1,530 (the bottom of the consolidation range in October 2023). Therefore, if an effective rebound cannot be initiated, the next support level may continue to look down to $1,350. However, based on the current selling volume, the trading volume has quickly decreased, and the $1,530 support may form a short-term bottom, with the first resistance level to watch directly around $1,760.
1.3. Fear & Greed Index

2. Public Chain Data
2.1. BTC Layer 2 Summary

Analysis
Formal Verification of Lightning Network:
A research paper published this week on arXiv marks significant progress. This study provides a rigorous, machine-verifiable mathematical proof of the security of the Lightning Network (LN) for the first time using formal methods. The results indicate that the Lightning Network ensures the safety of honest users' funds in all scenarios. This achievement greatly enhances confidence in the security and large-scale use of LN.
Stacks' Nakamoto Upgrade & Launch of sBTC: The Stacks network has launched the long-awaited Nakamoto upgrade. By anchoring its data on the Bitcoin main chain, this upgrade not only enhances security and finality but also paves the way for innovative applications. A major highlight of the upgrade is the introduction of sBTC (a decentralized asset pegged to Bitcoin), aimed at activating the capital efficiency of BTC and empowering more application scenarios.
Continuous Development of Rootstock (RSK): Rootstock is a sidechain system that brings smart contract capabilities to Bitcoin, relying on merged mining to share the hash power of the Bitcoin main chain. This week, Rootstock continued to enhance system performance, supporting its expanding decentralized application ecosystem while ensuring transaction security and providing richer off-chain interaction capabilities.
2.2. EVM & Non-EVM Layer 1 Summary

Analysis
EVM-Compatible Layer 1 Network Dynamics
Kadena Launches Chainweb EVM:
- On April 3, Kadena officially launched Chainweb EVM, integrating 20 new EVM-compatible chains as part of its multi-chain architecture.
- The system features ultra-low gas fees, unlimited scalability, and efficient proof-of-work (PoW), enhancing block processing speed and handling traffic surges through native parallelization technology.
- Kadena claims to be a decentralized alternative to Ethereum Layer 2, attracting hundreds of developers (some through early access programs at ETHDenver).
- Additionally, Kadena announced a $50 million ecosystem support fund to support projects in RWA (real asset tokenization), AI, and other innovative directions.
Breakthrough in Ethereum Parallel Execution Research:
- An academic study released on April 2 proposed a parallel transaction execution model for EVM, aimed at addressing performance bottlenecks caused by current sequential execution.
Non-EVM / Hybrid Architecture Layer 1 Network Dynamics
Shardeum Mainnet Launching Soon:
- Shardeum is known as the world's first auto-scaling blockchain, with its mainnet confirmed to launch on April 15, 2025.
- It is based on a dynamic state sharding mechanism, supported by over 170,000 validators and 81 million test transactions, achieving a new balance among decentralization, security, and throughput.
- While supporting EVM, Shardeum's auto-scaling mechanism classifies it as a next-generation Layer 1 solution.
SKALE Advances Gasless Model Ecosystem Expansion:
- SKALE continues to promote a "zero gas" experience to attract developers, particularly in gaming, DeFi, and AI applications.
- In addition to technical optimizations, SKALE is also expanding incentive programs to further enhance its developer infrastructure for Layer 1 networks.
2.3. EVM Layer 2 Summary

Analysis
Optimism Upgrade
- Protocol Improvement: Optimism announced an upgrade focusing on optimizing its Rollup architecture, further reducing transaction costs and enhancing throughput.
- Security Enhancement: A new consensus mechanism has been introduced to enhance the network's security, making it more resilient against potential attacks.
Arbitrum Development Toolkit Update
- Simplified Integration Process: Arbitrum released a new development toolkit that simplifies the deployment process for smart contracts and DApps, aiming to lower the entry barrier for new projects.
- Gas Cost Optimization: The toolkit includes updates for gas cost optimization, which is expected to attract more developers.
zkSync Upgrade
- Privacy and Efficiency Improvements: zkSync updated its zero-knowledge Rollup, enhancing privacy protection features and optimizing transaction processing efficiency.
- Enhanced Developer Support: Improved documentation and developer support tools were also released to promote ecosystem development.
StarkNet Progress
- Focus on Scalability: Although StarkNet uses unique Rollup technology, it continued to advance its scalability roadmap this week, with performance benchmarks showing significant improvements in throughput and reduced gas costs.
- Enhanced EVM Compatibility: Efforts are underway to improve interoperability with EVM systems, aiming for smoother cross-chain integration.
4. Macroeconomic Data Review and Key Data Release Nodes for Next Week
In March, the unemployment rate in the U.S. was 4.2%, up 0.1 percentage points from 4.1% in February, slightly higher than the market expectation of 4.1%. Despite the rise in the unemployment rate, the number of non-farm jobs added in March reached 228,000, far exceeding the expected 140,000 and higher than the 117,000 in February. The number of unemployed increased by 31,000, totaling 7.08 million, while the number of employed increased by 201,000, totaling 163.51 million. The labor force participation rate also slightly rose from 62.4% to 62.5%.
Important macroeconomic data nodes for this week (April 7-11) include:
April 10: U.S. March unadjusted CPI year-on-year.
5. Regulatory Policies
United States
Deregulation of Digital Assets: Kristalina Georgieva, the Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), expressed optimism about the Trump administration's initial measures for deregulating digital assets, aiming to find a balance between regulation and innovation.
Brazil
Salary Payments in Bitcoin: Brazil has passed a law allowing employees to receive part of their salaries in Bitcoin, aiming to modernize financial infrastructure and provide more flexibility for workers.
Pakistan
Cryptocurrency Committee Established: Pakistan has established the "Pakistan Cryptocurrency Committee" to regulate and promote the country's cryptocurrency market, enhancing remittance efficiency through faster and cheaper international transactions.
Dubai (UAE)
Real Estate Tokenization Pilot: Dubai has launched a pilot project for real estate ownership tokenization, aiming to revolutionize real estate transactions, with the market expected to reach $16 billion by 2033.
South Korea
Crackdown on Unregistered Exchanges: South Korea's Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) has launched a crackdown on unregistered overseas cryptocurrency exchanges (including BitMEX and KuCoin) to promote compliance with domestic regulations.
Australia
Upcoming Regulatory Framework: The Australian government has announced plans to introduce a cryptocurrency regulatory framework in 2025, aimed at enhancing consumer protection and addressing the issue of de-banking by major banks.
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
Inclusion of Cryptocurrency in Economic Statistics: The IMF has updated its "Balance of Payments Manual," classifying cryptocurrencies as "non-productive non-financial assets" and incorporating digital assets into global economic statistics.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




