Stalemate! Stalemate? Stalemate!! Why does the stalemate cause $BTC to drop, and when will the stalemate end?? What have been the outcomes of past stalemates in history??
The market's game has also begun to shift towards the stalemate, especially as this week's decline is largely related to the stalemate. With the Senate's 14th rejection of the House version of the "Continuing Resolution" (CR), the U.S. government's stalemate has now set a new historical record. The longest previous stalemate lasted 35 days during Trump's first term, and now it has reached 36 days, with no clear expectations on when it will end.
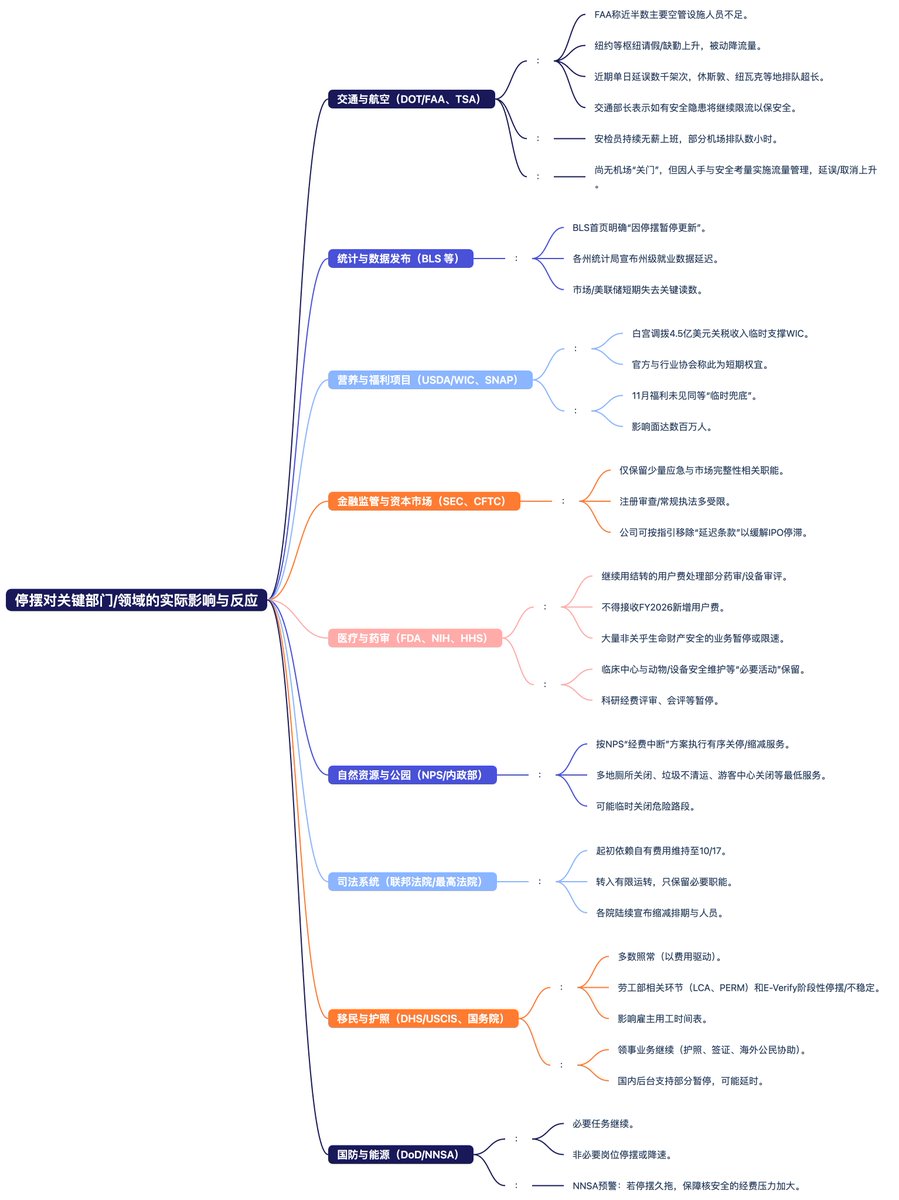
The longer the stalemate lasts, the more apparent the fiscal vacuum effect becomes. Government salaries and contract payments are delayed, and cash flow is transmitted from residents and businesses to the market level. Non-essential consumption is usually the first to feel the pressure, while the uncertainty of official data releases raises volatility premiums. The market shifts from data-driven to expectation-driven, with more frequent emotional fluctuations throughout the day.
