I. Outlook
1. Macroeconomic Summary and Future Predictions
The global market is experiencing increased volatility due to U.S. tariff policies and economic data. U.S. stocks are showing divergence; in the past week, the S&P 500 fell by 0.85%, the Dow Jones rose by 0.32%, and the Nasdaq dropped by 1.12%. The IMF downgraded the U.S. economic growth forecast for 2025 to 1.8% (down from 2.7% in January) due to trade confidence being impacted by tariff uncertainties. The EU and Canada plan to retaliate, and inflation expectations are rising. Germany's economic growth forecast for 2025 has been lowered to 0%. In the coming week, U.S. non-farm payroll data, Federal Reserve interest rate statements, and tariff negotiations will be the focus. If trade frictions escalate, supply chain pressures may drive up commodity prices and suppress risk assets, necessitating caution.
2. Market Movements and Warnings in the Crypto Industry
The crypto market has shown resilience, not following the significant downturn of U.S. stocks. Bitcoin is nearing $95,000, benefiting from net inflows into BTC ETFs. Coinbase Institutional's report indicates a slight decline in the total market capitalization of the crypto market (excluding BTC) in Q1, with venture capital slowing and confidence in altcoins being weak. On the regulatory front, the SEC's new regulations regarding stablecoins and DeFi platforms are drawing attention and may affect market sentiment. Technically, if Bitcoin does not break through recent highs, it may retest previous support levels. Investors should diversify their portfolios, be wary of high-volatility token risks, and pay attention to the long-term potential of blockchain in payment and decentralized application fields.
3. Industry and Sector Hotspots
The decentralized AI platform Fetch.ai has launched an enterprise toolkit that combines AI analytics with blockchain technology for supply chain and healthcare applications. The price of the FET token has increased month-on-month, thanks to enhanced data privacy from European logistics partnerships. The ReFi project Flowcarbon has secured $5 million in funding led by a16z to expand its carbon-negative blockchain and tokenize 10,000 carbon credits on the Polygon platform to fund reforestation. The decentralized identity protocol Litentry has released its v2.0 identity hub, enabling cross-chain identity control for Web3 and DeFi. Cointelegraph notes that Litentry has integrated with Polkadot and Ethereum, providing secure identity verification support for over 5,000 dApps, thereby enhancing user privacy and adoption rates.
II. Market Hotspot Sectors and Potential Projects of the Week
1. Performance of Potential Sectors
1.1. Analysis of MSafe, a core liquidity engine of the Move ecosystem built on Sui and Aptos, with over $5 million in funding
The MSafe wallet (Momentum Safe) is the first multi-signature, non-custodial digital asset management solution built on Move.
Key Advantages of MSafe Wallet
- **Security
**The MSafe wallet solution eliminates the risk of single points of failure, reducing the risks associated with a single individual authorizing fund transfers, providing peace of mind for financial institutions, businesses, and individuals. Built on Move, MSafe enhances security through its unique chain-level security system, which has been audited by several top auditing firms. - **Decentralization
**MSafe achieves true decentralization, which is lacking in custodial wallets and single-signature non-custodial wallets, and this decentralization is crucial to prevent malicious actors from transferring assets from the wallet. - **Interoperability
**MSafe can integrate with any Move-based decentralized application (dApp). Both dApp developers and end-users can enjoy peace of mind and complete interoperability for cross-dApp asset management.
Technical Details
MSafe provides developers with a tool for managing risks in decentralized protocol management. There are two main use cases:
Deploying Smart Contracts with MSafe
- Deploy smart contracts using an interactive command-line interface (CLI).
- (Recommended) Call the MSafe SDK via scripts.
Calling Entry Functions with MSafe
- Call entry functions using an interactive command-line interface (CLI).
- (Recommended) Call the MSafe SDK via scripts.
Components
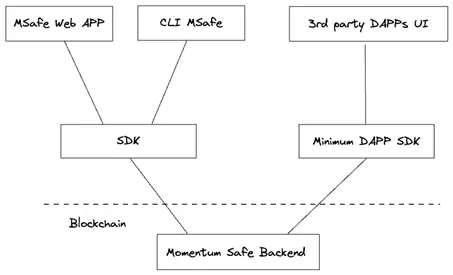
- MSafe Backend: The core part of MSafe. The MSafe backend combines MOVE modules and Aptos's native multi-signature multi-ed25519 to implement a multi-signature wallet.
- SDK: TypeScript SDK for interacting with the MSafe wallet. The SDK is used by the MSafe web application and MSafe CLI tool and can also be used for external third-party integrations.
- Web Application MSafe: The web application interface for interacting with MSafe.
- CLI MSafe: The command-line tool for interacting with MSafe, supporting MOVE module deployment and smart contract interaction.
- DAPP SDK (for dApp integration): Allows third-party dApps to interact with the MSafe wallet.
System
Based on the system architecture, the MSafe protocol has the following advantages:
- **Security
**The design of MSafe ensures that our product has the same level of security as the Aptos core protocol.
Since the final step of MSafe transactions is executed by Aptos's native multi-ed25519 standard, the MSafe wallet is secured by the Aptos core protocol. The only potential risk is if the signature function implemented in the Aptos core protocol is compromised, but this scenario is nearly impossible and has been secured through cryptographic principles.
