Author: ian@Foresight Ventures
1. Understanding DeSci —> Questioning DeSci —> Understanding DeSci
1.1 Understanding DeSci
Pain Points:
The lag in infrastructure regarding the maintenance, access, ownership, and revenue distribution of IP related to research or knowledge has always been a pain point, especially in academia.
So, in the complex realm of knowledge sharing and discovery, how to balance security, transparency, reward mechanisms, and accessibility has always been a persistent challenge. Traditional models often rely on centralized verification systems, which may limit inclusivity and broad participation. Additionally, existing systems may not adequately reward or recognize knowledge contributions, which can affect the development of a comprehensive, collective knowledge base.
Problems Addressed:
The central idea behind DeSci is that everyone should have equal access to any level of science and knowledge, and the process of scientific research should be open and transparent to all. Therefore, DeSci is committed to creating an ecosystem where knowledge contributors can be incentivized and share their research, allowing anyone to permissionlessly browse or even iterate on this content.
This creates a fundamentally different scientific system, where in this new model:
- Funding distribution is determined by the public through mechanisms like DAOs, contrasting with the traditional practice controlled by small, closed centralized groups in science.
- The vision of DeSci also promotes dynamic collaboration of various resources globally, breaking through the collaboration limitations set by centralized institutions in traditional science.
- The flow of funds is more transparent and explores a more efficient economic system under web3, which is starkly different from the time-consuming funding decision-making processes in traditional science. At the same time, the incentives of tokens and reputation, as well as the value of peer review, are emphasized more strongly.
- Knowledge contributors can transparently allocate the intellectual property they generate, which differs from the situation in traditional science where IP belongs to the affiliated institution and access routes are opaque. DeSci also encourages sharing all research data, including unsuccessful attempts, to address the publication bias in traditional science that only shares successful experimental results.
1.2 Questioning DeSci
The original intention of DeSci is to establish an ecosystem for scientists or scholars to share academic research and gain ownership of research IP, while for other users, the sense of participation is more about easier access to these academic studies. Essentially, the ivory tower of academia has not been broken; the core players in this ecosystem are still the top scholars.
In what scenarios would an ordinary person care about how to more easily access an academic report?
Perhaps apart from staying up late in college to finish a paper, it is hard to have such a need after graduation. From a certain perspective, we must admit that the ability to contribute valuable academic IP is held by a small number of people.
However, from the perspective of examining the track and narrative, this is where DeSci's problem lies; it is too pure and noble, making it difficult to realize the true value that web3 can provide, namely community effects and an efficient economic system. Focusing on one point, the foundation of DeSci is not an open knowledge contribution platform, but rather an active ecosystem based on an efficient token system and strong community effects. This economic foundation relies on widespread user participation; if users cannot truly engage in the gameplay, lacking sufficient motivation to hold and trade tokens, then the price, liquidity, and economic system cannot be sustained.
Therefore, having scientists as the core players alone clearly does not make sense and cannot form a sustainable mechanism.

2. What Kind of DeSci Makes More Sense
2.1 Understanding DeSci
Science =/= Knowledge
DeSci should not just be the domain of scientists; it should lower the threshold for ordinary people to access science. Therefore, it is better to avoid using "science" and instead emphasize "knowledge." Science inherently sets a barrier for DeSci, while knowledge can be data in any form and from any field.
Contributing knowledge from one's professional field or areas of interest is inherently attractive and can easily lead to viral growth. Thus, opening up the "science" framework makes community participation possible and allows web3 to realize its maximum value.
I believe DeSci should be structured like a pyramid, categorizing participants and contributors across the entire knowledge-sharing chain into different levels, with each role being indispensable. Scholars, as the top participants in the pyramid, contribute the core value of DeSci itself while also bringing explosive potential to projects. For instance, in the context of new drug development, if DeSci can participate in or facilitate the market launch of a certain drug, the impact on the track and project is immeasurable. Community users, as the base participants of the pyramid, also have foundational roles; they maintain the efficient operation of the entire ecosystem and economic system.
