Author: Lacie Zhang, Bitget Wallet Researcher
In the Solana ecosystem, known for its high speed and low cost, we observe a brand new trend rapidly emerging: a group of "invisible" giants—Proprietary Automated Market Makers (referred to as "Proprietary AMM")—that lack official websites and do not engage in publicity. They are reshaping the trading landscape in a more professional and efficient manner, becoming a new engine driving on-chain capital flow. The Bitget Wallet Research Institute will take you into this silent revolution in this article, analyzing the rise logic and industry impact of Proprietary AMMs.
Invisible Giants: The Operational Logic of Proprietary AMMs

Image Source: Helius
According to statistics from Blockworks, in August 2025 alone, Proprietary AMMs processed approximately $47 billion in spot trading on Solana, accounting for 31% of the total trading volume on Solana's DEX. This trend is even more astonishing for high liquidity trading pairs like SOL-stablecoin—since May 2025, Proprietary AMMs have consistently captured over 60% of the SOL-stablecoin trading pair each month, with even higher shares in trading pairs between stablecoins.
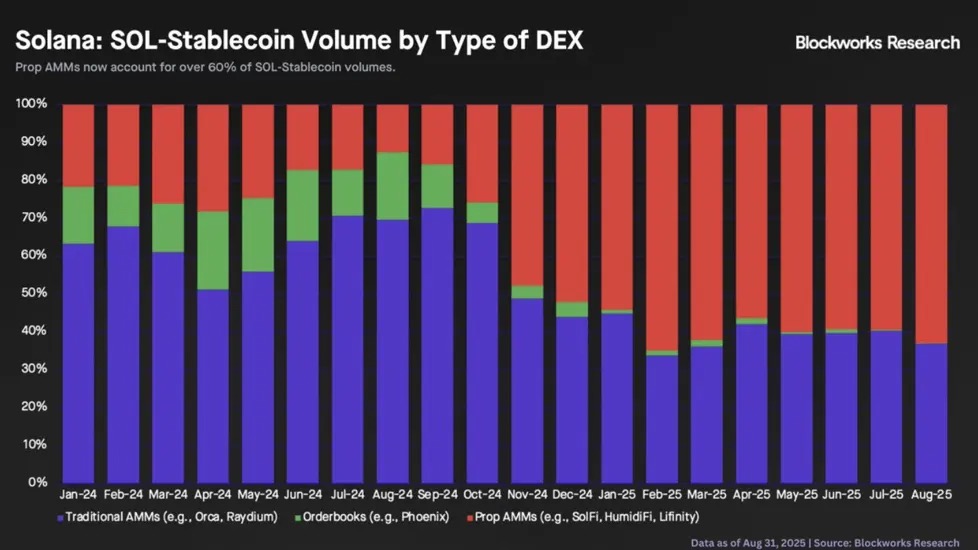
Data Source: Blockworks Research
To understand this transformation, it is essential to clarify the definition of Proprietary AMMs. Simply put, they are a type of on-chain market maker operated by a few professional teams using their own funds, and they do not open liquidity access to ordinary users. This sharply contrasts with traditional AMMs like Uniswap, which allow anyone to become a liquidity provider (LP) and earn fees, achieving "crowdsourced" liquidity; whereas Proprietary AMMs return the power of market making to professional teams, focusing on extreme efficiency and risk control, with the following characteristics in their specific operational model:
- Invisible Access: Most Proprietary AMMs do not have user-facing website access, and ordinary users cannot interact with them directly.
- Algorithm Secrecy: Market making algorithms and parameters are kept strictly confidential, with significantly lower transparency than traditional AMMs.
- Reliance on Aggregators: The way they obtain trading orders is by directly connecting to aggregators (like Jupiter), matching user trading requests to the platform with the best quotes through the aggregator.
