Original Title: "A Detailed Explanation of Cryptocurrency Mining Algorithms: The 'Digital Gold Rush' Code from Bitcoin to Dogecoin"
Original Source: Dr. Chai Talks Crypto
Today, we will delve into the "core engine" of mining—the mining algorithm. What is a mining algorithm? Why are the mining methods for Bitcoin, Dogecoin, and Litecoin so different? How should beginners choose the right algorithm for mining? This article will unlock these "digital gold rush" codes in simple language, guiding you from zero into the world of algorithms!
01 What is a Mining Algorithm? The "Mathematical Code" of Blockchain
A mining algorithm is the core rule of a cryptocurrency network, a set of complex mathematical instructions that guide miners in verifying transactions, generating new blocks, and maintaining the security of the blockchain. In simple terms, it is like a "super math problem" that needs computational power to solve; miners who successfully solve it can earn cryptocurrency rewards (such as Bitcoin or Dogecoin).
Everyday Analogy
Imagine the mining algorithm as a lock, and the miner's hardware as the key. The lock for Bitcoin (the cryptographic hash algorithm SHA-256) requires a super-powerful dedicated key (ASIC miner). Different algorithms determine what tools you need, how much it costs, and how much "gold" you can earn.
Core Applications of the Algorithm
· Transaction Verification: Ensures each transaction is legitimate and prevents double spending (spending the same money twice).
· Block Generation: Packages transactions into blocks and adds them to the blockchain ledger.
· Reward Mechanism: Miners who successfully solve the problem receive new coins and transaction fees.
· Network Security: The complexity of the algorithm makes it extremely costly to attack the network, ensuring decentralization.
02 Why Are There Different Mining Algorithms?
Since the birth of Bitcoin in 2009, cryptocurrencies have developed rapidly, giving rise to various mining algorithms. Why are there so many algorithms? The reasons are mainly threefold:
· Hardware Compatibility: Different algorithms have different hardware requirements. For example, SHA-256 is suitable for ASIC miners, while Scrypt and Ethash are more suitable for GPUs or CPUs, lowering the barrier for ordinary people to participate.
· Decentralization and Security: The design of the algorithm affects the concentration of computational power. ASIC-resistant algorithms (like Scrypt) encourage more people to participate, preventing a few large mining farms from monopolizing the network.
· Project Uniqueness: New algorithms can help projects stand out. For example, the Scrypt algorithm used by Dogecoin and Litecoin enhances network security through merged mining, attracting more miners.
03 Mainstream Mining Algorithms Explained: Bitcoin, Dogecoin, etc.
Currently, cryptocurrencies use various mining algorithms, each with unique hardware requirements and mining experiences. Below are four common algorithms, focusing on Bitcoin's SHA-256, Dogecoin/Litecoin's Scrypt, and briefly describing other algorithms.
1 SHA-256: Bitcoin's "Super Problem"
Introduction
SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit) is the proof-of-work (PoW) algorithm used by Bitcoin, designed by the National Security Agency (NSA) of the United States. It requires miners to compute a 256-bit hash value, finding a result that meets the difficulty requirement (starting with multiple zeros).
Features
· High Computational Power Requirement: The total network computational power is about 859.01 EH/s (85.9 quintillion hashes per second) in 2025.
· Dedicated Hardware: Requires ASIC miners (devices specifically designed for SHA-256).
· Block Time: Approximately 10 minutes.
Applicable Coins
· Bitcoin (BTC)
· Bitcoin Cash (BCH)
Pros and Cons
· Advantages: Extremely high security, with significant attack costs; high market recognition for Bitcoin, with relatively stable long-term value.
· Disadvantages: ASIC miners are expensive and consume a lot of energy.
Suitable Audience
Large professional miners or large mining farms with cheap electricity.
2 Scrypt: Dogecoin and Litecoin's "Beginner-Friendly" Algorithm
Introduction
Scrypt is a memory-intensive algorithm originally designed to be ASIC-resistant. It requires a large amount of memory to perform hash calculations, reducing reliance on computational power.
Features
· High Memory Requirement: Compared to SHA-256, Scrypt relies more on memory than pure computational power.
· Fast Block Time: Litecoin approximately 2.5 minutes, Dogecoin approximately 1 minute.
· Merged Mining: Dogecoin can be mined simultaneously with Litecoin, increasing profits.
Applicable Coins
· Litecoin (LTC)
· Dogecoin (DOGE)
Pros and Cons
· Advantages: Low barrier to entry, can participate with a GPU; fast block generation, frequent rewards; merged mining increases returns.
· Disadvantages: ASICs are gradually entering Scrypt mining, reducing GPU competitiveness; high price volatility.
Suitable Audience
Budget-conscious beginners or players looking to try Dogecoin/Litecoin.
3 Ethash: Ethereum Classic's "GPU Paradise"
Introduction
Ethash is the PoW algorithm used by Ethereum Classic (ETC), designed to be memory-intensive and ASIC-resistant, requiring hashing of a dynamic data set (DAG, approximately 6GB).
Features
· Memory Dependency: The size of the DAG grows over time, reaching about 6-8GB in 2025.
· Hardware: GPUs are mainstream, with lower efficiency for ASICs.
· Block Time: Approximately 15 seconds.