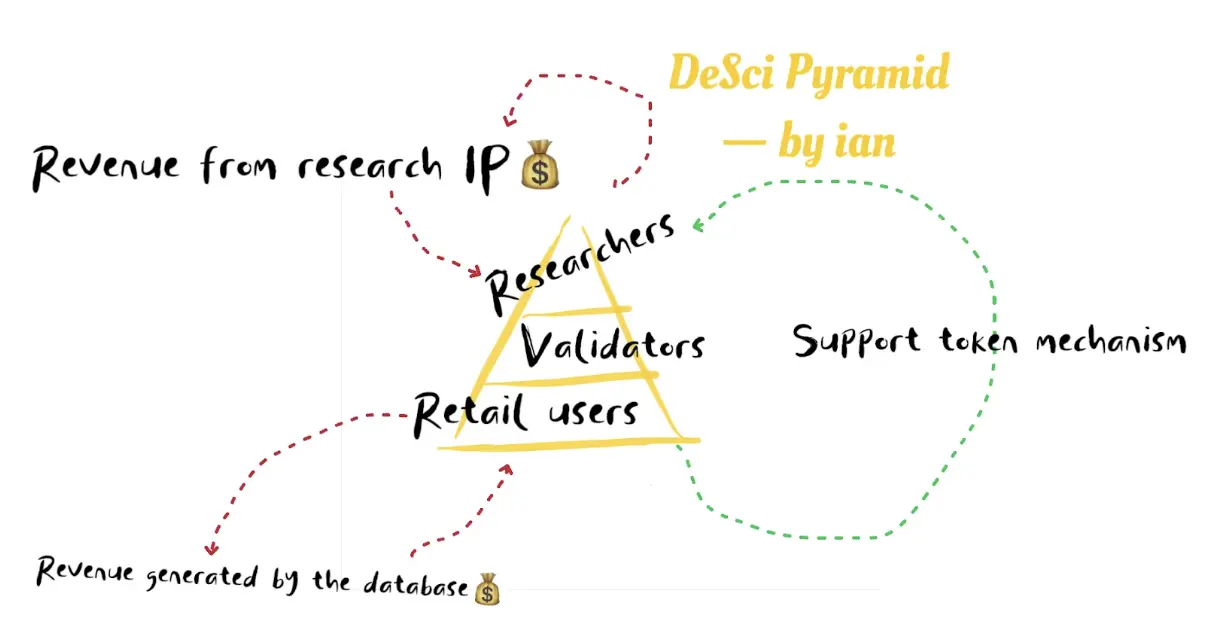
2.2 The Cornerstone of DeSci — BIO
2.2.1 Introduction to BIO
BIO Protocol is a decentralized scientific financial infrastructure aimed at promoting biotechnological innovation through community collaboration. It provides tools for funding, developing, and governing scientific intellectual property for a global community, including patients, scientists, and biotechnology professionals, to accelerate the commercialization of biotechnological research.
Core functions and operational mechanisms: Supporting decentralized organizations in biotechnology - BioDAOs.
2.2.2 In-depth Look at BIO
1) Technical Details
The technology stack and architectural design of Bio Protocol are aimed at supporting the tokenization and on-chain governance of biotechnology IP.
- By developing a customized public chain, it ensures that the technology, development, commercialization, and transaction processes of bio science are transparent, verifiable, and secure, while also reducing transaction costs.
- The IP-Token mechanism is based on smart contracts, where each IP asset has an independent token that defines its ownership and transaction rules. Users can obtain partial or full ownership through trading, creating possibilities for circulation and trading in the secondary market while protecting bio science research IP.
- Based on a DAO architecture, members manage and fund research projects through voting with BIO tokens. Each DAO can focus on specialized research fields, such as VitaDAO focusing on longevity research and CryoDAO focusing on cryobiology.