Comparison Table of Proprietary AMMs and Traditional AMMs
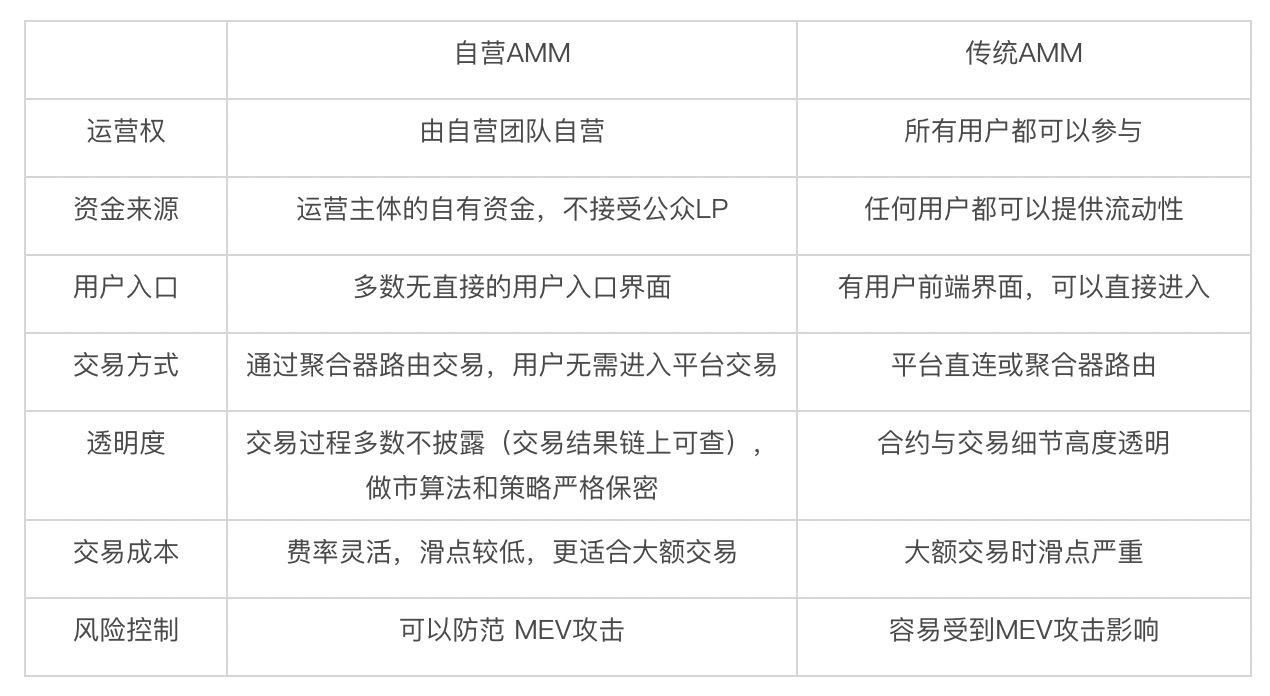
Note: A few Proprietary AMMs (like Lifinity) open user front ends, but their liquidity is still primarily based on the team's own funds, and the execution of trades is still completed through routing to aggregators.
This business model is built on pure execution efficiency rather than branding or community. Traditional DeFi projects need to invest heavily in marketing and community building to attract users and liquidity. In contrast, Proprietary AMMs convert all their "marketing budget" into small price advantages for users in trades, ultimately capturing massive trading volumes. This also indirectly confirms that the DeFi market is maturing, with market participants increasingly resembling rational economic agents—following the principle of "optimal price wins"—rather than merely idealists of "decentralization above all."
Concept Clarification: Is it "Dark Pool" or "Proactive Market Maker"?
With the rise of Proprietary AMMs, related terms such as "Dark AMM" and "Proactive Market Maker (PMM)" have also frequently appeared, making it crucial to clarify their differences. In fact, these three concepts are not mutually exclusive but differ in their definitional emphasis.
- Dark AMM: The core is information concealment. It describes a trading method that hides order intentions during the matching phase, aiming to reduce information leakage and price impact.
- Proactive Market Maker: The core is active pricing. It refers to dynamically adjusting quotes through the introduction of oracle services and active inventory management to pursue higher capital efficiency.
- Proprietary AMM: The core is in the ownership of funds and the operating entity. It defines a model where the operating team uses its own funds for market making.
Definition Clarification Table of the Three AMM Concepts
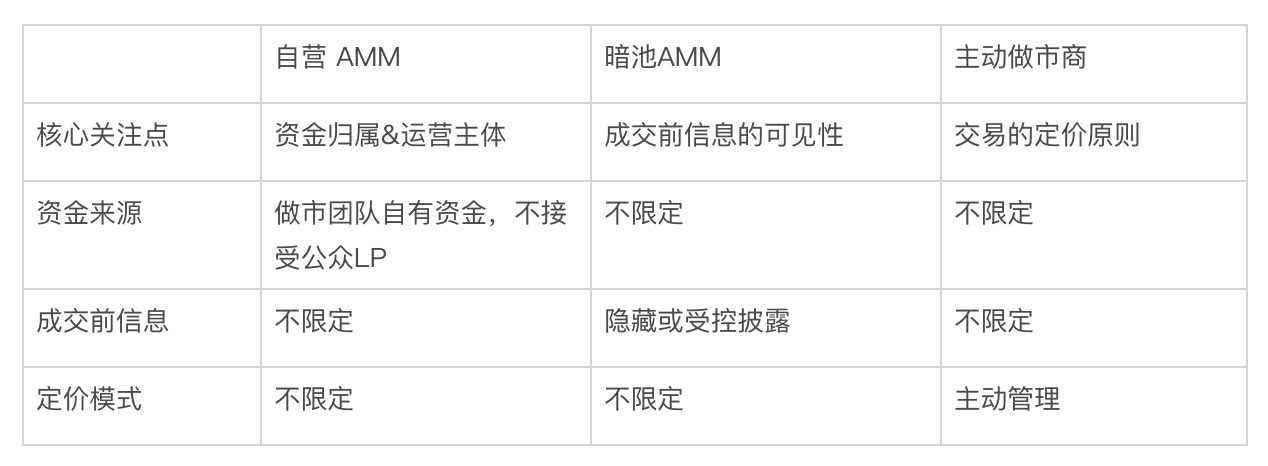
After clarifying the definitions, it is not difficult to see that these three concepts do not exclude each other but describe different dimensions of the same financial entity. In fact, a typical Proprietary AMM, in pursuit of extreme efficiency and safety, usually adopts a "dark pool" trading method, and its pricing strategy (though not publicly disclosed) is likely also "proactive."