Applicable Coins
Ethereum Classic (ETC)
Pros and Cons
· Advantages: ASIC-resistant, suitable for GPU mining; high degree of decentralization.
· Disadvantages: Lower returns, requires high-performance GPUs; increasing DAG size raises hardware requirements.
Suitable Audience
Players with high-performance graphics cards who want to try mining outside of Bitcoin.
4 Overview of Other Algorithms
· Equihash (Zcash): Memory-intensive, ASIC-resistant, suitable for GPU mining, focusing on privacy protection.
· RandomX (Monero): CPU-friendly, ASIC-resistant, encourages participation from ordinary computers, maintaining decentralization.
· X11 (Dash): Combines 11 hashing functions, energy-efficient and secure, supports both GPU and dedicated ASIC.
Chart: Comparison of Mainstream Mining Algorithms
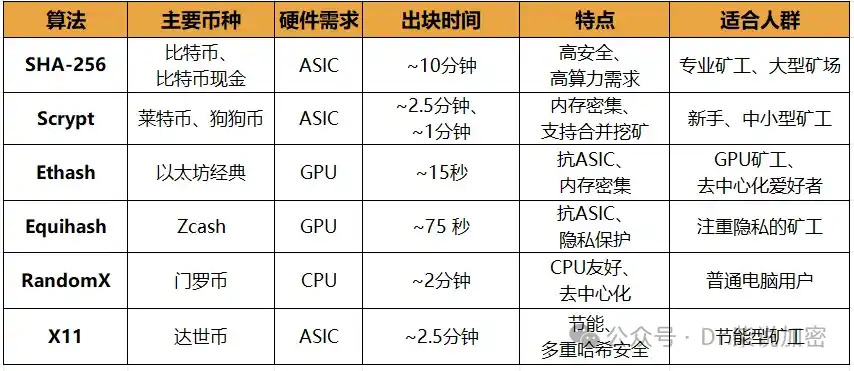
Note: Hardware requirements and block times may vary slightly due to network dynamics. Litecoin and Dash initially used GPU mining but were eventually replaced by ASICs, making GPUs largely uncompetitive.
04 Future Trends of Mining Algorithms
The evolution of mining algorithms is driven not only by technological advancements but also by energy costs, environmental policies, and the concept of decentralization. In the context of accelerated global computational power layout, iterative chip manufacturing technology, and diversified blockchain ecosystems, future trends in mining algorithms may present the following directions:
More Efficient Algorithms and Hardware Adaptation
As chip manufacturing enters the 3nm and even 2nm process era, future mining algorithms will focus more on matching hardware performance with energy efficiency. New algorithms may reduce redundant calculations without compromising security, enhancing power output per watt, extending hardware lifespan, and reducing equipment depreciation pressure.
ASIC-Resistant Design and Computational Power Distribution Optimization
To prevent excessive concentration of computational power in large mining farms, more projects may adopt CPU or GPU-friendly algorithms. For example, Monero's RandomX algorithm can fully utilize the cache and instruction set of general-purpose processors, making ASIC advantages nearly disappear.
Dynamic algorithms (such as periodically adjusting hash functions or memory requirements) may also emerge in the future to suppress the economic feasibility of ASIC development, allowing individual miners to have a longer participation cycle.
Green Mining and Carbon Neutrality Goals
By 2024, approximately 54% of Bitcoin's computational power is expected to use renewable energy (data source: Bitcoin Mining Council), but energy consumption still faces external criticism.
New algorithms may be better suited for intermittent energy sources (such as wind and solar) and combined with intelligent scheduling systems to automatically increase computational power when renewable energy is abundant and reduce load during low periods, thereby reducing carbon footprints and lowering electricity costs.
Balancing PoW and PoS
Ethereum completed its "merger" and transitioned to PoS in September 2022, reducing annual electricity consumption by over 99.95%, which has drawn attention from some projects towards PoS.
However, PoW still has unique advantages in security, trustlessness, and censorship resistance, so hybrid consensus models (such as PoW+PoS or PoW+PoA) may emerge in the future to balance decentralization and energy efficiency.
05 Choosing the Right "Digital Gold Rush" Code
The mining algorithm is the "mathematical code" of the cryptocurrency world, determining the barriers, costs, and returns of mining. Different algorithms have varying requirements for computational power, energy consumption, and hardware performance, thus affecting the profitability of mining.
The SHA-256 algorithm used by Bitcoin attracts professional miners with its high security and high returns, but it requires expensive ASIC miners and low electricity prices, making it a high barrier for small and medium miners. The Scrypt algorithm used by Dogecoin and Litecoin offers beginners a low-threshold "gold rush" opportunity, allowing them to get started with a GPU. Algorithms like Ethash and RandomX are designed to be ASIC-resistant, helping to attract more participants and promote decentralization.
Whether challenging Bitcoin's "super problem" or trying out Dogecoin's "meme wealth," understanding mining algorithms is the first step to success.
免责声明:本文章仅代表作者个人观点,不代表本平台的立场和观点。本文章仅供信息分享,不构成对任何人的任何投资建议。用户与作者之间的任何争议,与本平台无关。如网页中刊载的文章或图片涉及侵权,请提供相关的权利证明和身份证明发送邮件到support@aicoin.com,本平台相关工作人员将会进行核查。




