Written by: FinTax Owen
On August 7, Eastern Time, U.S. President Trump signed an executive order titled "Democratizing Access to Alternative Assets for 401(k) Investors" at the White House, directing the Treasury Department, Labor Department, and Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to initiate rule changes to include cryptocurrencies, real estate, private equity, and other "Alternative Assets" in the scope of 401(k) pension investments. This news struck like a bolt from the blue, quickly shaking the global financial markets—it not only has the potential to unlock a retirement fund pool of up to $8.7 trillion but is also seen as a key step for crypto assets moving from the fringes to the mainstream financial system.
Although the White House claims this move aims to "expand ordinary investors' access to diversified assets," a core question arises: does this open a new chapter for wealth appreciation in Americans' retirement futures, or is it a reckless national gamble?
1. The 401(k) Plan: The Cornerstone of the U.S. Retirement System
To understand the significance of this move, one must first grasp the weight of the 401(k) in the U.S. retirement security system. The U.S. pension system consists of three main pillars: the first pillar is the government-operated mandatory Social Security, which provides basic pensions to retirees monthly; the second pillar is employer-sponsored retirement savings plans, with the 401(k) being the most common, where employee pre-tax contributions and employer matching contributions accumulate funds, with limited investment options provided by the employer; the third pillar is Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs), which individuals voluntarily open, allowing for a broader range of investments, with some types of IRAs already permitting investments in cryptocurrencies.
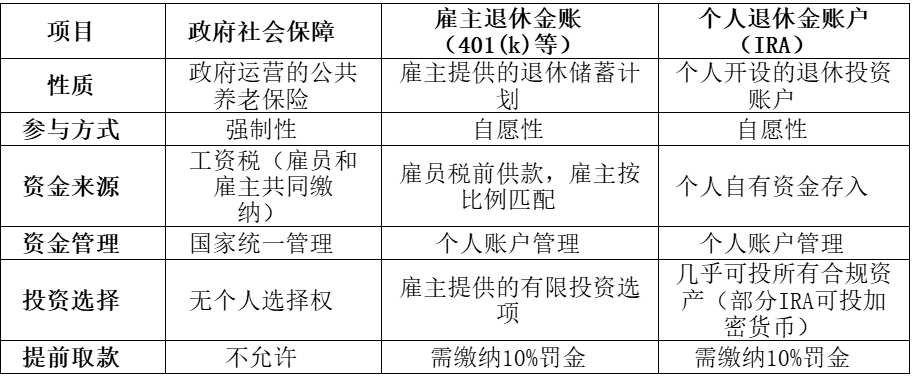
In the second pillar, the 401(k) is the most representative employer pension plan, with most employers supporting employee participation and accumulating funds through payroll deductions and matching contributions, achieving compound growth. Besides the 401(k), there are also 403(b) plans for public education institutions and some non-profit organization employees. As of the first quarter of 2025, the U.S. 401(k) market size has exceeded $8.7 trillion, serving as the core guarantee for the retirement lives of tens of millions of American families.
Compared to the mandatory government Social Security, the main difference between IRAs and 401(k)s as voluntary savings plans lies in investment autonomy: both types of accounts enjoy tax-deferred or tax-exempt treatment on investment earnings, but IRAs have a wider range of investment options, allowing direct holdings of various assets (including cryptocurrencies in some types); the investment scope of 401(k)s has long been restricted, with most funds directed towards low-risk products packaged by employer-selected asset management firms (such as mutual funds, bonds, etc.), rather than directly holding spot assets. Trump's reform specifically targets the investment restrictions of the 401(k), creating institutional conditions for high-volatility assets like cryptocurrencies to enter mainstream retirement investment portfolios.
2. From Prohibition to Release: A Shift in Regulatory Philosophy and Market Reality
For a long time, U.S. 401(k) plans strictly excluded high-risk assets like cryptocurrencies, primarily to protect the safety and stability of retirement savings. High volatility inherently contradicts the goal of steady pension growth, and regulators worry that ordinary investors lack the capacity to bear risks and make professional judgments; any severe market fluctuations would directly impact their retirement security. Additionally, financial institutions face extra costs and risks in custody, valuation, and compliance, which has led to a long-term tightening of policies.