This also protects MSafe from facing some other potential security issues in the implementation of multi-signature wallets for smart contracts, such as double spending and transaction execution order. These issues have been effectively resolved in the Aptos transaction model. - **Interoperability
**In addition to being used as a wallet, MSafe also enables interaction with other protocols/dApps in the MOVE ecosystem. By using Aptos's native multi-ed25519 wallet, MSafe can send any transaction payload supported by the Aptos core, particularly calling entry functions of any MOVE module.
This allows MSafe to interact with any system/third-party MOVE module and supports various use cases and functionalities implemented by MSafe, including:
- Treasury management
- Interaction with any third-party dApp
- Publishing MOVE modules owned by MSafe using the system function publish_function
- Acting as an administrator account for MOVE modules, controlling protocol-level parameters
- **True Decentralization
**In the current design, the data storage method of MSafe is as follows:
- Core data related to transactions (single-signature addresses, MSafe wallets, TxnBook) will be stored in on-chain MOVE modules. This will minimize the reliance of transactions on other factors and avoid single points of failure.
- User-customized/specific data is stored off-chain to provide a better user experience. This data is user-specific, and users may not want to make this data public on-chain. Therefore, we provide options to store this data in centralized databases or local storage to enhance user experience while maintaining flexibility and privacy.
Through this multi-layered data storage model, we can provide a decentralized system where the core dependency for transaction execution is solely the blockchain itself, while also offering scalability and flexibility for a better user experience.
Interactive CLI
The CLI tool is a command-line interface for interacting with the MSafe wallet. This tool serves as a professional tool for developers, offering several advanced features.
Functions supported by the CLI tool include:
- Wallet creation and registration;
- Transferring APT tokens;
- Registering other currencies (non-APT);
- Transferring other currencies (non-APT);
- Calling entry functions;
- Publishing MOVE modules.
Among these, items 5 and 6 are unique to the CLI and are only supported by this tool.
Currently, the CLI only supports Aptos Devnet. Smart contracts will be deployed on a long-running Testnet.
Commentary
In summary, the MSafe wallet possesses high security, decentralization features, and interoperability, making it suitable for developers and enterprises or individuals requiring high-security management, but the current network support and user-friendliness are relatively low.
1.2. What makes Optimum, a high-performance memory infrastructure dedicated to scaling various public chains with over $11 million in funding, unique?
Optimum is the world's first decentralized high-performance memory infrastructure designed to provide scalable data access for any blockchain, reduce network burdens, and drive the next generation of decentralized applications (dApps). It is based on Random Linear Network Coding (RLNC) technology, a mature data encoding method developed by MIT, transforming slow and redundant networks into fast, efficient, and scalable systems.
Optimum is a decentralized network of flexible nodes (flexnodes) that anyone can run and connect to any blockchain without permission. Through Optimum, blockchains gain a memory bus and RAM-like performance akin to modern computers. The core of Optimum is to build a provably optimal memory infrastructure that transforms blockchains into high-speed, scalable computing networks. Its architecture is modular, permissionless, and easily integrated via APIs.
Optimum's products include Optimum P2P and decentralized random access memory (DeRAM), providing the following benefits to the entire blockchain ecosystem:
- For validators: Accelerated data propagation, reduced operational costs, increased annual percentage yield (APY), and miner extractable value (MEV) income.
- For L1 and L2 blockchains: Faster block propagation, reduced bandwidth consumption, and optimized storage.
- For dApp developers: Improved transaction relaying and prioritization, supporting low-latency, high-throughput, and cost-sensitive applications.
- For end-users: Faster transaction speeds and smoother interfaces, enhancing user experience.
Architecture Overview
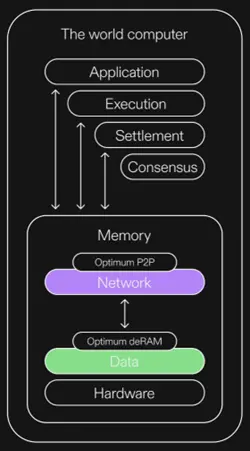
- OptimumP2P
OptimumP2P is a high-performance messaging (i.e., propagation) library that allows nodes in any network to communicate quickly under a publish-subscribe protocol. OptimumP2P is optimized for high speed, low latency, and low bandwidth. The system is based on mature propagation algorithms but employs an innovative approach using cutting-edge network coding technology developed by MIT—Random Linear Network Coding (RLNC).
- Messaging System
Propagation is a widely used information dissemination mechanism that occurs through a set of peer nodes that may not necessarily know each other. Such protocols are used in both Web2 and Web3 networks. In the Web3 domain, propagation is particularly used during transaction and block creation.
Propagation is one of the most critical performance aspects of Web3 systems. For example, slow propagation may result in proposed blocks by validators not being included in the ledger history, jeopardizing network stability and the block rewards for validators. Similarly, delays in receiving new transactions can affect the profitability of MEV optimizers, intent resolvers, and others. Therefore, faster message propagation is crucial for participants in Web3 protocols and the overall health of the network.