The direct impact is that food stamp relief will only continue after Trump announces the government reopening, which may increase social unrest. Data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics will only be released after the government stalemate ends. The Department of Transportation warns that if the stalemate continues and controllers remain in short supply, some airspace may be forced to close or traffic may be restricted next week. For the market, the impact is gradually accumulating in a pessimistic direction. The interruption of macro data means that the Federal Reserve and the market lack new economic information, relying solely on emotions and projections for pricing, leading to increased short-term volatility.
The combination of fiscal stalemate and pressure on people's livelihoods will weaken consumption expectations, posing potential pressure on the service industry and retail chain. Some regulatory agencies have entered a minimum operational mode, slowing down the pace of new issuances and approvals. Front-end trading in the capital market remains normal, but back-end reviews are restricted. More critically, the longer the stalemate lasts, the more pronounced the marginal tightening effect on financial conditions becomes. Investors will worry about fiscal execution risks and policy uncertainties, leading to increased cash demand and short-term benefits for safe-haven assets (short-term bonds, U.S. dollars), while the sentiment for growth assets and high-beta sectors will be more fragile.
A prolonged stalemate is essentially a form of short-term fiscal tightening, prompting the market to bet on whether monetary policy will become more dovish, speculating on expectations of interest rate declines and liquidity replenishment. However, Powell's statements are completely contrary to current market expectations, leading to investor pessimism. This is because the Treasury often speeds up bond issuance and raises the Treasury General Account (TGA) to fill the fiscal vacuum, extracting funds from overnight repos or the banking system, which can affect price changes in risk markets.
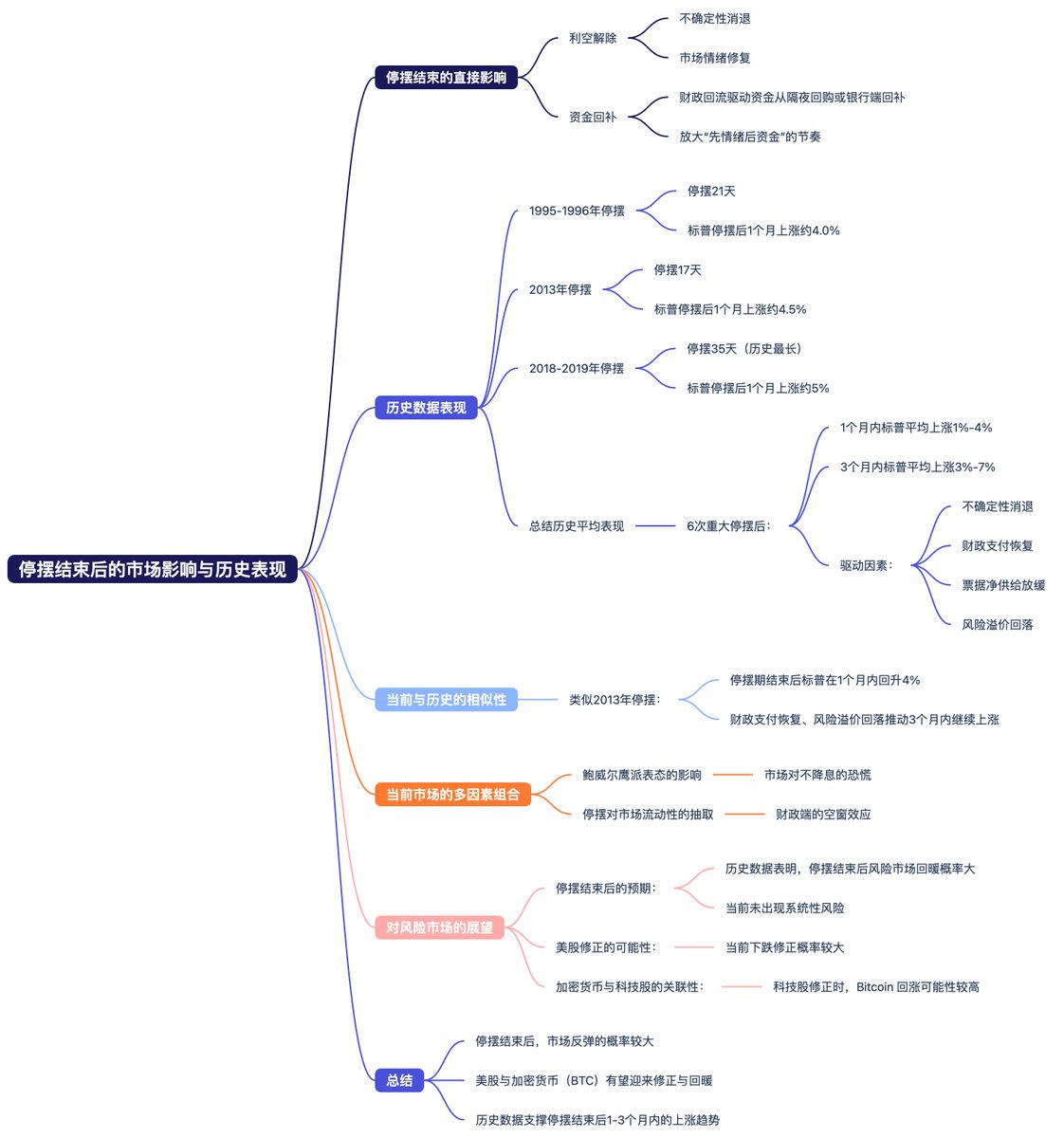