Therefore, although mainstream media sometimes mix these terms, the term "Proprietary AMM" fundamentally addresses the core issue: Who controls the funds, and who bears the risks? Compared to the "Dark AMM" or "Proactive Market Maker" that describe technical features, "Proprietary AMM" more accurately reveals the essence of this new force from the perspective of business model and operating entity.
Efficiency Revolution: Why Has Solana Become the Ultimate Testing Ground?
The rise of Proprietary AMMs stems from their precise targeting of the core pain points of traditional AMMs. The passive design of traditional liquidity pools inevitably leads to high slippage when facing large trades, and they have long suffered from impermanent loss and MEV attacks (such as sandwich attacks). Proprietary AMMs, through the meticulous management of professional teams and proactive pricing strategies, have almost perfectly solved these issues. They can provide users with narrower spreads, lower slippage, and more stable trading results, especially in large exchanges, where the experience is now nearly indistinguishable from that of top centralized exchanges.
The realization of all this is closely tied to Solana's unique blockchain architecture. First, Solana's high throughput and extremely low transaction fees make this "proactive" model, which requires frequent quote updates, economically viable. Second, the dominant position of aggregators (especially Jupiter) in the Solana ecosystem creates a "one-stop distribution channel" for these market makers. They do not need to establish their own brand, website, or user community, allowing them to focus all resources on their only core competitiveness—execution and pricing—this extreme specialization greatly simplifies their business model and reduces operational costs.
It can be said that Proprietary AMMs did not simply choose Solana; they are inherently a symbiotic and native market structure with Solana, representing a perfect example of the co-evolution between the high-performance architecture of the underlying public chain and the business model of upper-layer financial applications.
Future Outlook: The Wave of Specialization and the Ghost of "Centralization"
The rise of Proprietary AMMs indicates that on-chain markets are developing towards a more specialized and polarized direction, with a clear "dual-track market" gradually forming.
- Mature Asset Market: High liquidity trading pairs like SOL-stablecoin will increasingly be dominated by Proprietary AMMs that can provide extreme spreads.
- Long Tail Asset Market: Newly launched Meme coins and others will continue to rely on traditional AMMs like Raydium, which do not require permission, for early price discovery and liquidity guidance.
This trend is a victory of mechanism efficiency, marking a profound wave of specialization in on-chain market making. The market structure is shifting from open liquidity crowdsourcing to specialized market making by a few teams, significantly improving the execution efficiency and safety of on-chain trading, setting a new benchmark for the industry.
However, the other side of the coin is the renewed concern about the ghost of "centralization." While users enjoy better execution quality, they inadvertently make a trade-off and sacrifice: exchanging the core principles of DeFi—high transparency, permissionless access, and decentralization—for extreme efficiency. When most order flows are directed towards a few anonymous "black boxes," although trades are still settled on-chain, the opacity in the process undoubtedly introduces new trust risks and undermines the auditable foundation upon which DeFi is built.
From a broader perspective, the dominance of Proprietary AMMs is reshaping and solidifying Solana's ecological positioning. It further reinforces Solana's image as the "Blockchain Nasdaq"—a venue tailored for high-performance, institutional-grade financial applications, with execution speed and capital efficiency as the highest criteria. This gives Solana a differentiated advantage in the public chain competition, making it the preferred deployment platform for innovative protocols seeking both CEX-like performance and DeFi core.
Conclusion
The rapid rise of Proprietary AMMs on Solana is not coincidental but a logical and even inevitable evolution in the DeFi market's pursuit of extreme capital efficiency. Although it has sparked important discussions about the future of decentralization, this proactive and efficient liquidity supply model has already elevated industry performance to new heights. Regardless of how the final landscape evolves, this silent revolution has already written the prologue for the next chapter of on-chain finance.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