- RLNC and Propagation
Random Linear Network Coding (RLNC) is an advanced form of erasure coding that transforms data into smaller blocks and encodes them into random linear combinations before transmission. This method significantly improves network efficiency and fault tolerance, ensuring that data can be accurately reconstructed even if some data blocks are lost during transmission.
Current propagation protocols perform well in the final delivery of messages but have the following issues:
- Long Delivery Time (Latency): Messages must be fully received before they can be forwarded to other nodes, leading to longer delivery times.
- Bandwidth Waste: A node may receive multiple copies of the same message, consuming more bandwidth than necessary.
The use of RLNC addresses both of these issues. With RLNC, peer nodes do not need to transmit the complete message at once; instead, they transmit smaller fragments that are encoded parts of the original message. Each fragment is unique, and as long as nodes receive a sufficient number of fragments, they can decode the complete message regardless of which fragments they received.
This means:
- Peer nodes can start forwarding useful information as soon as they receive the first fragment.
- The size of any redundant information received by nodes is significantly reduced (e.g., only 1/32 the size of the original message), thus greatly lowering bandwidth usage.
Commentary
In summary, Optimum enhances the efficiency and reliability of data propagation by adopting RLNC technology, significantly improving the performance of blockchain systems. However, its implementation complexity is high, and it has greater requirements for node stability and system resources, necessitating a comprehensive consideration of its applicability in different scenarios.
1.3. Analysis of Resolv, a decentralized delta-neutral stablecoin protocol with over $10 million in funding led by Cyber, with participation from Animoca and Ether.fi
Resolv is a decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol that offers USR, a delta-neutral stablecoin fully backed by Ethereum (ETH). By adopting a delta-neutral strategy, Resolv hedges against volatility in the crypto market, aiming to provide price stability and yield generation. The platform also features the Resolv Liquidity Pool (RLP), which absorbs risks associated with the delta-neutral strategy, providing users with leveraged yield farming opportunities.
The main functions of the protocol include:
- Issuance and Redemption of USR: Users can exchange other tokens for USR or redeem USR back for other tokens.
- Always Maintain Sufficient Ethereum (ETH) Support: By using short perpetual futures contracts to hedge against ETH price fluctuations, the protocol ensures it always maintains adequate ETH support.
- Maintain RLP (Resolv Liquidity Pool): This is a liquid insurance pool designed to keep USR over-collateralized to ensure its stability.
Both USR and RLP can be minted and redeemed by users by depositing collateral at a 1:1 ratio.
Feature Analysis
- USR
USR is a stablecoin fully backed by ETH collateral. The main features of USR include:
- Minting and Redemption: Users can exchange liquid collateral for USR at a 1:1 ratio or redeem USR back for liquid collateral.
- Over-Collateralization: In addition to 100% ETH collateral, USR has an insurance layer formed by liquid ETH. The tokens of this insurance layer are RLP.
- Utility Token: USR has a fixed value of $1 and does not generate yield.
- Staking for Yield: Users can stake USR to earn yield. Staked USR is referred to as stUSR, which is the yield-bearing version of USR.
- RLP
The ETH portfolio supports USR at over 100%. The excess collateral serves as support for RLP (Resolv Liquidity Pool). The main features of RLP include:
- RLP has a price, representing the value of ETH supporting a single RLP token;
- RLP price fluctuates, and the amount of collateral required for minting or redeeming is based on the latest RLP price;
- RLP is designed to protect USR from market and counterparty risks. In return, RLP users will receive a larger share of the profits from the collateral pool.
- Resolv Collateral Pool
Resolv maintains a collateral pool composed of the following positions:
- ETH Inventory, including staked ETH, hedged against ETH through short futures contracts;
- Dollar-Neutral Assets: Tokens from the Superstate USCC fund;
- Stablecoins: USDC and USDT.
For the ETH inventory, the futures hedging positions closely track the amount of ETH to ensure that the collateral pool's sensitivity to ETH price changes is nearly zero (i.e., the collateral pool forms a delta-neutral portfolio).
The collateral pool consists of both on-chain and off-chain components. The off-chain component is necessary to maintain the futures positions.
The protocol handles several aspects of the collateral pool:
- Maintaining futures positions;
- Managing inventory allocation;
- Handling staking and unstaking of ETH;
- Managing short-term liquidity needs.
To estimate the prices of different parts of the collateral pool, the protocol uses a combination of several price sources:
- Integrated exchange data;
- Oracle networks;
- Pyth;
- RedStone.
- Profit Distribution
The Resolv collateral pool regularly realizes periodic profits (or losses) calculated in dollar equivalents. The changes in the value of the collateral pool come from:
- ETH staking rewards;
- Futures funding rate income (expenses).
Profit (Loss) Calculation
Profits (or losses) are calculated periodically by the protocol at the end of each reward cycle. The specifics of the reward cycle are:
- Cycle Duration: 24 hours
- Cycle Start/End Date: 12:00:00 UTC
Reward Distribution
Profits are distributed as follows:

If losses are realized during the reward cycle, these losses will be allocated to RLP.
Reward Distribution Reflection
- stUSR: Quantity increases (each stUSR is always equal to 1 USR)
- RLP: Value increases (or decreases)
Commentary
Advantages:
- Stability: The delta-neutral strategy effectively hedges against ETH volatility, maintaining USR stability.