Therefore, once the stalemate ends and temporary funding is implemented, the first occurrence will be the removal of negative factors, and uncertainty will begin to dissipate. The typical market path should be emotional recovery followed by capital replenishment, and this is not just a guess. Historical data shows that during the 21-day stalemate from 1995 to 1996, the S&P rose about 4.0% in the month following the stalemate. In 2013, during a 17-day stalemate, it rose about 4.5% in the following month. After the record 35-day stalemate from 2018 to 2019, the S&P rose 5% in the month after it ended. These historical data tell us that once the stalemate ends, the probability of a market rebound is very high.
In summary, since 1990, after six major stalemates in the U.S., the S&P has averaged a 1% to 4% increase in one month and a 3% to 7% increase within three months, mainly due to the reduction of uncertainty and the return of fiscal funds, driving capital replenishment from overnight repos or the banking side, amplifying the rhythm of first emotions and then funds. The current situation is actually very similar to 2013. After the end of that stalemate, the S&P gained over 4% in price recovery within a month, and subsequently continued to rise over three months due to the recovery of fiscal payments, a slowdown in net supply of bills, and a decline in risk premiums.
In simple terms, the current decline is a combination of multiple factors, which may include market panic over Powell's hawkish stance on not cutting interest rates, as well as the extraction of market liquidity due to the U.S. government stalemate. However, the stalemate has now exceeded the historical longest duration, and I believe the upcoming stalemate will not last much longer.
Once the stalemate ends, historically, there has almost never been a missed opportunity for the risk market to warm up, and there is currently no systemic risk in the risk market. I believe the probability of a correction in U.S. stocks will be very high, and the correlation between cryptocurrencies, especially BTC, and tech stocks remains strong. When tech stocks correct, it is also very likely that Bitcoin will rebound.
When is the stalemate likely to end?