2) Operational Model Analysis
1. BioDAO
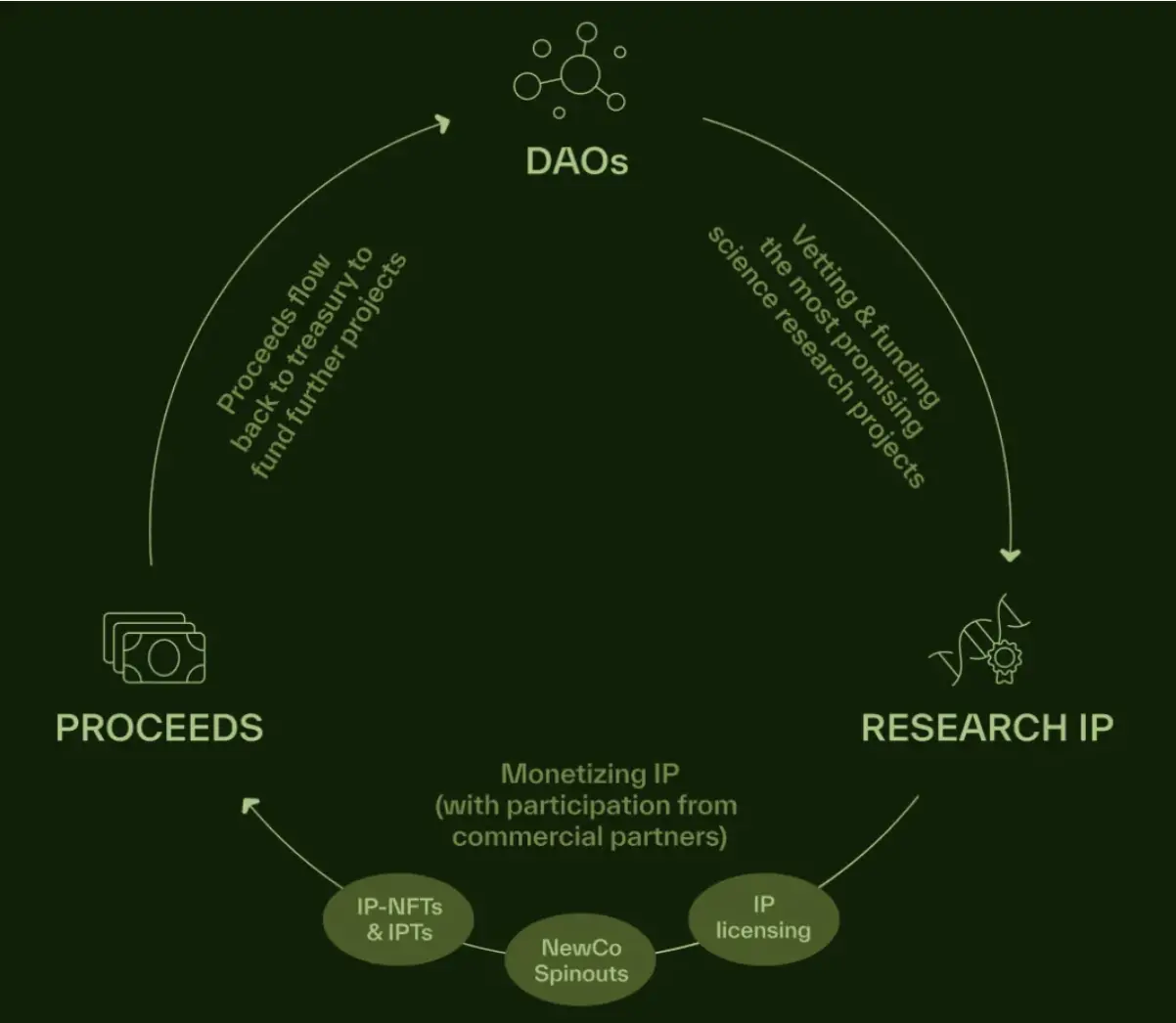
BioDAOs are decentralized autonomous organizations within the BIO Protocol ecosystem. Each BioDAO focuses on a specific scientific field, with the most notable being vitaDAO. BioDAOs receive continuous funding, liquidity, and infrastructure support through the BIO Protocol to accelerate research progress and improve project success rates.
The parent platform, BIO Protocol, provides BioDAOs with:
- Funding: Each BioDAO, upon approval, receives startup funds from the BIO Protocol treasury. This funding helps BioDAOs obtain initial capital to support early research projects and expand their influence.
- Liquidity support: BIO Protocol is responsible for providing on-chain liquidity for BioDAOs. This allows BioDAOs to focus on scientific research without worrying about market liquidity management issues. Through liquidity support, BIO Protocol helps enhance the liquidity and market value of BioDAOs' tokens.
- Governance: BIO Protocol establishes a meta-governance layer by holding tokens from multiple BioDAOs. BIO token holders can participate in and make decisions regarding the operations, funding allocation, and development direction of multiple BioDAOs through meta-governance. This mechanism ensures coordination among BioDAOs in terms of funding flow and research priorities within the ecosystem.