- Multi-layer Insurance: In addition to 100% ETH collateral, USR is further protected by the RLP insurance layer.
- Staking Yield: Users can stake USR to earn yield, enhancing investment attractiveness.
- Risk Management: Optimizes risk management and yield through futures positions and other means.
- Transparent Reward Distribution: The reward mechanism is clear, allowing users to understand the sources of their earnings.
Disadvantages:
- Market Risk: Despite the hedging strategy, there may still be risks such as market crashes.
- Futures Risk: Instability in the futures market may lead to operational risks.
- Complexity: The mechanism is relatively complex, requiring ordinary users to have some knowledge of cryptocurrency.
- RLP Value Fluctuation: The value of RLP may fluctuate, introducing uncertainty.
- External Dependencies: Reliance on external data sources (such as oracles) may affect system stability if the data is inaccurate.
2. Projects to Watch This Week
2.1. Detailed Analysis of Treehouse Finance, a potential DeFi analytics platform with over $400 million valuation led by Compound
Introduction
Treehouse is a decentralized finance (DeFi) analytics platform that provides data, analysis, and risk management services for DeFi users while promoting community innovation.
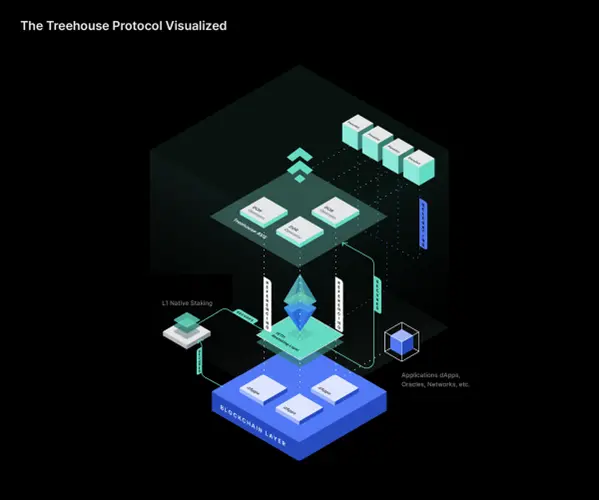
Treehouse Architecture
- tAsset is a liquidity staking token (LST) designed to provide real yields beyond the on-chain risk-free rate through interest rate arbitrage.
- Decentralized Offered Rate (DOR) is a reference rate setting consensus mechanism that incentivizes stakeholders in the market to provide accurate interest rate data and forecasts.
- Operators are initiators of DOR data sources, helping to maintain the integrity and success of existing DORs. Treehouse will act as the first operator, collaborating with select panel members to launch the first DOR, the Treehouse Ethereum Staking Rate (TESR) curve.
- Panelists are entities equipped with proprietary models and Treehouse DOR software that provide interest rate data or forecasts. Currently, only whitelisted panel members, who have undergone strict scrutiny, are allowed to perform this role to ensure the initial integrity of the Treehouse protocol.
- Referencers are entities that directly integrate DOR data sources into their own interest rate-related services or products, using DOR to price or settle financial instruments.
- Delegators are participants who delegate tAssets to panel members to fulfill DOR responsibilities on their behalf. Delegators still fully own their assets but grant proxy rights to their selected panel members.
Technical Analysis
- tETH
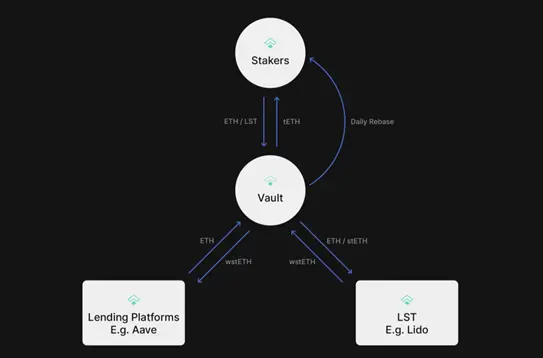
tETH is a liquidity staking token (LST) designed to consolidate the fragmented on-chain Ethereum interest rate market. Users holding tETH earn real yields exceeding Ethereum Proof of Stake (PoS) rewards through interest rate arbitrage while still being able to use tETH for DeFi activities. tETH also provides foundational support for the implementation of the Decentralized Offered Rate (DOR).
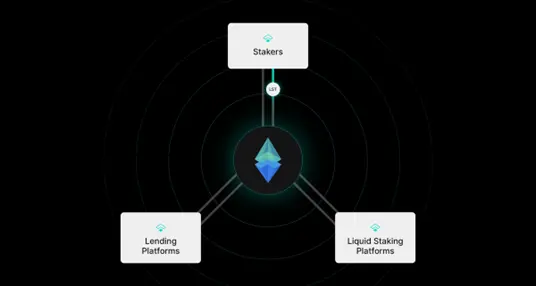
Ensuring On-Chain Rate Efficiency: tETH holders actively influence the on-chain market by aggregating rates to Ethereum's "risk-free" rate.
Democratizing Fixed Income Arbitrage Opportunities: tETH enables users to participate in arbitrage strategies typically accessible only to institutional investors.
Supporting Decentralized Offered Rate (DOR): By holding tETH, users help enhance the cryptoeconomic security of DOR.