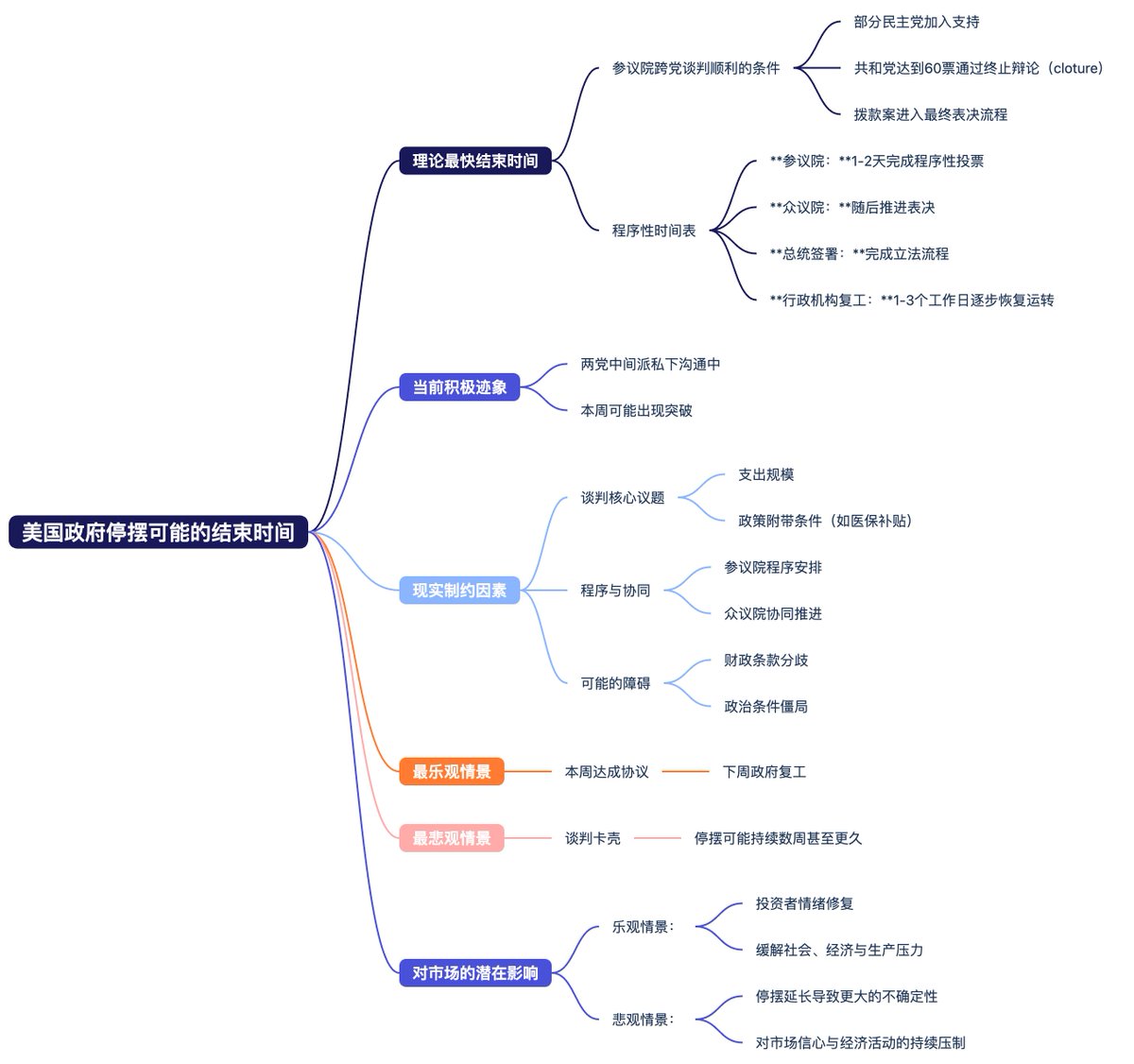
Although there is no clear timetable, based on current public information, if bipartisan negotiations in the Senate proceed smoothly, with some Democrats joining in support, the Republicans could reach 60 votes to end the debate (cloture), allowing the funding bill to enter the final voting process. There are signs that moderates from both parties are communicating privately, so theoretically, a breakthrough could occur this week. If a framework is reached, the Senate could complete procedural voting within 1 to 2 days, followed by the House moving forward with the vote. After the President signs, the executive branch will gradually resume operations within 1 to 3 working days.
However, significant realities constrain both sides, as they still need to reach a consensus on spending levels and policy conditions (including healthcare subsidies). The procedural arrangements in the Senate and coordination with the House are also key. If negotiations get stuck on fiscal terms or political conditions, the stalemate could last for several weeks or even longer.
Therefore, the most optimistic scenario is that an agreement is reached this week, and work resumes next week. If this can be achieved, it will greatly help restore investor sentiment, as the current decline is mainly due to concerns about the continued extension of the stalemate, which puts pressure on society, the economy, and production.
This article is sponsored by @Bitget | Save the most on fees, receive the most gifts, and become a VIP at Bitget
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