The recent executive order signed by the Trump administration to relax these restrictions is not a spur-of-the-moment decision but rather the result of multiple overlapping factors: on one hand, it responds to the public's demand for high-yield channels in an environment of low interest rates and high inflation, fulfilling the campaign promise of "de-regulation"; on the other hand, it is a realization of political capital— the crypto industry supported Trump's campaign, and his family has investments in the crypto space; more fundamentally, the crypto market is no longer a fringe experiment but is gradually being viewed as a mainstream asset, driven by institutional investment, ETF approvals, and accelerated global compliance processes.
It is noteworthy that this policy is not only aimed at cryptocurrencies but at a broader range of "Alternative Assets," which officially includes private equity, real estate, commodities, and digital currencies. This means the policy's intent is to comprehensively relax investment restrictions to expand the options available to individual investors, catering to society's enthusiasm for high-yield assets.
One could say that this shift from "prohibition" to "release" reflects both a loosening of U.S. regulatory philosophy and a reshaping of the capital market landscape and political ecology.
3. Far-Reaching Impact: A Gamble May Begin
Including cryptocurrencies and other Alternative Assets in the 401(k) investment scope means the U.S. government is embarking on an unprecedented high-risk experiment in its retirement system. If pension funds enter the crypto market on a large scale, it will not only significantly enhance market liquidity and price stability but also create a binding of interests between the government and the crypto market: when the retirement savings of millions of Americans are linked to crypto assets, the government will have to consider how to maintain market stability in its policy-making. This deep binding could greatly accelerate the compliance process for cryptocurrencies, compelling regulators to introduce clearer and more comprehensive regulations, thereby enhancing the overall market's maturity, transparency, and credibility, attracting more mainstream institutions and individual investors to participate.
At the same time, a deeper political consideration is that this binding of interests may even grant crypto-friendly policies continuity across party changes. It elevates the protection of cryptocurrencies from being a personal or partisan action of Trump to a "forced choice" by the government to protect citizens' assets—any measures that weaken the crypto market could be perceived by voters as "messing with retirement funds," potentially triggering political backlash.

(When your money is on the chain, do they still dare to say "no"? Image source: created by the author)
However, this gamble is fraught with concerns. The crypto market is known for its price volatility, with cyclical bull and bear transitions often accompanied by significant asset shrinkage. More critically, structural issues such as fraud, money laundering, and illegal financing still lurk in the market, with some assets lacking transparency and security incidents on trading platforms occurring frequently. If pension funds suffer severe losses in such an environment, the impact will not only be reflected on the balance sheets but will also trigger a trust crisis at the societal level—directly shaking the future security of millions of American families, and political pressure will quickly transmit to the White House and Congress. At that point, the government may be forced to intervene financially to stabilize the market, creating a dual binding of policy and market.
In other words, this move could either propel cryptocurrencies into an era of institutionalization and comprehensive regulation or, in the event of uncontrolled risks, backfire on policymakers, turning this "bold attempt" into a period of reflection or even criticism in history.
4. Another Perspective: The Fiscal Game Behind Tax Deferral
For a long time, the U.S. 401(k) plan has had two tax arrangement models: the traditional model adopts "pre-tax contributions, taxed as ordinary income upon withdrawal," while the Roth model is "after-tax contributions, tax-free withdrawals when qualified"—regardless of the model, both have the effect of delaying taxation on investment earnings, which is also the long-term appeal of these accounts. Therefore, including crypto assets in the 401(k) investment scope does not change these basic tax rules but means that this high-volatility asset is entering the compliant "shell" of tax deferral or exemption for the first time, allowing investors to enjoy the tax advantages of the account while betting on the long-term growth of the crypto market.
Within this framework, the fiscal impact resembles a temporal tax game. For investors choosing the "traditional account," current taxable income decreases, leading to a short-term reduction in government tax revenue, but in the future, during the withdrawal phase, it will be counted as taxable income all at once, which is a typical "letting water to raise fish" strategy—trading today's benefits for a larger tax base decades later. If crypto assets succeed in the long term, the returns realized at retirement could far exceed current levels, thus bringing higher tax revenue to the government; conversely, if the market is sluggish or the policy environment shifts, the short-term tax sacrifice could lead to long-term fiscal shortfalls. This is also the greatest risk and uncertainty of this move in terms of fiscal and tax implications.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