- Yield Optimization
tETH = LST + Market Efficiency Yield + Points
The yield generated by tETH comes from liquid staking tokens (LST) and is further enhanced through interest rate arbitrage opportunities within lending protocols.
How It Works:
- Base Yield
tETH uses LST as the underlying asset, which itself generates yield. This yield is further enhanced through interest rate arbitrage strategies within lending protocols. - Yield Enhancement through Lending
Based on security mechanisms and profitability assessments, the LST supporting tETH may be borrowed against as collateral to obtain ETH. The borrowed ETH is converted into LST to earn additional Ethereum PoS rewards, effectively amplifying the overall yield of tETH while helping to aggregate fragmented rates. - Additional Rewards
In addition to base yield, tETH holders can also earn rewards from point activities.
Token Accounting
- Measurement Unit
tETH is measured in wstETH. - Value Adjustment
tETH is a value-accumulating receipt token representing the user's share of the underlying assets in the tETH pool. - Yield Distribution
The yield generated by assets in the tETH pool is distributed to tETH holders once daily. This yield distribution is reflected in the tETH:wstETH exchange rate, which is updated regularly on the "Dashboard" page. - Synchronization Mechanism
The frequency of exchange rate updates in the dApp is deliberately limited to ensure synchronization with the rebalancing schedule of the underlying liquid staking tokens (LST). This synchronization helps maintain the accuracy of the tETH exchange rate relative to the value of its underlying assets. - Balance Maintenance
Unless new deposits or redemptions are made, the user's tETH balance will remain unchanged. This stability ensures that the value of tETH accurately reflects the underlying assets in the pool and the yield generated over time.
- Measurement Unit
Deployment Process
Users receive tETH proportional to their share in the overall tETH pool by depositing ETH or liquid staking tokens (LST), representing their stake in the pool. The protocol then executes a series of rebalancing operations to achieve real yields through arbitrage, including:
- Conversion and Wrapping
Native ETH deposits are automatically converted into LST. LST deposits can also be wrapped for further yield optimization strategies. - Leverage Operations on DeFi Platforms
Utilizing the protocol's security mechanisms and profitability assessments, LST can be used as collateral to borrow ETH on lending DeFi platforms. The borrowed ETH is converted into LST, further enhancing the yield of tETH through additional LST exposure. - Interest Rate Convergence
tETH holders earn yield enhancement by helping to converge fragmented ETH interest rate markets to Ethereum's "risk-free" rate. - Re-staking and Decentralized Offered Rate (DOR)
In the future, the underlying assets of tETH will enable re-staking to ensure DOR, allowing users the potential to earn more rewards. - Redemption Process
On the Treehouse dApp, the redemption of tETH will occur through a liquidity pool, involving on-chain exchanges to wstETH via the tETH/wstETH curve liquidity pool.
Treehouse will facilitate redemptions exceeding the Redemption Band value.
The Redemption Band refers to redemption operations conducted between 0 wstETH and 200 wstETH.
To maintain liquidity and reduce slippage in the tETH/wstETH curve liquidity pool, if the amount redeemed exceeds the redemption bandwidth, users can choose to interact directly with Treehouse. Through this process, users can burn their tETH and receive corresponding shares of the underlying assets at the current tETH:wstETH exchange rate displayed on the dApp.
However, such redemption operations will be subject to a withdrawal period of approximately 7 days. This period allows the protocol sufficient time to convert the underlying LST assets back to native ETH to fulfill the redemption request.
- Protocol-Owned Peg Protection Mechanism (PPP)
The tETH:wstETH exchange rate on the Treehouse dApp is designed to accurately reflect the intrinsic value comparison between tETH assets and wstETH. Currently, many protocols allow users to directly exchange their LST or LRT for underlying assets but impose withdrawal periods. This practice can pose issues during periods of high market volatility, as protocols rely solely on market forces to determine the price of LST or LRT, even when underlying assets are sufficient.
The Unique Role of tETH Asset Redemption
Through the protocol-owned Peg Protection Mechanism (PPP), Treehouse assumes exclusive responsibility for converting tETH into its underlying assets.
If tETH:wstETH decouples in the tETH/wstETH curve liquidity pool, causing the intrinsic value of tETH to exceed its market price, Treehouse will intervene and use the Treehouse insurance fund to purchase tETH from the open market for immediate redemption. This mechanism provides several benefits to tETH holders:
- Fair Intervention: Especially during periods of high market volatility, Treehouse can fairly fulfill this role. By acquiring tETH from the open market, Treehouse demonstrates confidence in the value of the underlying assets.
- Yield Redistribution: In the event of a decoupling, profits typically captured by market participants through arbitrage will instead benefit existing tETH holders, the protocol, and enhance liquidity (see below for yield distribution).
Yield Distribution
Profits generated from the operations of the protocol-owned Peg Protection Mechanism (PPP) will be distributed as follows to support various aspects of the protocol ecosystem:
- 25% allocated to the Treehouse insurance fund;
- 25% allocated to the tETH/wstETH curve liquidity pool;
- 25% allocated to existing tETH holders as arbitrage profits;
- 25% allocated to the Treehouse treasury.