- IP Commercialization: BIO Protocol helps BioDAOs convert scientific research results into tradable intellectual property assets through its IP tokenization mechanism. This process allows BioDAOs to tokenize the intellectual property of research projects and trade them on-chain, helping research results gain early capital support and realize the market value of intellectual property.
- Standardized Framework: BIO Protocol provides a standardized framework for the creation and operation of BioDAOs, including token economics design, governance structure, and data management tools. Through a standardized framework and support, BIO Protocol reduces the difficulty of creating new BioDAOs, allowing them to enter the market and operate effectively more quickly.
2. Curation
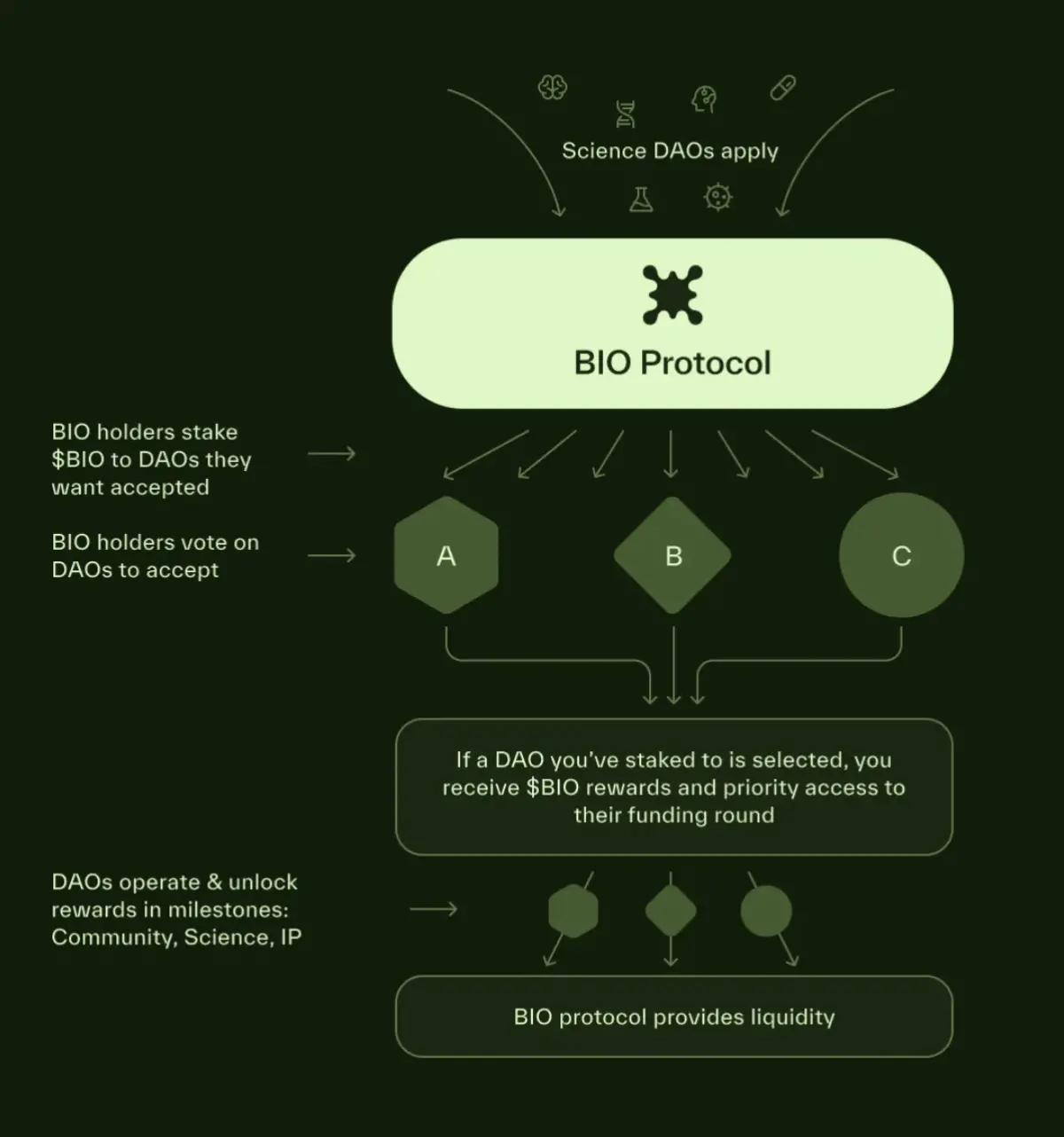
The curation mechanism of BIO Protocol aims to select and support the most promising BioDAOs to join the BIO ecosystem. Curation is a community-driven process, through which community members can help decide which emerging scientific organizations deserve funding support and ecological resources.