- Profitability Assessment
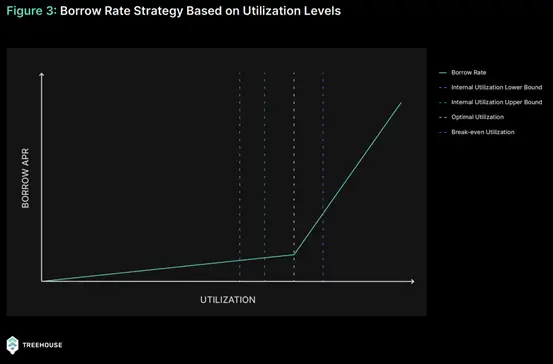
Utilization Rate
Treehouse will implement an internal rate to manage the utilization rate of borrowed ETH. This can ensure sustainable borrowing costs and address challenges that may arise from fluctuations in borrowing demand on lending platforms.
Internal Utilization Rate - Upper Limit
This rate serves as a preventive threshold aimed at preemptively addressing situations where the utilization rate of the ETH treasury on lending platforms approaches levels that could lead to unfavorable borrowing costs. When the actual utilization rate on the lending platform exceeds the upper limit of the protocol's internal utilization rate, Treehouse will rebalance to mitigate potential impacts, thereby protecting the strategy of tETH.
Loan Repayment Strategy
The protocol continuously monitors the utilization rate of the ETH treasury. For example, in Aave, when the internal utilization rate upper limit (>89%) is breached and remains above that threshold for more than two days, the system triggers an intervention. This approach aims to distinguish between temporary fluctuations and stable trends, the latter of which requires intervention from the protocol.
Treehouse will continuously calculate the amount of LST that needs to be converted into ETH to maintain the utilization rate within the designated range. Nevertheless, if the utilization rate further increases during the LST to ETH conversion window (e.g., from 90% to 91%), the protocol will recalculate and prepare additional LST for conversion. This ensures that the repayment amount always adjusts the utilization rate, moving towards the internal optimal level.
Summary
Treehouse offers numerous advantages in DeFi and yield optimization through its innovative tETH, DOR, and PPP mechanisms, particularly in interest rate arbitrage and market stability. However, its complexity and reliance on DeFi platforms may pose challenges for some users. Overall, Treehouse is suitable for those who can understand its mechanisms and are willing to engage in complex operations, while it may not be entirely suitable for users seeking straightforward operations and quick liquidity.
III. Industry Data Analysis
1. Market Overall Performance
1.1 Spot BTC & ETH ETF
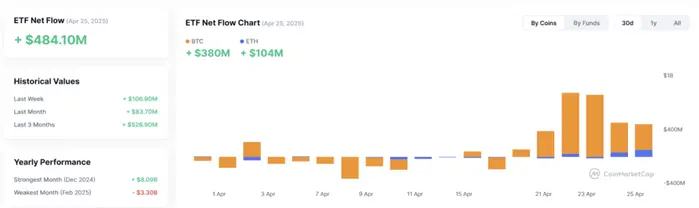
(On November 1, Eastern Time) Ethereum spot ETF had a total net outflow of $10,925,600.
1.2 Spot BTC vs ETH Price Trends
BTC
Analysis
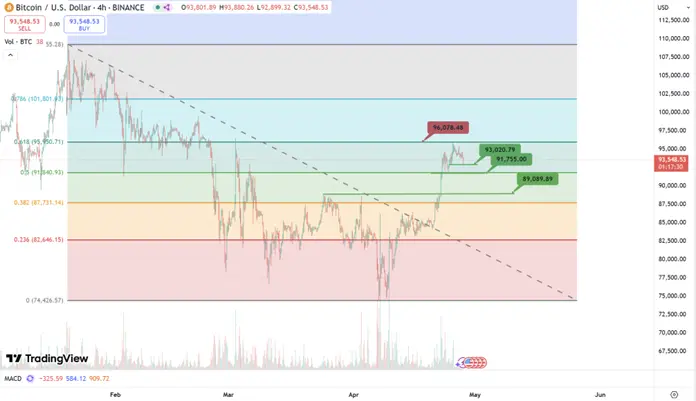
Last week, BTC continued to rebound and broke through the two important resistance zones of $89,000 and $91,000, but faced resistance around the $96,000 price range. It is evident from the chart that $96,000 coincides with the Fibonacci resistance line, indicating strong selling pressure near this price level. Therefore, for users, the short-term support to watch can be seen at $93,000, but given the lack of high-density chips near this support, the probability of a breakdown is relatively high. Focus should be on the second strong support at $91,700; if it holds, continue to monitor the strength of the next rebound. If there is a significant downward volume, it could directly target the strong support range of $87,700 to $89,000. Unless there is significant negative fundamental news this week, the aforementioned area can be considered a solid short-term bottom.
ETH
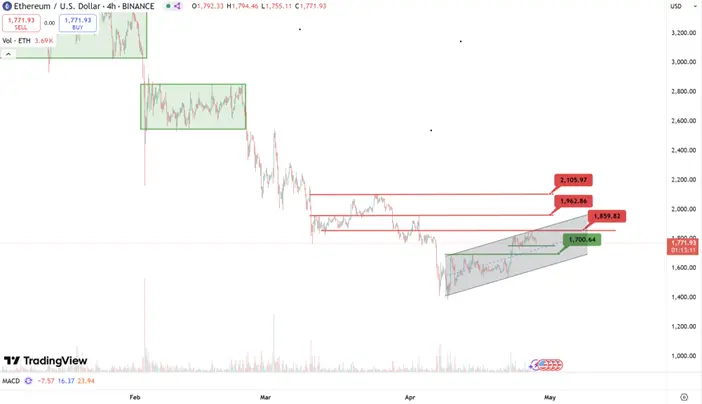
Analysis
For ETH, the rebound remains challenging due to facing multiple strong resistances above. The most recent first-line resistance can be observed at $1,860, followed by the second-line resistance at $1,960 and the third-line resistance at $2,100. Given the current trend of uncertainty in fundamentals, a rebound above $2,100 is temporarily difficult this week or even next week.
As for support, the short-term support can be observed at $1,760; if it breaks, it could directly target the strong support at the neckline of $1,700. If a pullback stabilizes near this area, a second rebound can be expected, testing the range of $1,860 to $1,960.
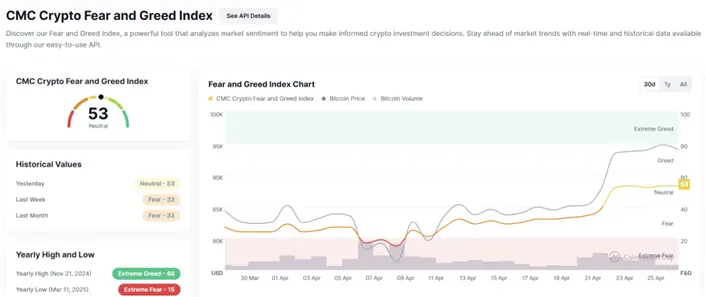
1.3 Fear & Greed Index
2. Public Chain Data
2.1 BTC Layer 2 Summary
Analysis
The Nakamoto upgrade of Stacks officially launched on April 22, aiming to address network congestion issues and decouple Stacks' block production from the Bitcoin main chain. This upgrade will introduce a new block production mechanism and update its unique transfer consensus algorithm. The new block "signers" will begin to go online to validate "term" transactions. This process will undergo "practice" before the upgrade is fully activated.
Stacks aims to introduce greater utility, such as smart contracts and other decentralized finance (DeFi) features, leveraging Bitcoin as the base layer. To this end, Stacks has also launched sBTC, an asset pegged 1:1 to Bitcoin, allowing users to bridge BTC into the Stacks ecosystem.
Before the Nakamoto upgrade, the deployment of smart contracts on Stacks reached a new historical high, exceeding 1,400 deployments per month, demonstrating developers' confidence in the Stacks ecosystem. Additionally, Stacks' native token STX rose over 16% in the past 24 hours, entering the top 25 by market capitalization, reflecting positive market response to the upgrade.
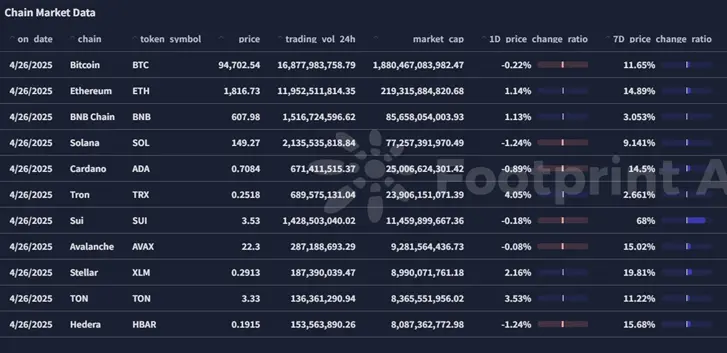
2.2 EVM & Non-EVM Layer 1 Summary
Analysis
EVM Layer 1 Blockchain Dynamics
- EOS EVM Officially Launched
The EOS Network Foundation successfully launched its EVM mainnet on April 14, claiming its performance as the "fastest EVM," capable of processing over 800 swaps per second, three times faster than Solana and BNB, and 25 times faster than Avalanche.
- Telos Launches ZK-EVM Roadmap
The Telos Foundation announced a full integration of SNARKtor by 2025, adopting hardware acceleration technology, using TLOS as the native token, and conducting Rollup on Ethereum.
- Polkadot Supports EVM and Solidity
Polkadot's 2025 roadmap was released, planning to support EVM and Solidity, adopting a multi-core architecture to enhance scalability, and improving interoperability through the XCM v5 upgrade for cross-chain messaging.
Non-EVM Layer 1 Blockchain Dynamics
- Solana Increases Transaction Throughput
Solana's non-voting transaction throughput has continued to grow over the past year, with an expected average throughput exceeding 5,000 transactions per second by 2025, with peak rates potentially higher.
- N1 Blockchain Set to Launch
The N1 blockchain has confirmed support from original investors and plans to launch its mainnet in the coming months. The platform supports multiple programming languages and aims to provide a decentralized application platform with ultra-low latency and high throughput.