Curation Process
- Submit Application: New BioDAO applications to join the BIO ecosystem must have a clear scientific research direction and preliminary governance structure to ensure they can effectively promote their research goals.
- Voting Support: BIO token holders can choose to lock their BIO tokens and gain voting rights (vBIO). vBIO holders use these voting rights to vote on candidate BioDAOs to decide whether to support their entry into the ecosystem.
- Curation Rewards: If a BioDAO's application is successful, the vBIO holders who voted in support of that BioDAO can receive the following rewards:
- Voting supporters will have the opportunity to participate in the whitelist financing of that BioDAO, gaining priority in investing in that BioDAO's tokens.
- Supporters will receive priority access or discounts on products, data, or services provided by that BioDAO.
- Joining the Ecosystem: BioDAOs that successfully pass the curation process will receive initial funding and support from the BIO Protocol and will be incorporated into the BIO ecosystem. The BIO Protocol will continue to provide funding, liquidity, and governance support.
3. Reward Mechanism
Bio/Acc rewards are provided in the form of BIO tokens, including the following scenarios:
- Initial token auctions conducted through the BIO launchpad
- Research funding, i.e., the issuance of IP tokens
- Sale of IP-related consumer products
- Products entering the clinical trial phase
At the same time, rewards can also flow directly to users of BioDAO products:
- Participation in clinical trials or self-reporting health data
- Using/purchasing products, such as Follistatin, Vitarna, electronic implants, etc.
4. IP-Token
- BioDAOs develop and hold ownership of IP tokens. Each BioDAO typically holds a portfolio of IP tokens related to its specific scientific research field. For example, VitaDAO develops and owns equity in the IPTs of VitaRNA and VITA-FAST.
- The operation of IP Tokens: In addition to potential profit-sharing rights, when obtaining IPTs, IPT holders can benefit from the following:
- Governance Rights: Participation in key decisions related to the development, management, and licensing of intellectual property.
- Priority Access: Priority or discounted access to innovations, collaborations, or future opportunities related to that intellectual property.
2.2.3 Why We Invest in BIO
There has been no solution to balance security, transparency, and incentives in the field of scientific research. BIO has built the largest DeSci platform, ensuring security and transparency while financializing science research with significant financial value. Through numerous community-curated BIO subnets (e.g., vitaDAO), the value created by users is commercialized and returned to users through profit-sharing. Therefore, $BIO will continuously capture the value created by all DeSci subnets, making it the most valuable token in the DeSci field. In the long term, the demand for health and longevity will continue to increase, and BIO significantly lowers the participation and usage thresholds in related fields, making it a project worth long-term investment.
The product has undergone a long period of accumulation and iteration, with star projects like vitaDAO emerging in the ecosystem, proving the feasibility of the product's operational model and the existing demand from capital and academia. At the same time, the founding team has strong experience in both scientific research and web3; James is the founder of orangeDAO and participated as a founder in YC19W; Paul is the founder of vitaDAO and molecule, and the team has top-tier influence in the DeSci field.
3. More than DeSci
The imaginative space that DeSci brings to the industry is not limited to conducting research or drug discovery. As previously discussed, if the scope of DeSci is confined to science, the value and scalability of this track will be greatly restricted. By incorporating the concept of co-building knowledge, where knowledge can be data from any field, dimension, or size, the process of building DeSci resembles constructing a vast dynamic database.