- W Chain Launches Layer 1 Mainnet Soft Launch
W Chain has initiated a soft launch of its Layer 1 mainnet in Singapore, with plans for a full launch in March 2025. The platform aims to become a central hub for digital currencies, ensuring seamless interoperability to meet evolving business needs.
2.3 EVM Layer 2 Summary
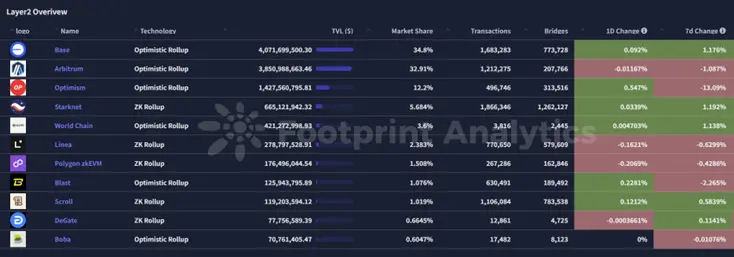
Analysis
Ethereum Core Layer: EVM Evolution Proposal
On April 21, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin proposed replacing the current EVM with a new execution environment based on the open-source RISC-V instruction set. He believes this could "greatly enhance the efficiency of Ethereum's execution layer," reducing interpretation overhead and simplifying the execution environment.
He simultaneously released a phased plan to gradually phase out the existing EVM while maintaining compatibility with Solidity and Vyper, supporting faster zero-knowledge proof generation, and reducing resource requirements for Layer 2 Rollups.
zkSync: Security Incident and Recovery
On April 22, the zkSync security team disclosed that attackers exploited a vulnerability in the project's airdrop smart contract, minting approximately 111 million ZK tokens, resulting in a loss of about $5 million in protocol funds.
By April 24, the hacker accepted a 10% bounty clause during the "safe harbor" period, returning nearly $5 million of the stolen assets, marking a near-complete resolution of the incident and demonstrating the effectiveness of zkSync's bounty handling process through the security committee.
Polygon Agglayer: Value Accumulation and Breakout Incubation Program
On April 22, Polygon released the report "POL Value Accumulation #1," showcasing how POL staking powers both the Polygon PoS chain and Agglayer, allowing stakers to earn cross-chain rewards and strengthening liquidity incentive mechanisms.
Subsequently, on April 24, Polygon Labs officially launched the Agglayer Breakout Program, a supported incubator project by the Polygon Foundation, providing funding and technical support to participants, and distributing 5-15% of project native token airdrops to POL stakers to support high-potential on-chain projects and further align ecosystem growth with token holders' interests.
Arbitrum: Exits NVIDIA AI Accelerator Program
On April 27, the Arbitrum Foundation announced its exit from the NVIDIA Ignition AI Accelerator Program due to branding usage disputes. This reflects certain frictions between blockchain projects and traditional tech companies in collaboration.
Previous reports indicated that Arbitrum had completely withdrawn from NVIDIA's AI project, raising market concerns about Arbitrum's external cooperation strategy and its impact on ARB token sentiment.
Optimism: Governance and 14th Upgrade Proposal
The Optimism Collective is preparing to execute the 14th On-Chain Upgrade (Upgrade #14), which involves the deployment of the Isthmus L1 contract and MT-Cannon, scheduled to be completed through a multi-signature ceremony on April 25, 2025.
If approved, this proposal will be an important step in Optimism's multi-chain governance blueprint, laying the foundation for the evolving Superchain architecture and improving the Sequencer contract and core foundational modules.
IV. Macroeconomic Data Review and Key Data Release Nodes for Next Week
In April 2025, the Consumer Confidence Index (University of Michigan) final value was 52.2, a decrease of 8% from March's 57.0, marking the fourth consecutive month of decline, reflecting growing consumer concerns about the economic outlook. As of the week ending April 19, the number of initial jobless claims in the U.S. was recorded at 222,000, in line with market expectations of 222,000, up from the previous value of 215,000, indicating that the labor market remains resilient overall.
This week (April 28 - May 2), important macroeconomic data points include:
April 30: U.S. Q1 GDP preliminary value, U.S. March Core PCE Price Index year-on-year
May 1: Bank of Japan interest rate decision, U.S. April ISM Manufacturing PMI
V. Regulatory Policies
Russia
Launching a cryptocurrency exchange for elite investors: Russia will launch a state-supported cryptocurrency exchange for elite investors to promote cryptocurrency asset trading and support market development in a controlled environment.
South Korea
Actively participating in stablecoin regulation formulation: The Bank of Korea announced that it will actively participate in the formulation of regulations related to stablecoins to mitigate risks to monetary and financial stability, protect investors, and ensure financial stability.
Panama
Supporting cryptocurrency payments for municipal fees: Panama City announced that it will accept cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), USDC, and USDT for municipal fees (such as taxes, bus tickets, etc.), which will be officially enabled after technical integration is completed, promoting the application of cryptocurrencies.
Puerto Rico (U.S. territory)
Tax bill targeting cryptocurrency tax evasion: U.S. lawmakers have proposed the "Puerto Rico Digital Assets Fair Taxation Act," aimed at strengthening the regulation of cryptocurrency taxation and curbing the use of Puerto Rico as a tax haven for cryptocurrencies.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