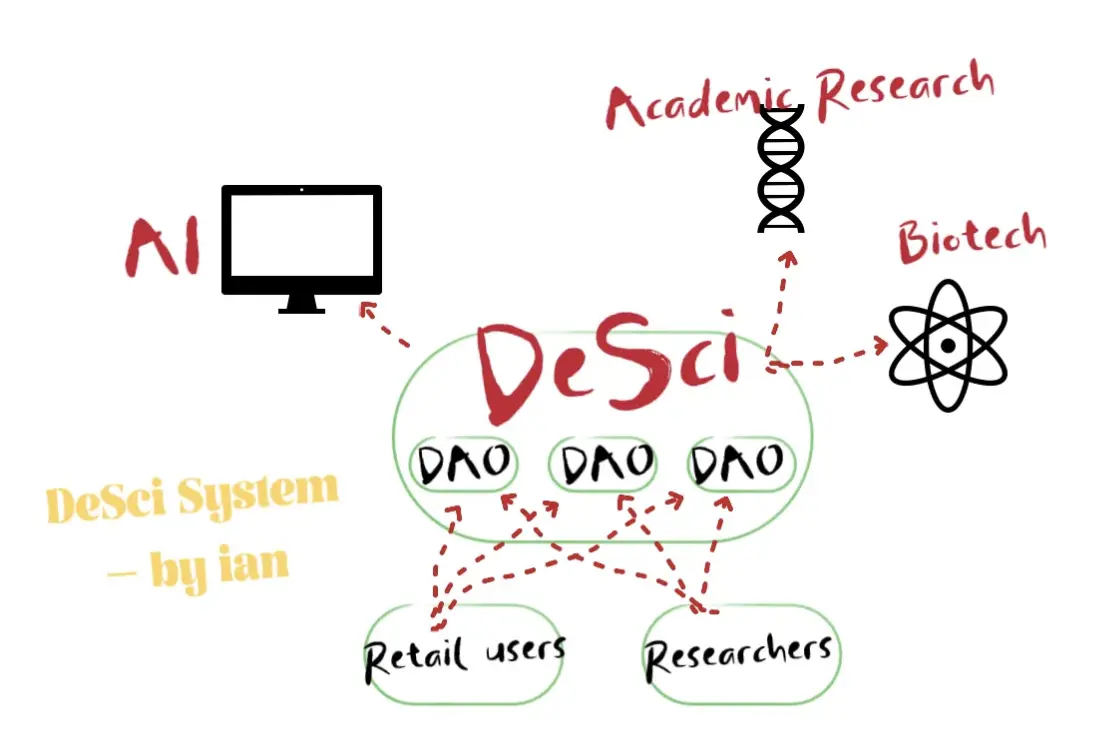
How to Combine DeSci + AI?
Furthermore, DeSci should fragment knowledge; rather than saying DeSci has built a decentralized research platform, it is more accurate to say that DeSci is creating a system where everyone has the opportunity to participate in co-building knowledge. This approach naturally complements the community attributes of web3, where the DeSci ecosystem will facilitate data organization across different fields. For example, Gym DAO gathers a group of people interested in fitness or possessing relevant knowledge, while Longevity DAO brings together individuals interested in biomedicine, and even bounty task DAOs. For instance, a navigation model may require traffic flow and terrain data from different streets in a region; this is not very systematic data, but it is indeed data that can be collected by individuals. The users participating in this may be experts or enthusiasts in the field, and under the support of DeSci, any knowledge contributed by individuals has the opportunity to be continuously enriched by other contributors. DeSci also allows every participant's contributed data to generate value and receive ongoing profit-sharing.
The greatest appeal here is that any individual's knowledge and data are inherently limited, but it is undeniable that this data holds value, whether large or small. Any research conduct must start from the accumulation of the most basic knowledge. If fragmented data can be collected through community co-building to form a scalable dataset, it will create a chemical reaction where 1 + 1 > 2.
If we truly want to establish this web3-based knowledge base, the primary task is to build the community and enhance the user base to generate viral growth; even onboarding researchers during the cold start phase is secondary. This differs from most DeSci approaches, but I believe this method is more crypto-native. The motivation for individuals to participate and hold tokens is to contribute data by joining data organizations through staking, in order to earn incentives or staking income. The more valuable the contributed data, the more frequently it will be cited or associated, leading to more valuable data enabling the corresponding data organization to gain more external income and native incentives. Thus, this mechanism not only incentivizes user participation but also promotes data quality.
However, in such a vast system, there will inevitably be users who contribute little or provide low-quality data. Nevertheless, the generation of this garbage data does not affect the operation of the system; these users will also be allowed to provide data, thus participating in staking and potentially earning minimal community incentives through luck.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




